Abstract
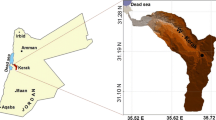
This study evaluated soil erosion rates in the Shaqlawa district using the Geographical Information System (GIS)-based Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model. The primary objective was to identify areas within the district that are prone to significant erosion and develop appropriate soil conservation schemes accordingly. A combination of primary and secondary data from diverse sources was utilized to achieve this objective. The GIS-based RUSLE model used variables like soil erodibility (K), soil coverage (C), topographic effect (LS), rainfall runoff (R), and erosion control practices (P) to estimate the amount of soil that had been washed away in the study area. The study provided valuable information that can be used to plan and administer soil protection in the Shaqlawa district. The average yearly soil loss in the study region is estimated to be 65.66 t ha−1 year−1. The district is experiencing significant soil erosion rates, which may have detrimental effects on agricultural productivity, water quality, and environmental health. The analysis revealed that Balisan, Hiran, Shaqlawa center, and part of the Salahaddin subdistrict are the most affected areas, with high values of LS and R factors contributing to significant soil erosion rates. These results underscore the importance of soil protection and management efforts in the Shaqlawa district. The combination of the RUSLE with GIS and remote sensing techniques has been recognized as an essential, cost-effective, and highly accurate approach for estimating soil erosion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The corresponding author can provide access to the original data sets used and analyzed in this article upon receiving a reasonable request.
References
Abdo, H., & Salloum, J. (2017). Mapping the soil loss in Marqya basin: Syria using RUSLE model in GIS and RS techniques. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-017-6424-0/METRICS
Agha, O. M. A. M., & Şarlak, N. (2016). Spatial and temporal patterns of climate variables in Iraq. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12517-016-2324-Y/METRICS
Aiello, A., Adamo, M., & Canora, F. (2015). Remote sensing and GIS to assess soil erosion with RUSLE3D and USPED at river basin scale in southern Italy. CATENA, 131, 174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2015.04.003
Al-Ansari, N. (2021). Topography and climate of Iraq. Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, 11(2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.47260/JESGE/1121
Al-Quraishi, A. M. F., & Negm, A. M. (2020). Updates, conclusions, and recommendations for environmental remote sensing and GIS in Iraq. Springer Water, 517–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21344-2_21/COVER
Alewell, C., Borrelli, P., Meusburger, K., & Panagos, P. (2019). Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7(3), 203–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ISWCR.2019.05.004
Alexakis, D. D., Hadjimitsis, D. G., & Agapiou, A. (2013). Integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and precipitation data for the assessment of soil erosion rate in the catchment area of “Yialias” in Cyprus. Atmospheric Research, 131, 108–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2013.02.013
Alexakis, D. D., Tapoglou, E., Vozinaki, A. E. K., & Tsanis, I. K. (2019). Integrated use of satellite remote sensing, artificial neural networks, field spectroscopy, and GIS in estimating crucial soil parameters in terms of soil erosion. Remote Sensing, 11(9), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS11091106
Alshehri, F., Sultan, M., Karki, S., Alwagdani, E., Alsefry, S., Alharbi, H., Sahour, H., & Sturchio, N. (2020). Mapping the distribution of shallow groundwater occurrences using remote sensing-based statistical modeling over Southwest Saudi Arabia. Remote Sensing, 12(9), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS12091361
Amsalu, T., & Mengaw, A. (2014). GIS based soil loss estimation using RUSLE model: The case of Jabi Tehinan Woreda, ANRS. Ethiopia. Natural Resources, 05(11), 616–626. https://doi.org/10.4236/nr.2014.511054
Atoma, H., Suryabhagavan, K. V., & Balakrishnan, M. (2020). Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Huluka watershed. Central Ethiopia. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 6(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40899-020-00365-Z/METRICS
