Abstract
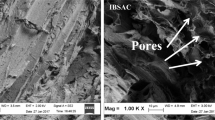
Ash collected from thrown-away by-products while preparing a popular traditional food additive, kolakhar of the Assamese community of North East, India, was used as an alternate cost-effective, porous bioadsorbent option from the conventional activated carbon for the purification of carcinogenic dyes laden water. The base material for kolakhar preparation was taken from the discarded banana stem waste to stimulate agricultural waste management. Methylene blue (MB) and basic fuchsin (BF) dyes were used as model cationic dyes. Characterization techniques like CHN, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis of the prepared banana stem ash (BSA) reveal the presence of high inorganic contents and functional groups in the irregular, porous bioadsorbent with surface area 55.534 m2 g−1. Various regulating parameters studied to optimize the adsorption capacity of BSA were bioadsorbent dose (0.1–3 g/L), temperature (298–318 K), contact time (0–150 min), pH (2–9), and initial dye concentrations (10–40 mg/L). Non-linear kinetic models suggested Elovich for both MB and BF adsorption, while the non-linear isotherm model suggested Langmuir and Temkin for MB and BF adsorption, respectively, as best-fitted curves. The monolayer adsorption capacity (qm) for MB and BF was 15.22 mg/g and 24.08 mg/g at 318 K, respectively, with more than 95% removal efficiency for both dyes. The thermodynamic parameters studied indicated that the adsorption is spontaneous. The ∆H0 values of MB and BF adsorptions were 2.303 kJ/mol (endothermic) and − 29.238 kJ/mol (exothermic), respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials of the research are available and can be obtained on request.
References
Adebayo, M. A., Jabar, J. M., Amoko, J. S., Openiyi, E. O., & Shodiya, O. O. (2022). Coconut husk-raw clay-Fe composite: Preparation, characteristics and mechanisms of Congo red adsorption. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 14370.
Adetuyi, A. O., & Jabar, J. M. (2011). Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of indigo adsorption on some activated bio-solids. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan, 33(6), 158.
Ahmad, T., & Danish, M. (2018). Prospects of banana waste utilization in wastewater treatment: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 206, 330–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.10.061
Ahmaruzzaman, M., & Gupta, V. K. (2011). Rice husk and its ash as low-cost adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 50(24), 13589–13613.
Ali, N. S., Jabbar, N. M., Alardhi, S. M., Majdi, H. S., & Albayati, T. M. (2022). Adsorption of methyl violet dye onto a prepared bio-adsorbent from date seeds: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Heliyon, 8(8), e10276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10276
Aljeboree, A. M., & Alkaim, A. F. (2019). Role of plant wastes as an ecofriendly for pollutants (crystal violet dye) removal from Aqueous Solutions. Plant Archives, 19(2), 902–905.
Anastopoulos, I., & Kyzas, G. Z. (2016). Are the thermodynamic parameters correctly estimated in liquid-phase adsorption phenomena? Journal of Molecular Liquids, 218, 174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.02.059
Arulkumar, M., Sathishkumar, P., & Palvannan, T. (2011). Optimization of Orange G dye adsorption by activated carbon of Thespesia populnea pods using response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(1), 827–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.067
Bello, K., Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Rao, A., & Byrappa, K. (2018). A study on adsorption behavior of newly synthesized banana pseudo-stem derived superabsorbent hydrogels for cationic and anionic dye removal from effluents. Carbohydrate Polymers, 181, 605–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.106
Bello, O. S., Adegoke, K. A., & Akinyunni, O. O. (2017). Preparation and characterization of a novel adsorbent from Moringa oleifera leaf. Applied Water Science, 7(3), 1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0345-4
Belmabrouk, H., Selmi, M., Alshahrani, T., Bajahzar, A., & Jabli, M. (2022). Experimental and theoretical study of methylene blue biosorption using a new biomaterial Pergularia tomentosa L. fruit. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(12), 12039–12056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03979-2
Bessashia, W., Berredjem, Y., Hattab, Z., & Bououdina, M. (2020). Removal of basic fuchsin from water by using mussel powdered eggshell membrane as novel bioadsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Research, 186, 109484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109484
Blackburn, R. S. (2004). Natural polysaccharides and their interactions with dye molecules: Applications in effluent treatment. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(18), 4905–4909. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049972n
Borgohain, X., Das, E., & Rashid, M. H. (2023). Facile synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles for enhanced removal of malachite green dye from an aqueous environment. Materials Advances.
