Abstract
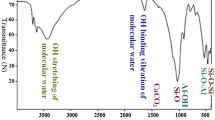
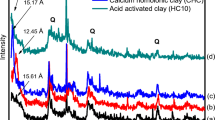
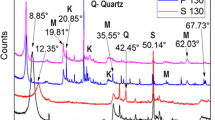
Natural bentonite was treated by hydrochloric, nitric, and phosphoric acids followed by washing with sodium hydroxide in order to enhance its adsorption capacity. The sample that treated with hydrochloric acid followed by further treatment with NaOH showed the highest cation exchange capacity with a value of 51.20 meq/100 g. The zero-point of charge for this sample was found to be 4.50. Adsorption isotherms for both cobalt and zinc were fitted using Langmuir, Freundlich, and Redlich-Peterson and showed an adsorption capacity of 138.1 mg Co2+ and 202.6 mg Zn2+ per gram of treated sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Degs, Y., Tutunjy, M., & Shawabkeh, R. (2000). The feasibility of using diatomite and Mn-diatomite for remediation of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ from water. Separation Science and Technology, 35, 2299–2310.
Al-Omari, H. (2003). Study of the adsorption of Ni2+ and Cu2+ by Tripoli. Mutah Lil-Buhuth wad-Dirasat, 18, 77–94.
Alvarez-Ayuso, E., & Garcia-Sanchez, A. (2003). Removal of heavy metals from waste water by natural and Na-exchanged bentonites. Clays and Clay Minerals, 51, 475–480.
Appel, G., Ma, L., Rhue, R., & Kennelley, E. (2003). Point of zero charge determination in soils and minerals via traditional methods and detection of electroacoustic mobility. Geoderma, 113, 77–93.
Bhattacharyya, D., Hestekin, J., Brushaber, P., Cullen, L., Bachas, L., & Sikdar, S. (1998). Novel poly-glutamic acid functionalized microfiltration membranes for sorption of heavy metals at high capacity. Journal of Membrane Science, 141, 121–135.
Barbier, F., Duc, G., & Petit-Ramel, M. (2000). Adsorption of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solutions to the montmorillonite/water interface. Colloid and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 166, 153–159.
Chen, G., Dussert, B., & Suffet, I. (1997). Evaluation of granular activated carbons for removal of methyllisoborneol to below odor threshold concentrations in drinking water. Water Research, 31, 1155–1163.
Chiou, M., & Li, H. (2002). Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 93, 233–248.
Chu, H., & Hashim, M. (2003). Kinetic studies of copper(II) and nickel(II) adsorption by oil palm ash. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 9, 163–167.
Corey, R. B. (1981). Adsorption vs. precipitation. In: M. A. Anderson & A. J. Rubin (Eds.), Adsorption of inorganics at solid–liquid interfaces (pp. 161–182). Ann Arbor, MI: Annals of Arbor Science Publisher.
Freundlich, H. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal for Physical Chemistry, 57A, 385–470.
Ho, Y., & McKay, G. (2000). The kinetics of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Research, 34, 735–742.
James, R., & Healy, T. (1972). Adsorption of hydrolysable metal ions at the oxide—water interface. II. Charge reversal of SiO2 and TiO2 colloids by adsorbed Co(II), La(III), and Th(IV) as model systems. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 40, 53–64.
Jandova, J., Maixner, J., & Grygar, T. (2002). Processing of zinc galvanic waste sludge by selective precipitation. Ceramics, 46, 52–55.
Kahr, G., & Madsen, F. (1995). Determination of cation exchange capacity and the surface area of bentonite, illite and kaolinite by methylene blue sorption. Applied Clay Science, 9, 327–363.
Karahan, S., Yurdakoç, M., Seki, Y., & Yurdakoç, K. (2006). Removal of boron from aqueous solution by clays and modified clays. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 293, 36–42.
Kaya, A., & Oren, A. (2005). Adsorption of zinc from aqueous solutions to bentonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 125, 183–189.
Khan, S., Riaz-ur-Rehhman, & Khan, M. (1995). Adsorption of chromium (III), chromium (VI) and silver (I) on bentonite. Waste Management, 15, 255–312.
Konishi, S., Saito, K., Furusaki, S., & Takanobu, S. (1996). Binary metal ion sorption during permeation through chelating porous membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 111, 1–6.
Kosmulski, M. (2002). The pH-dependent surface charging and the points of zero charge. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 253, 77–87.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38(11), 2221–2295.
Lin, S., & Juang, R. (2002). Heavy metal removal from water by sorption using surfactant-modified montmorillonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 92, 315–326.
Manning, B., & Goldberg, S. (1997). Adsorption and stability of arsenic at the clay mineral-water interface. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 2005–2011.
Mavrov, V., Erwe, T., Blöcher, C., & Chmiel, H. (2003). Study of new integrated processes combining adsorption, membrane separation and flotation for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Desalination, 157, 97–104.
Murray, J. (1975). The interaction of colbalt with hydrous manganese dioxide. Geochimica et Cosmochima Acta, 39, 635–647.
Noble, R. (1995). Membrane Separations Technology: Principles and applications. Elsevier.
Oren, A., & Kaya A. (2006). Factors affecting adsorption characteristics of Zn2+ on two natural zeolites. Journal of Hazardous Material B, 131, 59–65.
Rashed, M. (2001). Lead removal from contaminated water using mineral adsorbents. The Environmentalists, 21, 187–195.
Sengupta, A. (1997). Ion Exchange Technology. Pennsylvania: Technomic Publ. Co. Inc.
Shawabkeh, R., Rockstraw, D., & Bhada, R. (2002). Copper and strontium adsorption by a novel carbon material manufactured from pecan shells. Carbon, 40, 781–786.
Sheta, A., Falatah, A., Al-Sewailem, M., Khaled, E., & Sallam, A. (2003). Sorption characteristics of␣zinc and iron by natural zeolite and bentonite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 61, 127–136.
Smiciklas, I., Milonjic, S., Pfendt, P., & Raicevic, S. (2000). The point of zero charge and sorption of cadmium (II) and strontium (II) ions on synthetic hydroxyapatitew. Separation and Purification Technology, 18, 185–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shawabkeh, R.A., Al-Khashman, O.A., Al-Omari, H.S. et al. Cobalt and zinc removal from aqueous solution by chemically treated bentonite. Environmentalist 27, 357–363 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-007-9048-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-007-9048-1