Babu, R., Tejwani, K. G., & Agarwal, H. (1978). Distribution of erosion index and iso-erodent map of Vidarbha. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation, 17(3), 31–38. https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=2307951
Behera, D. K., Jamal, S., Ahmad, W. S., Taqi, M., & Kumar, R. (2023). Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE model and GIS tools: A study of Chilika Lake, Odisha. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 99(3), 406–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12594-023-2324-Y/METRICS
Bennett, S. J., & Wells, R. R. (2019). Gully erosion processes, disciplinary fragmentation, and technological innovation. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 44(1), 46–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.4522
Bensekhria, A., & Bouhata, R. (2022). Assessment and mapping soil water erosion using RUSLE approach and GIS tools: Case of Oued el-Hai watershed, Aurès West, Northeastern of Algeria. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020084
Betz-Nutz, S., Heckmann, T., Haas, F., & Becht, M. (2023). Development of the morphodynamics on Little Ice Age lateral moraines in 10 glacier forefields of the Eastern Alps since the 1950s. Earth Surface Dynamics, 11(2), 203–226. https://doi.org/10.5194/ESURF-11-203-2023
Borrelli, P., Alewell, C., Alvarez, P., Anache, J. A. A., Baartman, J., Ballabio, C., Bezak, N., Biddoccu, M., Cerdà, A., Chalise, D., Chen, S., Chen, W., De Girolamo, A. M., Gessesse, G. D., Deumlich, D., Diodato, N., Efthimiou, N., Erpul, G., Fiener, P., … Panagos, P. (2021). Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. In Science of the Total Environment, 780, 146494. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146494
Borrelli, P., Robinson, D. A., Fleischer, L. R., Lugato, E., Ballabio, C., Alewell, C., ... & Panagos, P. (2017). An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nature Communications, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/S41467-017-02142-7
Borrelli, P., Robinson, D. A., Panagos, P., Lugato, E., Yang, J. E., Alewell, C., Wuepper, D., Montanarella, L., & Ballabio, C. (2020). Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(36), 21994–22001. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.2001403117/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.2001403117.SAPP.PDF
Bottinelli, N., Maeght, J. L., Pham, R. D., Valentin, C., Rumpel, C., Pham, Q. V., Nguyen, T. T., Lam, D. H., Nguyen, A. D., Tran, T. M., Zaiss, R., & Jouquet, P. (2021). Anecic earthworms generate more topsoil than they contribute to erosion – Evidence at catchment scale in northern Vietnam. CATENA, 201, 105186. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2021.105186
Burger, D. J., Bauke, S. L., Amelung, W., & Sommer, M. (2023). Fast agricultural topsoil re-formation after complete topsoil loss – Evidence from a unique historical field experiment. Geoderma, 434, 2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEODERMA.2023.116492
Chalise, D., Kumar, L., & Kristiansen, P. (2019a). Land degradation by soil erosion in Nepal: A review. Soil Systems, 3(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/SOILSYSTEMS3010012
Chalise, D., Kumar, L., Spalevic, V., & Skataric, G. (2019b). Estimation of sediment yield and maximum outflow using the IntErO model in the Sarada River Basin of Nepal. Water (switzerland), 11(5), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050952
Chougule, V. A., Sapkale, J. B., & Pawar-Patil, V. S. (2021). Rusle and sdr model for erosional risk assessment and sediment yield estimation of achara basin, western coast, india. Disaster Advances, 14(7), 19–31. https://doi.org/10.25303/147DA1921
Dawod, R. K., Hemn, O. S., & Ismail, A. S. (2017). Reducing the salinity risks on shaqlawa calcareous soil by adding sulfur. Polytechnic Journal, 7(4), 1–11. https://journals.epu.edu.iq/index.php/polytechnic/article/view/1255
Dissanayake, D., Morimoto, T., & Ranagalage, M. (2019). Accessing the soil erosion rate based on RUSLE model for sustainable land use management: A case study of the Kotmale watershed, Sri Lanka. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5(1), 291–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40808-018-0534-X/METRICS
Dutta, S. (2016). Soil erosion, sediment yield and sedimentation of reservoir: A review. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2(3), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40808-016-0182-Y