Castro, R. S. D., Caetano, L., Ferreira, G., Padilha, P. M., Saeki, M. J., Zara, L. F., & Castro, G. R. (2011). Banana peel applied to the solid phase extraction of copper and lead from river water: Preconcentration of metal ions with a fruit waste. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 50(6), 3446–3451. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101499e
Coughlin, R. W., & Ezra, F. S. (1968). Role of surface acidity in the adsorption of organic pollutants on the surface of carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 2(4), 291–297. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60016a002
Cusioli, L. F., Quesada, H. B., Baptista, A. T. A., Gomes, R. G., & Bergamasco, R. (2020). Soybean hulls as a low-cost biosorbent for removal of methylene blue contaminant. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 39(2), e13328.
Deokar, S. K., & Mandavgane, S. A. (2015). Rice husk ash for fast removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution. Adsorption Science & Technology, 33(5), 429–440.
Dome, K., Podgorbunskikh, E., Bychkov, A., & Lomovsky, O. (2020). Changes in the crystallinity degree of starch having different types of crystal structure after mechanical pretreatment. Polymers, 12(3), 641.
Feng, N., Guo, X., & Liang, S. (2009). Adsorption study of copper (II) by chemically modified orange peel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2), 1286–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.096
Feng, Y., Yang, F., Wang, Y., Ma, L., Wu, Y., Kerr, P. G., & Yang, L. (2011). Basic dye adsorption onto an agro-based waste material – Sesame hull (Sesamum indicum L.). Bioresource Technology, 102(22), 10280–10285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.090
Forgacs, E., Cserháti, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environment International, 30(7), 953–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001
Ghani, Z. A., Yusoff, M. S., Zaman, N. Q., Zamri, M. F. M. A., & Andas, J. (2017). Optimization of preparation conditions for activated carbon from banana pseudo-stem using response surface methodology on removal of color and COD from landfill leachate. Waste Management, 62, 177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.02.026
Giles, C. H., MacEwan, T. H., Nakhwa, S. N., & Smith, D. (1960). A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. Journal of the Chemical Society, 111, 3973–3993.
Gogoi, C., Saikia, J., Bhomick, P., Sinha, D., & Goswamee, R. L. (2022). Functionalised carbon from Musa Balbisiana stems - A byproduct of edible alkali preparation and a suitable adsorbent for fluoride and arsenic from contaminated water. Materials Today: Proceedings, 68, 223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.08.284
Grabi, H., Ouakouak, A., Kadouche, S., Lemlikchi, W., Derridj, F., & Din, A. T. M. (2022). Mechanism and adsorptive performance of ash tree seeds as a novel biosorbent for the elimination of methylene blue dye from water media. Surfaces and Interfaces, 30, 101947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101947
Hazzaa, R., & Hussein, M. (2015). Adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solution onto activated carbon prepared from olive stones. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 4, 36–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2015.04.002
Horwitz, W., & International, A. (2002). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (17. ed., current through revision ed.). Gaithersburg, Md.: AOAC International.
Isik, B., Ugraskan, V., & Cankurtaran, O. (2022). Effective biosorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using wild macrofungus (Lactarius piperatus). Separation Science and Technology, 57(6), 854–871.
Jabar, J. M., & Odusote, Y. A. (2020). Removal of cibacron blue 3G-A (CB) dye from aqueous solution using chemo-physically activated biochar from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 13(5), 5417–5429.
Jabar, J. M., & Odusote, Y. A. (2021). Utilization of prepared activated biochar from water lily (Nymphaea lotus) stem for adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–12.
