Abstract
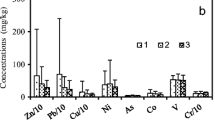
Heavy metals in indoor dust are associated with health risks in humans. However, in Shijiazhuang, a city in northern China with severe haze, no research has been published on this topic. To determine the content, distribution characteristics, and sources of heavy metals in indoor dust in the city of Shijiazhuang, indoor dust samples from 33 sampling points in the main urban area of Shijiazhuang were collected and tested. Concentrations of Cu, Ni, Cr, Zn, Cd, and Pb were 87.0, 35.1, 104.4, 568.0, 1.980, and 187.6 mg·kg−1, respectively; their levels have been discussed statistically in comparison with the reported values in other cities in China. The sources of heavy metals were analyzed using enrichment factor, correlation coefficient, and principal component analysis. The results showed that the levels of all six elements in indoor dust in Shijiazhuang exceeded the background values of soil in Hebei Province. Among these, Cd, Pb, and Zn were significantly enriched. The enrichment factors of Cu, Ni, and Cr were below 10, and their levels at different sampling points were similar, indicating their geogenic source. The corresponding pollution levels of Cd, Pb, and Zn were relatively high, and their levels at different points were significantly different and correlated, indicating that they were derived mainly from transportation. Additionally, the level of Zn was significantly affected by the indoor environment. Our findings provide a basis for conducting health risk assessments in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Al-Rajhi, M. A., Seaward, M. R. D., & Al-Aamer, A. S. (1996). Metal levels in indoor and outdoor dust in Riyadh Saudi Arabia. Environment International, 22(3), 315–324.
Cai, K., Luan, W. L., Li, S. M., Li, C., & Li, Q. Q. (2012). Analysis of the source of heavy metal elements in atmosphere over Shijiazhuang city. Earth and Environment, 40(1), 1108–1115.
Cai, Y. M., Huang, H. S., Ren, L. L., & Zhang, Y. L. (2017). Levels, sources, and health risk assessments of heavy metals in indoor dust in a college in the Pearl River Delta. Environmental Science, 38(9), 3620–3627.
Cao, Z. G., Yu, G., Lü, X. Y., Wang, M. L., Li, Q. L., Feng, J. L., Yan, G. X., Yu, H., & Sun, J. H. (2016). Particle size distribution, seasonal variation characteristics and human exposure assessment of heavy metals in typical settled dust from Beijing. Environmental Science, 37(4), 1272–1278.
Charlesworth, S., Everett, M., Mccarthy, R., Ordonnez, A., & de Miguel, E. (2003). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands. UK. Environment International, 29(5), 563–573.
Chattopadhyay, G., Lin, C. P., & Feitz, A. J. (2003). Household dust metal levels in the Sydney metropolitan area. Environmental Research, 93(3), 301–307.
Chen, Y. N., & Ma, J. H. (2016). Assessment of pollution and health risks of heavy metals in surface dusts from driving schools in a city of Henan China. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(8), 3017–3026.
Cheng, H. X., Li, K., Li, M., Yang, K., Liu, F., & Chang, X. (2014). Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(3), 265–306.
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Center). (1990). The background values of elements in Chinese soils (pp. 334–379). Environmental Science Press China.
Cui, X. T., & Li, S. M. (2013). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and the environmental quality in the atmosphere near the ground surface of city Shijiazhuang. Journal of Safety and Environment, 13(6), 138–142.
Glorennec, P., Lucas, J. P., Mandin, C., & Le Bot, B. (2012). French children’s exposure to metals via ingestion of indoor dust, outdoor playground dust and soil: Contamination data. Environment International, 45(1), 129–134.
Han, Y. M., Du, P. X., Cao, J. J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186.
Huang, H., Xu, Z. Q., & Yan, J. X. (2021). Character of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk evaluation in indoor dust from urban and rural areas in Taiyuan city during heating season. Environmental Science, 42(5), 2143–2152.
Hwang, H. M., Park, E. K., Young, T. M., & Hammock, B. D. (2008). Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in indoor dust. Science of the Total Environment, 404, 26–35.
Jin, D. (2016). Assessing heavy metals contamination and potential health risk from indoor dust in Shenyang, China. Dissertation, Shenyang: Shenyang University, 1–47.
Latif, M. T., Othman, M. R., Chong, L. K., Murayadi, S. A., Nazri, K., & Sahaimia, A. (2009). Composition of household dust in semi-urban areas in Malaysia. Indoor and Built Environment, 18(2), 155–161.
Li, X. Y., Wang, L., & Zhang, S. T. (2016). Level and the courses of heavy metals and its risk assessment in indoor dust of city: Take Guiyang as a case. Environmental Science, 37(8), 2889–2896.
