Abstract
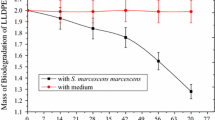
The present study deals with capacity of Cephalosporium species to degrade high-density polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE was treated with nitric acid to make it susceptible to microorganisms. Chemical treatment with nitric acid introduces carbonyl and nitro functional groups in HDPE as confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis. Gravimetric analysis showed a decrease in weight of the polymer by 7.18 ± 0.15% after 20 days of incubation period. Reduction in the weight of polymer confirmed the ability of Cephalosporium species to utilize HDPE for their growth. The pH of liquid culture media was found to decrease, whereas total dissolved solids and conductivity increase with the incubation period. Scanning electron microscopy analysis showed changes in morphology of films inoculated with Cephalosporium species. Decrease in crystallinity observed using X-ray diffraction studies further confirmed the degradation of pre-treated HDPE. The observed results reveal that the Cephalosporium species could be effectively used for the degradation of pre-treated HDPE under laboratory conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertsson, A. C., & Banhidi, Z. G. (1980). Microbial and oxidative effects in degradation of polyethene. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,25(8), 1655–1671. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1980.070250813.
Álvarez-Barragán, J., Domínguez-Malfavón, L., Vargas-Suárez, M., González-Hernández, R., Aguilar-Osorio, G., & Loza-Tavera, H. (2016). Biodegradative activities of selected environmental fungi on a polyester polyurethane varnish and polyether polyurethane foams. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,82(17), 5225–5235. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01344-16.
Arutchelvi, J., Sudhakar, M., Arkatkar, A., Doble, M., Bhaduri, S., & Uppara, P. V. (2008). Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. Indian Journal of Biotechnology,7(1), 9–22.
Auta, H. S., Emenike, C. U., Jayanthi, B., & Fauziah, S. H. (2018). Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin Journal,127, 15–21.
Avalos-Belmontes, F., Zapata-Gonzalez, I., Ramos-Devalle, L. F., Zitzumbo-Guzman, R., & Alonso-Romero, S. (2009). Thermo-oxidative degradation of HDPE as a function of its crystalline content. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,47, 1906–1915. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.21785.
Awasthi, S., Srivastava, P., Singh, P., Tiwary, D., & Mishra, P. K. (2017). Biodegradation of thermally treated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) by Klebsiella pneumoniae CH001. 3 Biotech,7(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0959-3.
Balasubramanian, V., Natarajan, K., Hemambika, B., Ramesh, N., Sumathi, C. S., Kottaimuthu, R., et al. (2010). High-density polyethylene (HDPE)-degrading potential bacteria from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Letters in Applied Microbiology,51(2), 205–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02883.x.
Brown, S. B., Millls, J., & Husle, M. J. (1974). Chemical and biological degradation of waste plastics. Nature,250, 161–163.
Cassidy, D. P., Werkema, D. D., Sauck, W. A., Atekwana, E. A., Rossbach, S., & Duris, J. (2001). The effects of LNAPL biodegradation products on electrical conductivity measurements. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics,6(1), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.4133/JEEG6.1.47.
Coates, J. (2006). Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a5606.
Das, P. M., Santosh, D., & Jayabrata, K. (2018). Fungal-mediated deterioration and biodegradation study of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) isolated from municipal dump yard in Chennai, India. Energy, Ecology and Environment,3(4), 229–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-018-0085-z.
Devi, S. R., Rajesh Kannan, V., Nivas, D., Kannan, K., Chandru, S., & Robert Antony, A. (2015). Biodegradation of HDPE by Aspergillus spp. from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin,96(1–2), 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.050.
Eriksson, O., & Finnveden, G. (2009). Plastic waste as a fuel—CO2-neutral or not? Energy & Environmental Science,2(9), 907. https://doi.org/10.1039/b908135f.
Esmaeili, A., Pourbabaee, A. A., Alikhani, H. A., Shabani, F., & Esmaeili, E. (2013). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by mixed culture of Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus and Aspergillus niger in soil. PLoS ONE,8(9), e71720. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071720.
Garaeva, S. R., Aydin, A. A., Aydin, A., Yalçin, B., Fatullaeva, P. A., & Medzhidov, A. A. (2010). Composition, properties, and application of products formed in oxidation of polyethylene by nitric acid. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry,83(1), 97–101. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427210010192.
Gu, J. D. (2003). Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: Recent research advances. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation,52(2), 69–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00177-4.
Gulmine, J. V., Janissek, P. R., Heise, H. M., & Akcelrud, L. (2002). Polyethylene characterization by FTIR. Polymer Testing,21(5), 557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9418(01)00124-6.
Hahladakis, J. N., Velis, C. A., Weber, R., Iacovidou, E., & Purnell, P. (2018). An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. Journal of Hazardous Materials,344, 179–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.014.
Jeon, H. J., & Kim, M. N. (2013). Isolation of a thermophilic bacterium capable of low-molecular-weight polyethylene degradation. Biodegradation,24(1), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9560-y.
Kita, D. A., & Heights, J. (1957). Production of glutamic acid by Cephalosporium. US patent no-2789939 (PP. 2–3).
Koutny, M., Lemaire, J., & Delort, A. M. (2006). Biodegradation of polyethylene films with prooxidant additives. Chemosphere,64(8), 1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.060.
