Abstract
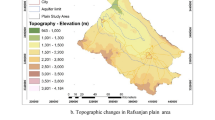
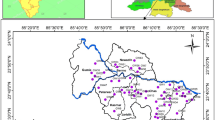
The lower Vellar river basin is the study site for the assessment of hydrogeochemical characters of groundwater using GIS and Water Quality Index (WQI). The study site is entirely covered by the sediment topography of alluvium and Cuddalore sandstone. The site faces the water scarcity and water quality problem when rainfall failure occurs. Under these situations, a GIS- and WQI-based groundwater quality has been deliberate in this basin. To appraise the groundwater geochemical characteristics, in total eighty samples were collected, viz., PREM (pre-monsoon) and POSTM (post-monsoon), and examined for important physicochemical (Na+, Mg+, Ca++, K+, Cl−, HCO3, NO3, SO4, SiO2, TDS, EC, and pH) parameters. The results of the sample analysis and interpretation of groundwater data reveal that the maximum samples fall in Ca-Cl2, Ca-SO4 followed by Na-Cl2 water type. Gibb’s diagram shows that most samples plotted in weathering and followed by evaporation field. Percentage of sodium (Na%) results indicate that 18% samples were poor; 8.75%—permissible; and 72.5%—good category. According to SAR classification, 80% of the groundwater samples fall under C3S1 followed by C2S1 and C4S1 water type. The water quality index (WQI) shows that 70% of the samples fall good, 21.25% of the samples fall poor, and 8.75% of the samples fall excellent category. Hence, the study site is an alarming stage to become deterioration of the groundwater quality and could be problem to the public health.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaya, M. B., Saidi, S., Zemni, T., & Zargouni, F. (2014). Suitability assessment of deep groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in the Djeffara aquifers (Northern Gabes, south-eastern Tunisia). Environmental Earth Sciences,71, 3387–3421.
Anitha, P., Charmaine, J., & Nagaraja, S. (2011). Evaluation of groundwater quality in and around Peenya industrial area of Bangalore, South India using GIS techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2244-y.
Baruah, M., Bhattacharyya, K. G., & Patgiri, A. D. (2008). Water quality of shallow groundwater of core city area of Guwahati. In Proceedings of sixteenth national symposium on environment, Haryana, India (pp. 101–106).
Brindha, K., & Elango, L. (2012). Impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality near a metropolitan city in India. Water Resource Management,26, 1747–1761.
Burrough, P. A., & Mc Donell, R. A. (1998). Principles of geographical information systems (p. 333). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Chae, G. T., Yun, S. T., Mayer, B., Kim, K. H., Kim, S. Y., Kwon, J. S., et al. (2007). Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Science of the Total Environment,385, 272–283.
Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, A. L., Srinivasamoorthy, K., & Anandhan, P. (2003). WATCLAST—A computer program for hydrogeochemical studies, recent trends in hydrogeochemistry (case studies from surface and subsurface waters of selected countries) (pp. 203–207). NewDelhi: Capital Publishing Company.
Chung, S. Y., Venkatramanan, S., Kim, T. H., Kim, D. S., & Ramkumar, T. (2014). Influence of hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of suitability for groundwater uses in Busan City, Korea. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9552-7.
Dar, I. A., Sankar, K., Shafi, T., & Dar, M. A. (2011). Investigation of groundwater quality in Hardrock Terrain using geoinformation system. Environmental Monitoring Assessment,176(1–4), 575–595.
El-Hames, A. S., Ahmadi, A., & Al Amri, N. (2011). A GIS approach for the assessment of groundwater quality in Wadi Rabigh aquifer, Saudi Arabia. Environmental Earth Sciences,63, 1319–1331.
Elton, N. W., Elton, W. J., & Narzareno, J. P. (1963). Pathology of acute salt poisoning in infants. American Journal of Clinical Pathology,39, 252–264.
Freeze, A., & Cherry, J. (1979). Groundwater (p. 604). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling worlds water chemistry. Science,170, 1088–1090.
Gnanachandrasamy, G., Ramkumar, T., Vasudevan, S., Venkatramanan, S., Chung, S. Y., & Bagyaraj, M. (2015). Accessing groundwater quality in lower part of Nagapattinam district, Southern India: using hydrogeochemistry and GIS interpolation techniques. Applied Water Science,5, 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0172-z.