Ejaz, N., Elhag, M., Bahrawi, J., Zhang, L., Gabriel, H. F., & Rahman, K. U. (2023). Soil erosion modelling and accumulation using RUSLE and remote sensing techniques: Case study Wadi Baysh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 15(4), 3218. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU15043218
FAO. (2015). Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production. Viale delle Terme di Caracalla 00153 Rome, Italy. In The importance of soil organic matter. https://www.fao.org/3/i4405e/i4405e.pdf. Accessed 22 Jan 2023
FAO. (2019). Soil erosion. In Fao (Ed.), Soil erosion: The greatest challenge to sustainable soil management. Rome. 100 pp. Licence: (Vol. 8, Issue 5). FAO. https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/ca4395en
Ganasri, B. P., & Ramesh, H. (2016). Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS - A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(6), 953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GSF.2015.10.007
Gao, L., Wang, X., Johnson, B. A., Tian, Q., Wang, Y., Verrelst, J., Mu, X., & Gu, X. (2020). Remote sensing algorithms for estimation of fractional vegetation cover using pure vegetation index values: A review. In ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 159, 364–377. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.018
Gholami, V., Sahour, H., & Hadian Amri, M. A. (2021). Soil erosion modeling using erosion pins and artificial neural networks. Catena, 196, 104902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104902
Ghosh, A., Rakshit, S., Tikle, S., Das, S., Chatterjee, U., Pande, C. B., Alataway, A., Al-Othman, A. A., Dewidar, A. Z., & Mattar, M. A. (2022). Integration of GIS and remote sensing with RUSLE model for estimation of soil erosion. Land 2023, Vol. 12, Page 116, 12(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/LAND12010116
Gray, D. (2016). Effect of slope shape on soil erosion. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 6(3), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-784X.1000231
Group, W. B. (2017). Iraq - Systematic country diagnostic. https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/542811487277729890/iraq-systematic-country-diagnostic
Guo, Z. Q., Li, P., Yang, X. M., Wang, Z. H., Lu, B. B., Chen, W. J., Wu, Y., Li, G. W., Zhao, Z. W., Liu, G. B., Ritsema, C., Geissen, V., & Xue, S. (2022). Soil texture is an important factor determining how microplastics affect soil hydraulic characteristics. Environment International, 165, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2022.107293
Hussein, M. H., & Othman, A. K. (1988). Soil and water losses in a low intensity rainfall region in Iraq. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 33(3), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626668809491247
Isik, S., Kalin, L., Schoonover, J. E., Srivastava, P., & Graeme Lockaby, B. (2013). Modeling effects of changing land use/cover on daily streamflow: An Artificial Neural Network and curve number based hybrid approach. Journal of Hydrology, 485, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2012.08.032
Karaburun, A. (2010). Estimation of C factor for soil erosion modeling using NDVI in Buyukcekmece watershed. Ozean Journal of Applied Sciences, 3(1), 77–85. http://ozelacademy.com/OJAS_v3n1_8.pdf
Kayet, N., Pathak, K., Chakrabarty, A., & Sahoo, S. (2018). Evaluation of soil loss estimation using the RUSLE model and SCS-CN method in hillslope mining areas. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 6(1), 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ISWCR.2017.11.002
Keesstra, S. D., Bouma, J., Wallinga, J., Tittonell, P., Smith, P., Cerdà, A., Montanarella, L., Quinton, J. N., Pachepsky, Y., Van Der Putten, W. H., Bardgett, R. D., Moolenaar, S., Mol, G., Jansen, B., & Fresco, L. O. (2016). The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations sustainable development goals. The Soil, 2(2), 111–128. https://doi.org/10.5194/SOIL-2-111-2016
Khaleel, A., Ngah, I., & Ossman, T. (2011). Distribution and spatial arrangement of rural population in Shaqlawa district, Kurdistan region-Iraq. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 4(16), 785–791. https://doi.org/10.5897/JGRP11.119
Khayyat, H. A. K. A., Sharif, A. J. M., & Crespi, M. (2020). Assessing the impacts of climate change on natural resources in Erbil area, the Iraqi Kurdistan using geo-information and landsat data. Springer Water, 463–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21344-2_19/COVER