Jabar, J. M., Adebayo, M. A., Odusote, Y. A., Yılmaz, M., & Rangabhashiyam, S. (2023). Valorization of microwave-assisted H3PO4-activated plantain (Musa paradisiacal L) leaf biochar for malachite green sequestration: Models and mechanism of adsorption. Results in Engineering, 18, 101129.
Jabar, J. M., Adebayo, M. A., Owokotomo, I. A., Odusote, Y. A., & Yılmaz, M. (2022a). Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous ZnCl2–activated cocoa (Theobroma cacao L) leaves biochar derived via pyrolysis for crystal violet dye removal. Heliyon, 8(10), e10873.
Jabar, J. M., Odusote, Y. A., Alabi, K. A., & Ahmed, I. B. (2020). Kinetics and mechanisms of congo-red dye removal from aqueous solution using activated Moringa oleifera seed coat as adsorbent. Applied Water Science, 10(6), 1–11.
Jabar, J. M., Odusote, Y. A., Ayinde, Y. T., & Yılmaz, M. (2022b). African almond (Terminalia catappa L) leaves biochar prepared through pyrolysis using H3PO4 as chemical activator for sequestration of methylene blue dye. Results in Engineering, 14, 100385.
Jabar, J. M., Owokotomo, I. A., Ayinde, Y. T., Alafabusuyi, A. M., Olagunju, G. O., & Mobolaji, V. O. (2021). Characterization of prepared eco-friendly biochar from almond (Terminalia catappa L) leaf for sequestration of bromophenol blue (BPB) from aqueous solution. Carbon Letters, 1–14.
Kalita, P., & Kander, C. C. (2014). Kolakhar-a traditional herbal soda of Assam. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Research and Bioscience, 2(5), 122–123.
Kalita, S., Pathak, M., Devi, G., Sarma, H. P., Bhattacharyya, K. G., Sarma, A., & Devi, A. (2017). Utilization of Euryale ferox Salisbury seed shell for removal of basic fuchsin dye from water: Equilibrium and kinetics investigation. RSC Advances, 7(44), 27248–27259.
Khan, I., Saeed, K., Zekker, I., Zhang, B., Hendi, A. H., Ahmad, A., & Shah, L. A. (2022). Review on methylene blue: Its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water, 14(2), 242.
Khodabandehloo, A., Rahbar-Kelishami, A., & Shayesteh, H. (2017). Methylene blue removal using Salix babylonica (Weeping willow) leaves powder as a low-cost biosorbent in batch mode: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 244, 540–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.108
Kumar, N. S., Shaikh, H. M., Asif, M., & Al-Ghurabi, E. H. (2021). Engineered biochar from wood apple shell waste for high-efficient removal of toxic phenolic compounds in wastewater. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 2586.
Lam, C. Y. (2020). Removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution using banana peel.
Leite, A. J. B., Lima, E. C., dos Reis, G. S., Thue, P. S., Saucier, C., Rodembusch, F. S., & Dotto, G. L. (2017). Hybrid adsorbents of tannin and APTES (3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane) and their application for the highly efficient removal of acid red 1 dye from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(5), 4307–4318.
Li, H., Niu, S., Lu, C., Liu, M., & Huo, M. (2014). Transesterification catalyzed by industrial waste—Lime mud doped with potassium fluoride and the kinetic calculation. Energy Conversion and Management, 86, 1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.06.082
Liu, L., Gao, Z. Y., Su, X. P., Chen, X., Jiang, L., & Yao, J. M. (2015). Adsorption removal of dyes from single and binary solutions using a cellulose-based bioadsorbent. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 3(3), 432–442. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500848m
Madhu, R., Veeramani, V., & Chen, S.-M. (2014). Heteroatom-enriched and renewable banana-stem-derived porous carbon for the electrochemical determination of nitrite in various water samples. Scientific Reports, 4(1), 4679. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04679
Mattson, J. A., Mark, H. B., Malbin, M. D., Weber, W. J., & Crittenden, J. C. (1969). Surface chemistry of active carbon: Specific adsorption of phenols. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 31(1), 116–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(69)90089-7
Mishra, P. C., & Patel, R. K. (2009). Use of agricultural waste for the removal of nitrate-nitrogen from aqueous medium. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(1), 519–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.12.003
Mishra, S., Prabhakar, B., Kharkar, P. S., & Pethe, A. M. (2023). Banana peel waste: An emerging cellulosic material to extract nanocrystalline cellulose. ACS Omega, 8(1), 1140–1145. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c06571
Misran, E., Bani, O., Situmeang, E. M., & Purba, A. S. (2018). Removal efficiency of methylene blue using activated carbon from waste banana stem: Study on pH influence.