Gnanachandrasamy, G., Ramkumar, T., Venkatramanan, S., Anitha Mary, I., & Vasudevan, S. (2012). GIS based hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater quality in Nagapattinam district, Tamilnadu, India. Carpathian Journal Earth and Environmental Sciences,7(3), 205–210.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS water supply paper (Vol. 2254, pp. 117–120).
Hofmann, H., & Cartwright, I. (2013). Using hydrogeochemistry to understand inter-aquifer mixing in the on-shore part of the Gippsland Basin, southeast Australia. Applied Geochemistry,33, 84–103.
Jeevanandam, M., Kannan, R., Srinivasalu, S., & Rammohan, V. (2006). Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of lower part of the Ponnaiyar River Basin, Cuddalore District, South India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,132, 263–274.
Jeevanandam, M., Nagarajan, R., Manikandan, M., Senthilkumar, M., Srinivasalu, S., & Prasanna, M. V. (2012). Hydrogeochemistry and microbial contamination of groundwater from Lower Ponnaiyar Basin, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1534-1.
Jiang, Y., Wu, Y., Groves, C., Yuan, D., & Kambesis, P. (2009). Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,109, 49–61.
Karanth, K. R. (1987). Groundwater assessment, development and management (p. 720). New Delhi: Tate McGraw Hill.
Ketata, M., Hamzaoui, F., Gueddari, M., Bouhlila, R., & Ribeiro, L. (2011). Hydrochemical and statistical study of groundwaters in Gabes south deep aquifer (southeastern Tunisia). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,36, 187–196.
Khodapanah, L., Sulaiman, W. N. A., & Khodapanah, N. (2009). Groundwater quality assessment for different purposes in Eshtehard District, Tehran, Iran. European Journal of Scientific Research,36, 543–553.
Kim, T. H., Chung, S. Y., Park, N., Hamm, S. Y., Lee, S. Y., & Kim, B. W. (2012). Combined analyses of chemometrics and kriging for identifying groundwater contamination sources and origins at the Masan coastal area in Korea. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1582-6.
Krishna Kumar, S., Bharani, R., Magesh, N. S., Godson, P. S., & Chandrasekar, N. (2014). Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality appraisal of part of south Chennai coastal aquifers, Tamil Nadu, India using WQI and fuzzy logic method. Applied Water Science,4, 341–350.
Kumar, S. K., Rammohan, V., Sahayam, J. D., & Jeevanandam, M. (2009). Assessment of groundwater quality and hydrogeochemistry of Manimuktha River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,159, 341–351.
Kurdi, M., & Eslamkish, T. (2017). Hydro-geochemical classification and spatial distribution of groundwater to examine the suitability for irrigation purposes (Golestan Province, north of Iran). Paddy and Water Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-017-0587-x.
Lermontov, A., Yokoyama, L., Lermontov, M., & Machado, M. A. S. (2009). River quality analysis using fuzzy water quality index: Ribeira do Iguape river watershed, Brazil. Ecological Indicators,9, 1188–1197.
Li, P., Wu, J., Qian, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, N., Jing, L., et al. (2016). Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Exposure Health,8, 331–348.
Ma, J. Z., Wang, X. S., & Edmunds, W. M. (2005). The characteristics of ground-water resources and their changes under the impacts of human activity in the arid northwest china—A case study of the Shiyang river basin. Journal of Arid Environments,61, 277–295.
Madison, R. J., & Brunett, J. O. (1984). Overview of the occurrence of nitrate in ground water of the United States. In National Water Summary 1984. U.S. Geological Survey, Water supply paper (Vol. 2275).
Magesh, N. S., Jitheshlal, K. V., Chandrasekar, N., & Jini, K. V. (2013). Geographical information system-based morphometric analysis of Bharathapuzha river basin, Kerala, India. Applied Water Science,3, 467–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0095-0.
Matta, G., Srivastava, S., Pandey, R. R., & Saini, K. K. (2017). Assessment of physicochemical characteristics of Ganga Canal water quality in Uttarakhand. Environment, Development and Sustainability,19, 419–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9735-x.