Khosravi, K., Rezaie, F., Cooper, J. R., Kalantari, Z., Abolfathi, S., & Hatamiafkoueieh, J. (2023). Soil water erosion susceptibility assessment using deep learning algorithms. Journal of Hydrology, 618, 129229. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2023.129229
Khwarahm, N. R. (2020). Mapping current and potential future distributions of the oak tree (Quercus aegilops) in the Kurdistan Region. Iraq. Ecological Processes, 9(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13717-020-00259-0/FIGURES/10
Malinowski, J. (2002). Iraq Geography, U.S. Military Academy West Point, West Point, NJ. Department of Geography & Environmental Engineering, United States Military Academy West Point NY. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED476013.pdf. Accessed 10 Feb 2023
Kinnell, P. I. A. (2000). The effect of slope length on sediment concentrations associated with side-slope erosion. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64(3), 1004–1008. https://doi.org/10.2136/SSSAJ2000.6431004X
Koirala, P., Thakuri, S., Joshi, S., & Chauhan, R. (2019). Estimation of soil erosion in Nepal using a RUSLE modeling and geospatial tool. Geosciences (switzerland), 9(4), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9040147
Lamane, H., Moussadek, R., Baghdad, B., Mouhir, L., Briak, H., Laghlimi, M., & Zouahri, A. (2022). Soil water erosion assessment in Morocco through modeling and fingerprinting applications: A review. Heliyon, 8(8), e10209. https://doi.org/10.101a6/J.HELIYON.2022.E10209
Li, D., Chen, X., Tao, T., Tan, W., & Ma, L. (2022). Quantifying the sheet-rill erosion process along a saturated soil slope. CATENA, 219, 106631. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2022.106631
Lorenz, K., Lal, R., & Ehlers, K. (2019). Soil organic carbon stock as an indicator for monitoring land and soil degradation in relation to United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Land Degradation & Development, 30(7), 824–838. https://doi.org/10.1002/LDR.3270
Luetzenburg, G., Bittner, M. J., Calsamiglia, A., Renschler, C. S., Estrany, J., & Poeppl, R. (2020). Climate and land use change effects on soil erosion in two small agricultural catchment systems Fugnitz – Austria, Can Revull – Spain. Science of The Total Environment, 704, 135389. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.135389
Marondedze, A. K., & Schütt, B. (2020). Assessment of soil erosion using the rusle model for the Epworth district of the harare metropolitan province. Zimbabwe. Sustainability (switzerland), 12(20), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
McCool, D. K., Brown, L. C., Foster, G. R., Mutchler, C. K., & Meyer, L. D. (1987). Revised slope steepness factor for the universal soil loss equation. Transactions of the ASAE, 30(5), 1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.30576
Moges, D. M., & Bhat, H. G. (2017). Integration of geospatial technologies with RUSLE for analysis of land use/cover change impact on soil erosion: Case study in Rib watershed, north-western highland Ethiopia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(22), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-017-7109-4
Napoli, M., Cecchi, S., Orlandini, S., Mugnai, G., & Zanchi, C. A. (2016). Simulation of field-measured soil loss in Mediterranean hilly areas (Chianti, Italy) with RUSLE. CATENA, 145, 246–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2016.06.018
Negese, A., Fekadu, E., & Getnet, H. (2021). Potential soil loss estimation and erosion-prone area prioritization using RUSLE, GIS, and remote sensing in Chereti watershed, Northeastern Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622120985814
Nkonya, E., Mirzabaev, A., & von Braun, J. (2015). Economics of land degradation and improvement - A global assessment for sustainable development. Springer Cham, 1–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19168-3/COVER
Okenmuo, F. C., & Ewemoje, T. A. (2023). Estimation of soil water erosion using RUSLE, GIS, and remote sensing in Obibia River watershed, Anambra, Nigeria. DYSONA - Applied Science, 4(1), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.30493/DAS.2022.349144
Ostovari, Y., Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S., Bahrami, H. A., Naderi, M., & Dematte, J. A. M. (2017). Soil loss estimation using RUSLE model, GIS and remote sensing techniques: A case study from the Dembecha Watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. Geoderma Regional, 11, 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEODRS.2017.06.003