Kowalczyk, A., Chyc, M., & Latowski, D. (2016). Achromobacter xylosoxidans as a new microorganism strain colonizing high-density polyethylene as a key step to its biodegradation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,23, 11349–11356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6563-y.
Krueger, M. C., Seiwert, B., Prager, A., Zhang, S., Abel, B., Harms, H., et al. (2017). Degradation of polystyrene and selected analogues by biological Fenton chemistry approaches: Opportunities and limitations. Chemosphere,173, 520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.089.
Leaversuch, R. (2002). Biodegradable polyesters: Packaging goes green. Plastics Technology, (800), 2–7. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=13924382
Leja, K., & Lewandowicz, G. (2010). Polymer biodegradation and biodegradable polymers—A review. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 19, 255–266.
Morancho, J. M., Ramis, X., Fernández, X., Cadenato, A., Salla, J. M., Vallés, A., et al. (2006). Calorimetric and thermogravimetric studies of UV-irradiated polypropylene/starch-based materials aged in soil. Polymer Degradation and Stability,91(1), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.04.029.
Mukherjee, S., Roy Chowdhuri, U., & Kundu, P. P. (2016). Bio-degradation of polyethylene waste by simultaneous use of two bacteria: Bacillus licheniformis for production of bio-surfactant and Lysinibacillus fusiformis for bio-degradation. RSC Advances,6(4), 2982–2992. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA25128A.
Musuc, A. M., Badea-Doni, M., Jecu, L., Rusu, A., & Popa, V. T. (2013). FTIR, XRD, and DSC analysis of the rosemary extract effect on polyethylene structure and biodegradability. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,114(1), 169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2909-y.
Nowak, B., Pajak, J., Drozd-Bratkowicz, M., & Rymarz, G. (2011). Microorganisms participating in the biodegradation of modified polyethylene films in different soils under laboratory conditions. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation,65(6), 757–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.04.007.
Ojha, N., Pradhan, N., Singh, S., Barla, A., Shrivastava, A., Khatua, P., et al. (2017). Evaluation of HDPE and LDPE degradation by fungus, implemented by statistical optimization. Scientific Reports,7(January), 39515. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39515.
Otake, Y., Kobayashi, T., Ashabe, H., Murakami, N., & Ono, K. (1995). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinylchloride and urea- formaldehyde resin buried under soil for over 32 years. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,56, 1789–1796.
Pathak, V. M., & Navneet, (2017). Review on the current status of polymer degradation: A microbial approach. Bioresources and Bioprocessing,4(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0145-9.
Rajandas, H., Parimannan, S., Sathasivam, K., Ravichandran, M., & Yin, L. S. (2012). Analysis method A novel FTIR–ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation. Polymer Testing,31(8), 1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.07.015.
Rivard, C., Moens, L., Roberts, K., Brigham, J., & Kelley, S. (1995). Starch esters as biodegradable plastics: Effects of ester group chain length and degree of substitution on anaerobic biodegradation. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,17(9), 848–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(94)00120-G.
Sheik, S., Chandrashekar, K. R. R., Swaroop, K., & Somashekarappa, H. M. M. (2015). Biodegradation of gamma irradiated low density polyethylene and polypropylene by endophytic fungi. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation,105, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.08.006.
Skariyachan, S., Patil, A. A., Shankar, A., Manjunath, M., Bachappanavar, N., & Kiran, S. (2018). Enhanced polymer degradation of polyethylene and polypropylene by novel thermophilic consortia of Brevibacillus sps. and Aneurinibacillus sp. screened from waste management landfills and sewage treatment plants. Polymer Degradation and Stability,149, 52–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.01.018.
Sowmya, H. V., Ramalingappa, Krishnappa, M., & Thippeswamy, B. (2015). Degradation of polyethylene by Penicillium simplicissimum isolated from local dumpsite of Shivamogga district. Environment, Development and Sustainability,17(4), 731–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9571-4.
Stasinopoulos, S. J., & Seviour, R. J. (1989). Exopolysaccharide formation by isolates of Cephalosporium and Acremonium. Mycological Research,92(1), 55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(89)80096-6.
Tolinski, M. (2012). Plastics and sustainability: Towards a peaceful coexistence between bio-based and fossil fuel-based plastics. Beverly: Scrivener Publishing LLC.
Tribedi, P., & Sil, A. K. (2013). Low-density polyethylene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 biofilm. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,20(6), 4146–4153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1378-y.
Wang, H., Chen, S. J., & Zhang, J. (2009). Surface treatment of LLDPE and LDPE blends by nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and chromic acid etching. Colloid and Polymer Science,287(5), 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-009-2000-9.
Witt, U., Einig, T., Yammoto, M., Kleeberg, I., Deckwer, W. D., & Muller, R. J. (2001). Biodegradation of aliphatic–aromatic copolyesters: Evaluation of the final biodegradability and ecotoxicological impact of degradation intermediates. Chemosphere,44, 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00162-4.
Zahra, S., Abbas, S. S., Mahsa, M. T., & Mohsen, N. (2010). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by isolated fungi in solid waste medium. Waste Management,30(3), 396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.09.027.
Zheng, Y., Yanful, E. K., & Bassi, A. S. (2005). A review of plastic waste biodegradation. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology,25(4), 243–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550500346359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, A.K., Vijayakumar, R.P. Effect of chemical treatment on biological degradation of high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Environ Dev Sustain 22, 1093–1104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0236-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0236-6