Misran, E., Bani, O., Situmeang, E. M., & Purba, A. S. (2022). Banana stem based activated carbon as a low-cost adsorbent for methylene blue removal: Isotherm, kinetics, and reusability. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 61(3), 1946–1955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.07.022
Mohammad, S. G., Ahmed, S. M., & Badawi, A. F. M. (2015). A comparative adsorption study with different agricultural waste adsorbents for removal of oxamyl pesticide. Desalination and Water Treatment, 55(8), 2109–2120. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.930797
Mondal, B., Bairagi, D., Nandi, N., Hansda, B., Das, K. S., Edwards-Gayle, C. J. C., & Banerjee, A. (2020). Peptide-based gel in environmental remediation: Removal of toxic organic dyes and hazardous Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions from wastewater and oil spill recovery. Langmuir, 36(43), 12942–12953. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02205
Mopoung, S. (2008). Surface image of charcoal and activated charcoal from banana peel. Journal of Microscopy Society of Thailand, 22, 15–19.
Nguyen, T. N., Le, P. A., & Phung, V. B. T. (2022). Facile green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and biomass-derived activated carbon from banana peels: Synthesis and investigation. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 12(7), 2407–2416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00839-2
Pal, S., Ghorai, S., Das, C., Samrat, S., Ghosh, A., & Panda, A. B. (2012). Carboxymethyl tamarind-g-poly(acrylamide)/silica: A high performance hybrid nanocomposite for adsorption of methylene blue dye. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 51(48), 15546–15556. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie301134a
Patel, H., & Vashi, R. T. (2015). Characterization and treatment of textile wastewater: Elsevier.
Pathak, P. D., Mandavgane, S. A., & Kulkarni, B. D. (2017). Fruit peel waste: Characterization and its potential uses. Current Science, 444–454.
Paul, J. J., Surendran, A., & Thatheyus, A. J. (2020). Efficacy of orange peel in the decolourization of the commercial auramine yellow dye used in textile industry.
Pirzada, T., Mathew, R., Guenther, R. H., Sit, T. L., Opperman, C. H., Pal, L., & Khan, S. A. (2020). Tailored lignocellulose-based biodegradable matrices with effective cargo delivery for crop protection. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8(17), 6590–6600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05670
Raghav, S., & Kumar, D. (2018). Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies of fluoride adsorbed by tetrametallic oxide adsorbent. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 63(5), 1682–1697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b00024
Rajkumari, K., & Rokhum, L. (2020). A sustainable protocol for production of biodiesel by transesterification of soybean oil using banana trunk ash as a heterogeneous catalyst. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 10(4), 839–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00647-8
Ramalingam, B., Parandhaman, T., Choudhary, P., & Das, S. K. (2018). Biomaterial functionalized graphene-magnetite nanocomposite: A novel approach for simultaneous removal of anionic dyes and heavy-metal ions. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6(5), 6328–6341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00139
Saha, T. K., Bishwas, R. K., Karmaker, S., & Islam, Z. (2020). Adsorption characteristics of Allura Red AC onto sawdust and hexadecylpyridinium bromide-treated sawdust in aqueous solution. ACS Omega, 5(22), 13358–13374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01493
Sahu, S., Pahi, S., Tripathy, S., Singh, S. K., Behera, A., Sahu, U. K., & Patel, R. K. (2020). Adsorption of methylene blue on chemically modified lychee seed biochar: Dynamic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 315, 113743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113743
Sewu, D. D., Boakye, P., & Woo, S. H. (2017). Highly efficient adsorption of cationic dye by biochar produced with Korean cabbage waste. Bioresource Technology, 224, 206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.009
Shamsollahi, Z., & Partovinia, A. (2019). Recent advances on pollutants removal by rice husk as a bio-based adsorbent: A critical review. Journal of Environmental Management, 246, 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.145