Ostovari, Y., Moosavi, A. A., Mozaffari, H., Poppiel, R. R., Tayebi, M., & Demattê, J. A. M. (2022). Soil erodibility and its influential factors in the Middle East. Computers in Earth and Environmental Sciences, 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-89861-4.00037-3
Panagos, P., Borrelli, P., & Poesen, J. (2019). Soil loss due to crop harvesting in the European Union: A first estimation of an underrated geomorphic process. Science of the Total Environment, 664, 487–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.02.009
Panagos, P., Borrelli, P., Poesen, J., Ballabio, C., Lugato, E., Meusburger, K., Montanarella, L., & Alewell, C. (2015a). The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environmental Science & Policy, 54, 438–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVSCI.2015.08.012
Panagos, P., Borrelli, P., & Robinson, D. A. (2015b). Common agricultural policy: Tackling soil loss across Europe. In Nature, 526(7572), 195. Nature Publishing Group. https://doi.org/10.1038/526195d
Pande, C. B., Kadam, S. A., Jayaraman, R., Gorantiwar, S., & Shinde, M. (2022). Prediction of soil chemical properties using multispectral satellite images and wavelet transforms methods. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 21(1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSSAS.2021.06.016
Pande, C. B., Moharir, K. N., & Khadri, S. F. R. (2021). Watershed planning and development based on morphometric analysis and remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of semi-arid watershed in Maharashtra, India. Groundwater Resources Development and Planning in the Semi-Arid Region, 199–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68124-1_11/COVER
Parsons, A. J. (2019). How reliable are our methods for estimating soil erosion by water? Science of the Total Environment, 676, 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.04.307
Patowary, S., & Sarma, A. K. (2018). GIS-based estimation of soil loss from hilly urban area incorporating hill cut factor into RUSLE. Water Resources Management, 32(10), 3535–3547. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11269-018-2006-5/METRICS
Prasannakumar, V., Shiny, R., Geetha, N., & Vijith, H. (2011). Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: A case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala. India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(4), 965–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-011-0913-3/METRICS
Prasuhn, V., Liniger, H., Gisler, S., Herweg, K., Candinas, A., & Clément, J. P. (2013). A high-resolution soil erosion risk map of Switzerland as strategic policy support system. Land Use Policy, 32, 281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LANDUSEPOL.2012.11.006
Preetha, P. P., & Al-Hamdan, A. Z. (2022). Synergy of remotely sensed data in spatiotemporal dynamic modeling of the crop and cover management factor. Pedosphere, 32(3), 381–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(21)60081-4
Ranzi, R., Le, T. H., & Rulli, M. C. (2012). A RUSLE approach to model suspended sediment load in the Lo river (Vietnam): Effects of reservoirs and land use changes. Journal of Hydrology, 422–423, 17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2011.12.009
Roz Price. (2018). Environmental risks in Iraq. In UK Department for International Development (Issue June). https://opendocs.ids.ac.uk/opendocs/handle/20.500.12413/13838
Roziyeva, I. J., Tursunova, S. A., & Chаriyeva, N. N. (2022). Morphogenetic Properties Of Grass-Gray Soils. Texas Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 3, 20–22. https://zienjournals.com/index.php/tjabs/article/view/1280
Saratha, M., Angappan, K., Karthikeyan, S., Marimuthu, S., & Chozhan, K. (2021). Exploration of soil and weather factors on mulberry root rot incidence in the western zone of Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, 11(12), 18–29. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJECC/2021/V11I1230552
Sastre, B., Barbero-Sierra, C., Bienes, R., Marques, M. J., & García-Díaz, A. (2017). Soil loss in an olive grove in Central Spain under cover crops and tillage treatments, and farmer perceptions. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17(3), 873–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11368-016-1589-9/METRICS
Seitz, S., Goebes, P., Puerta, V. L., Pereira, E. I. P., Wittwer, R., Six, J., van der Heijden, M. G. A., & Scholten, T. (2019). Conservation tillage and organic farming reduce soil erosion. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 39(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13593-018-0545-Z/FIGURES/3