Li, X. Y., & Xie, X. J. (2013). A study on heavy metals in household dusts in 3 cities in Southwestern China. China Environmental Science, 33(2), 365–371.
Lin, Y. S. (2016). Distribution characteristic, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust in residential areas of Huainan city. Dissertation, Wuhu: Anhui Normal University, 25–65.
Lin, Y. S., Fang, F. M., Wang, F., & Xu, M. (2015a). Pollution distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust in Anhui rural China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(9), 565.
Lin, Y. S., Fang, F. M., Xu, M. L., & Wang, F. (2015b). Research progress of heavy metal pollution in indoor dust. Urban Environment and Urban Ecology, 28(3), 29–34.
Liu, Q. T., Diamond, M. L., Gingrich, S. E., Ondov, J. M., Maciejczyk, P., & Stern, G. A. (2003). Accumulation of metals, trace elements and semi-volatile organic compounds on exterior window surfaces in Baltimore. Environmental Pollution, 122(1), 51–61.
Lucas, J. P., Bellanger, L., Le Strat, Y., Le Tertre, A., Glorennec, P., Le Bot, B., Etchevers, A., Mandin, C., & Sebille, V. (2014). Source contributions of lead in residential floor dust and within-home variability of dust lead loading. Science of the Total Environment, 470–471, 768–779.
Madany, I. M., Akhter, M. S., & Jowder, O. A. A. (1994). The correlations between heavy metals in residential indoor dust and outdoor street dust in Bahrain. Environment International, 20(4), 483–492.
Rasmussen, P. E., Levesque, C., Chenier, M., Gardner, H. D., Jones-Otazo, H., & Petrovic, S. (2013). Canadian House Dust Study: Population-based concentrations, loads and loading rates of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc inside urban homes. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 520–529.
Rasmussen, P. E., Subramanian, K. S., & Jessiman, B. J. (2001). A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 267, 125–140.
Shijiazhuang Municipal Bureau of Statistics. (2018). Shijiazhuang Statistical Yearbook (pp. 3–4). China Statistics Press.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Tong, S. T., & Lam, K. C. (1998). Are nursery schools and kindergartens safe for our kids? The Hong Kong study. Science of the Total Environment, 216, 217–225.
Tong, S. T., & Lam, K. C. (2000). Home sweet home? A case study of household dust contamination in Hong Kong. Science of the Total Environment, 256, 115–123.
Turner, A., & Ip, K. H. (2007). Bioaccessibility of metals in dust from the indoor environment: Application of a physiologically based extraction test. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(22), 7851–7856.
Wan, D. J., Han, Z. X., Yang, J. S., Yang, G., & Liu, X. (2016). Heavy metal pollution in settled dust associated with different urban functional areas in a heavily air-polluted city in North China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(11), 1119.
Yang, X. Z., Chen, Y., Xu, D. D., & He, T. T. (2011). Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment in subway dust in Beijing. China Environmental Science, 31(6), 944–950.
Zhang, K. (2018). Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surfave dust of Shijiazhuang city. Dissertation, Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University. 33–34.
Zhao, Z. (2009). Research on heavy metal pollution in theof street dusts in Shijiazhuang City (pp. 21–22). Hebei Normal University.
Zheng, J., Chen, K. H., Yan, X., Chen, S. J., Hu, G. C., Peng, X. W., Yuan, J. G., Mai, B. X., & Yang, Z. Y. (2013). Heavy metals in food, house dust, and water from an e-waste recycling area in South China and the potential risk to human health. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 96(6), 205–212.
Zhou, P., Qin, W., Guo, S., An, S., Xiao, J., Liu. J., & Ji, Y. (2018). Pollution characteristics and source analysis of metal elements in PM2. 5 of paved road dust in Shijiazhuang City during winter. Research of Environmental Sciences, 31(8), 1366–1372.
Zhu, Z., Han, Z., Bi, X., & Yang, W. (2012). The relationship between magnetic parameters and heavy metal contents of indoor dust in e-waste recycling impacted area, Southeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 433, 302–308.
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant number D2018403095) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 41903018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TD and WX carried out the investigation and sample chemical analysis. LX participated in the methodology discussion and creating the figures. YL helped in study conceptualization and data reduction. ZP took part in most aspects of the study and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and agree to final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent statement
Not applicable.
Institutional review board statement
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, P., Liu, X., Yin, L. et al. Levels, distribution characteristics, and sources of heavy metals in indoor dust in Shijiazhuang, China. Environ Monit Assess 194, 857 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10543-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10543-5