Milovanovic, M. (2007). Water quality assessment and determination of pollution sources along the Axios/Vardar River, South-eastern Europe. Desalination,213, 159–173.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. S., Puranik, S. C., & Singh, V. P. (2010). Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,163, 215–227.
Namibian, M. (2007). A new Water Quality Index for environmental contamination contributed by mineral processing: a case study of Amang (tin tailing) processing activity. Journal of Applied Sciences,7, 2977–2987.
Narany, T. Z., Ramli, F. Z., Aris, A. Z., & Sulaiman, F. K. (2014). Groundwater irrigation quality mapping using geostatistical techniques in Amol–Babol Plain, Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,3, 7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1271-8.
Nas, B., & Berktay, A. (2010). Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,160, 215–227.
Pierre, D., Glynn, L., & Plummer, N. (2005). Geochemistry and the understanding of ground water systems. Journal of Hydrology,13, 263–287.
Piper, A. M. (1953). A graphic procedure I the geo-chemical interpretation of water analysis. USGS groundwater note no. 12.
Qiyan, F., & Baoping, H. (2002). Hydrogeochemical simulation of water- rock interaction under water flood recovery in Renqiu Oilfield, Hebei Province, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry,21, 156–162.
Raman, V. (1983). Impact of corrosion in the conveyance and distribution of water. Journal of Indian Water Works Association,15(1), 115–121.
Rao, G. T., Rao, V. V. S. G., Rao, Y. S., & Ramesh, G. (2013). Study of hydrogeochemical processes of the groundwaters in Ghatprabha river sub-basin, Bagalkot District, Karnataka, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(7), 2447–2459.
Rasouli, F., Pouya, A. K., Ali, S., & Cheraghi, M. (2012). Hydrogeochemistry and water quality assessment of the Kor-Sivand Basin, Fars province, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,184, 4861–4877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2308-z.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. In Agricultural handbook (Vol. 60, p. 160). Washington, DC: USDA.
Ryznre, J. W. (1944). A new index for determining amount of calcium carbonate scale formed by water. Journal of American Water Works Association,36, 472–486.
Saeedi, M., Abessi, O., Sharifi, F., & Meraji, H. (2010). Development of groundwater quality index. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,163, 327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0837-5.
Sanjai Kumar, P. J., Elango, L., & James, E. J. (2013). Assessment of hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in the coastal area of South Chennai, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0940-3.
Sarath Prasanth, S. V., Magesh, N. S., Jitheshlal, K. V., Chandrasekar, N., & Gangadhar, K. (2012). Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Applied Water Science,2, 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-012-0042-5.
Selvam, S., Manimaran, G., Sivasubramanian, P., Balasubramanian, N., & Seshunarayana, T. (2014). GIS-based evaluation of Water Quality Index of groundwater resources around Tuticorin coastal city, south India. Environmental Earth Sciences,71, 2847–2867.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research,37, 4119–4124.
Singh, U. V., Abhishek, A., Kunwar, K. P., Dhakate, R., & Singh, N. P. (2014). Groundwater quality appraisal and its hydrochemical characterization in Ghaziabad (a region of indo-gangetic plain), Uttar Pradesh, India. Applied Water Science,4, 145–157.
Singh, C. K., Kumar, A., Shashtri, S., Kumar, A., Kumar, P., & Mallick, J. (2017). Multivariate statistical analysis and geochemical modeling for geochemical assessment of groundwater of Delhi, India. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,175, 59–71.
Singh, A. K., Mondal, G. C., Kumar, S., Singh, T. B., Tewary, B. K., & Sinha, A. (2008). Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin, India. Environmental Geology,54, 745–758.
Sivasubramanian, P., Balasubramanian, N., Soundranayagam, J. P., & Chandrasekar, N. (2013). Hydrochemical characteristics of coastal aquifers of Kadaladi, Ramanathapuram District, Tamilnadu, India. Applied Water Science,3, 603–612.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M. V., Vasanthavihar, M., Peter, J., & Anandhan, P. (2008). Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a hard rock terrain—A case study from Mettur taluk, Salem District, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Earth System Science,117(1), 49–58.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaraghavan, K., Vasanthavigar, M., Sarma, S., Chidambaram, S., Anandhan, P., et al. (2012). Assessment of groundwater quality with special emphasis on fluoride contamination in crystalline bed rock aquifers of Mettur region, Tamilnadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,5, 83–94.