Shelar, R. S., Shinde, S. P., Pande, C. B., Moharir, K. N., Orimoloye, I. R., Mishra, A. P., & Varade, A. M. (2022). Sub-watershed prioritization of Koyna river basin in India using multi criteria analytical hierarchical process, remote sensing and GIS techniques. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 128, 103219. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PCE.2022.103219
Shi, P., Li, P., Li, Z., Sun, J., Wang, D., & Min, Z. (2022). Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau, China. Agricultural Water Management, 259, 107231. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2021.107231
Sissakian, V. K., Al-Ansari, N., & Knutsson, S. (2013). Sand and dust storm events in Iraq. Natural Science, 5(10), 1084–1094. https://doi.org/10.4236/NS.2013.510133
Stefanidis, S., Alexandridis, V., & Ghosal, K. (2022). Assessment of water-induced soil erosion as a threat to natura 2000 protected areas in Crete Island. Greece. Sustainability (switzerland), 14(5), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052738
TENG, H. fen, HU, J., ZHOU, Y., ZHOU, L. qing, & SHI, Z. (2019). Modelling and mapping soil erosion potential in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 18(2), 251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62045-3
Teng, H., Liang, Z., Chen, S., Liu, Y., Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Chappell, A., Yu, W., & Shi, Z. (2018). Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. The Science of the Total Environment, 635, 673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.04.146
Tesfaye, G. (2018). Soil erosion modeling using GIS based RUSEL model in Gilgel Gibe-1 catchment, South West Ethiopia. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources, 15(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.19080/ijesnr.2018.15.555923
Thapa, E. P., & Pradeep Sapkota. (2020). Riverbed water extraction and utilization of Rural Communities Kavre, Nepal. IEEE-SEM, 8(1). https://www.ieeesem.com/researchpaper/Riverbed_water_extraction_and_utilization_of_Rural_Communities_Kavre_Nepal.pdf
Thapa, P. (2020). Spatial estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE modeling: A case study of Dolakha district. Nepal. Environmental Systems Research, 9(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-020-00177-2
Turner, K. G., Anderson, S., Gonzales-Chang, M., Costanza, R., Courville, S., Dalgaard, T., Dominati, E., Kubiszewski, I., Ogilvy, S., Porfirio, L., Ratna, N., Sandhu, H., Sutton, P. C., Svenning, J. C., Turner, G. M., Varennes, Y. D., Voinov, A., & Wratten, S. (2016). A review of methods, data, and models to assess changes in the value of ecosystem services from land degradation and restoration. Ecological Modelling, 319, 190–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLMODEL.2015.07.017
Vatandaşlar, C., & Yavuz, M. (2017). Modeling cover management factor of RUSLE using very high-resolution satellite imagery in a semiarid watershed. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(2), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6388-0
Vizentin-Bugoni, J., Maruyama, P. K., Debastiani, V. J., da Duarte, L., & S., Dalsgaard, B., & Sazima, M. (2016). Influences of sampling effort on detected patterns and structuring processes of a Neotropical plant–hummingbird network. Journal of Animal Ecology, 85(1), 262–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12459
Wang, R., Zhang, S., Yang, J., Pu, L., Yang, C., Yu, L., Chang, L., & Bu, K. (2016a). Integrated use of GCM, RS, and GIS for the assessment of hillslope and gully erosion in the mushi river sub-catchment. Northeast China. Sustainability (switzerland), 8(4), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8040317
Wang, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, Z., Yi, L., Zuo, L., Wen, Q., Liu, F., Xu, J., Hu, S., & Liu, B. (2016b). Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. CATENA, 137, 256–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATENA.2015.10.004
Waseem, M., Iqbal, F., Humayun, M., Latif, M. U., Javed, T., & Leta, M. K. (2023). Spatial assessment of soil erosion risk using RUSLE embedded in GIS environment: A case study of Jhelum River watershed. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP13063775