Silva, C. R., Gomes, T. F., Andrade, G. C. R. M., Monteiro, S. H., Dias, A. C. R., Zagatto, E. A. G., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2013). Banana peel as an adsorbent for removing atrazine and ametryne from waters. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(10), 2358–2363. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304742h
Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2007). Adsorption thermodynamics and isosteric heat of adsorption of toxic metal ions onto bagasse fly ash (BFA) and rice husk ash (RHA). Chemical Engineering Journal, 132(1), 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.01.007
Subramanyam, B., & Das, A. (2014). Linearised and non-linearised isotherm models optimization analysis by error functions and statistical means. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12, 1–6.
Tran, H. N., Wang, Y.-F., You, S.-J., & Chao, H.-P. (2017). Insights into the mechanism of cationic dye adsorption on activated charcoal: The importance of π–π interactions. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 107, 168–180.
Villabona-Ortíz, Á., Figueroa-Lopez, K. J., & Ortega-Toro, R. (2022). Kinetics and adsorption equilibrium in the removal of azo-anionic dyes by modified cellulose. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063640
Wang, J., & Guo, X. (2020). Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 390, 122156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122156
Weng, C.-H., Lin, Y.-T., & Tzeng, T.-W. (2009). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pineapple leaf powder. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(1), 417–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.080
Xu, B., Hou, S., Cao, G., Wu, F., & Yang, Y. (2012). Sustainable nitrogen-doped porous carbon with high surface areas prepared from gelatin for supercapacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(36), 19088–19093.
Yang, K., & Xing, B. (2010). Adsorption of organic compounds by carbon nanomaterials in aqueous phase: Polanyi theory and its application. Chemical Reviews, 110(10), 5989–6008.
Yu, D., Wang, L., & Wu, M. (2018). Simultaneous removal of dye and heavy metal by banana peels derived hierarchically porous carbons. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 93, 543–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.038
Zhao, W.-D., Chen, L.-P., & Jiao, Y. (2023). Preparation of activated carbon from sunflower straw through H3PO4 activation and its application for acid fuchsin dye adsorption. Water Science and Engineering, 16(2), 192–202.
Zhou, D., Li, D., Li, A., Qi, M., Cui, D., Wang, H., & Wei, H. (2021). Activated carbons prepared via reflux-microwave-assisted activation approach with high adsorption capability for methylene blue. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104671
Zhul-quarnain, A., Ogemdi, I. K., Modupe, I., Gold, E., & Chidubem, E. E. (2018). Adsorption of malachite green dye using orange peel. Journal of Biomaterials, 2(2), 31–40.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Center (SAIC), Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), Guwahati (under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Government of India) for providing necessary laboratory facilities and workspace to complete the work. The authors also thank DST, Govt. of India, for providing financial support in the execution of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Emee Das: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, software, visualization, original draft, review, and editing; Suprakash Rabha: review and data curation; Karishma Talukdar: collection of the biomaterial; Manisha Goswami: laboratory work and reviewing; Arundhuti Devi: guidance and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable as the study did not include human subjects.
Consent for publication
All authors, funding agencies, and the institute where the analysis was done have the consent for the publication and have no objections. All authors read and approve this submission.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Das, E., Rabha, S., Talukdar, K. et al. Propensity of a low-cost adsorbent derived from agricultural wastes to interact with cationic dyes in aqueous solutions. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1044 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11656-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11656-1