Stuyfzand, P. J. (1989). Nonpoint source of trace element in potable groundwater in Netherland. In Proceedings of the 18th TWSA Water Working, Testing and Research Institutek, KIWA, Nieuwegein.
Subba Rao, N., & Devadas, D. J. (2003). Fluoride incidence in groundwater in an area of peninsular India. Environmental Geology,45, 243–251.
Subramani, T., Rajmohan, N., & Elango, L. (2009). Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0781-4.
Thiyagarajan, M., & Baskaran, R. (2011). Groundwater quality in the coastal stretch between Sirkazhi and Manampandal, Tamil Nadu, India using Arc GIS Software. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0500-7.
Tirkey, P., Bhattacharya, T., & Chakraborthy, S. (2013). Water quality indices-important tools for water quality assessment: A review. International Journal of Advanced Chemistry,1, 15–28.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Ground water hydrology. New York: Wiley.
Tomer, T. (2015). Water quality indices used for groundwater quality assessment. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,5, 76–80.
USSL. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soils. USDA handbook (Vol. 60, pp. 147)
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Prasanna, M. V. (2012). Evaluation of ground water suitability for domestic, irrigational, and industrial purposes: A case study from Thirumanimuttar river basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1977-y.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaragavan, K., Rajiv Ganthi, R., Chidambaram, S., Sarama, V. S., et al. (2010). Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Monitoring Assessment,171, 595–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1302-1.
Venkatramanan, S., Chung, S. Y., Ramkumar, T., Gnanachandrasamy, G., & Vasudevan, S. (2013). A multivariate statistical approaches on physicochemical characteristics of groundwater in and around Nagapattinam district, Cauvery deltaic region of Tamil Nadu, India. Earth Sciences Research Journal,17, 97–103.
Venkatramanan, S., Chung, S. Y., Ramkumar, T., Gnanachandrasamy, G., Vasudevan, S., & Lee, S. Y. (2014). Application of GIS and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater pollution status of Nagapattinam district of Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Earth Sciences,73(8), 4429–4442.
Venkatramanan, S., Chung, S. Y., Selvam, S., Lee, S. Y., & Elzain, H. Y. (2017). Factors controlling groundwater quality in the Yeonjegu District of Busan City, Korea, using the hydrogeochemical processes and fuzzy GIS. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9990-5.
Vetrimurugan, E., Elango, L., & Rajmohan, N. (2013). Sources of contaminants and groundwater quality in the coastal part of a river delta. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,10, 473–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0138-3.
Vijith, H., & Satheesh, R. (2007). Geographical information system based assessment of spatiotemporal characteristics of groundwater quality of upland sub-watersheds of Meenachil River, parts of Western Ghats, Kottayam District, Kerala, India. Environmental Geology,53, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0612-7.
WHO. (1993). Guidelines for drinking water quality (2nd ed., Vol. 1, p. 188). Recommendations, Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality vol. 1 recommendations (p. 130). Geneva: WHO.
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking water quality (3rd ed.). Geneva: WHO.
WHO. (2009). Calcium and magnesium in drinking water public health significance (p. 85). Geneva: World Heath Organizations.
WHO. (2014). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, world health organization (3rd ed., Vol. 1, p. 515). Geneva, Recommendations.
Wilcox, L. V. (1948). Classification and use of irrigation water. U.S. Geological Department Agri Arc 969, 19.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation water. US Geological Department of Agriculture Circular,969, 19.
World Bank Report. (2010). Deep wells and prudence: Towards pragmatic action for addressing groundwater overexploitation in India. The World Bank, Washington Report No. 51676.
Yammani, S. (2007). Groundwater quality suitable zones identification: application of GIS, Chittoor area, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology,53(1), 201–210.
Yisa, J., & Jimoh, T. (2010). Analytical studies on Water Quality Index of River Landzu. American Journal of Applied Sciences,7, 453. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajassp.2010.453.458.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnanachandrasamy, G., Dushiyanthan, C., Jeyavel Rajakumar, T. et al. Assessment of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in the lower Vellar river basin: using Geographical Information System (GIS) and Water Quality Index (WQI). Environ Dev Sustain 22, 759–789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0219-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0219-7