Wetterauer, K., Scherler, D., Anderson, L. S., & Wittmann, H. (2022). Temporal evolution of headwall erosion rates derived from cosmogenic nuclide concentrations in the medial moraines of Glacier d’Otemma. Switzerland. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 47(10), 2437–2454. https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.5386
Wilkinson, M. T., & Humphreys, G. S. (2006). Slope aspect, slope length and slope inclination controls of shallow soils vegetated by sclerophyllous heath—Links to long-term landscape evolution. Geomorphology, 76(3–4), 347–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOMORPH.2005.11.011
Wischmeier, W. H., & Smith D. D. (1978). Predicting rainfall erosion losses—A guide to conservation planning. https://naldc.nal.usda.gov/download/CAT79706928/PDF
Wu, G. L., Liu, Y. F., Cui, Z., Liu, Y., Shi, Z. H., Yin, R., & Kardol, P. (2020). Trade-off between vegetation type, soil erosion control and surface water in global semi-arid regions: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 57(5), 875–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13597
Wuepper, D., Borrelli, P., & Finger, R. (2019). Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nature Sustainability, 3(1), 51–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0438-4
Yang, J. L., & Zhang, G. L. (2011). Water infiltration in urban soils and its effects on the quantity and quality of runoff. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(5), 751–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11368-011-0356-1/METRICS
Yesuph, A. Y., & Dagnew, A. B. (2019). Soil erosion mapping and severity analysis based on RUSLE model and local perception in the Beshillo catchment of the Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 8(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/S40068-019-0145-1
Yue, Y., Ni, J., Ciais, P., Piao, S., Wang, T., Huang, M., Borthwick, A. G. L., Li, T., Wang, Y., Chappell, A., & Van Oost, K. (2016). Lateral transport of soil carbon and land-atmosphere CO2 flux induced by water erosion in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(24), 6617–6622. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1523358113
Yusof, F. M., Jamil, N. R., Laew, N. I., Aini, N., & Manaf, L. A. (2016). Land use change and soil loss risk assessment by using geographical information system (GIS): A case study of lower part of Perak River. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 37(1), 012065. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/37/1/012065
Zhao, W. W., Fu, B. J., & Chen, L. D. (2012). A comparison between soil loss evaluation index and the C-factor of RUSLE: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 16(8), 2739–2748. https://doi.org/10.5194/HESS-16-2739-2012
Zhu, A. X., Wang, P., Zhu, T., Chen, L., Cai, Q., & Liu, H. (2013). Modeling runoff and soil erosion in the Three-Gorge Reservoir drainage area of China using limited plot data. Journal of Hydrology, 492, 163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2013.03.038
Zhu, G., Tang, Z., Shangguan, Z., Peng, C., & Deng, L. (2019). Factors affecting the spatial and temporal variations in soil erodibility of China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 124(3), 737–749. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JF004918
Zidan, H. F. (2017). Republic of Iraq ministry of agriculture land degradation neutrality target setting national report. In Ministry of Agriculture. https://knowledge.unccd.int/sites/default/files/ldn_targets/2019-08/Iraq%20LDN%20TSP%20Country%20Report.pdf. Accessed 15 Feb 2023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kamal Kolo, Badeea Abdi, and Himan Shahabi contributed importantly to the study. Kamal Kolo conceptualized and designed the study. Kamal Kolo and Badeea Abdi conducted the field data collection and analysis. Badeea Abdi performed RS and GIS analysis. Kamal Kolo and Badeea Abdi applied the RUSLE model and soil erosion analysis. Badeea Abdi, Kamal Kolo, and Himan Shahabi wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Kamal Kolo, Badeea Abdi, and Himan Shahabi contributed jointly to providing critical revisions and discussion of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdi, B., Kolo, K. & Shahabi, H. Soil erosion and degradation assessment integrating multi-parametric methods of RUSLE model, RS, and GIS in the Shaqlawa agricultural area, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1149 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11796-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11796-4