Abstract
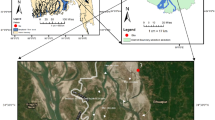
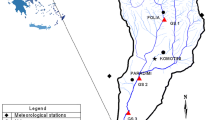
Water quality indices (WQIs) are numerical measures used by researchers and water managers to communicate water quality status to the public. This study analyzes the official databases from the CONAGUA monitoring network of the main tributary rivers in the middle basin of the San Pedro-Mezquital River in Durango, Mexico, for a 6-year period (2013–2018). We applied three WQIs to 432 data (18 sampling sites, four samples per year, 6 years): Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) WQI, National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) WQI, and Secretariat of Urban Development and Ecology (SEDUE) WQI. The Canadian index proved to be a flexible, appropriate, and rigorous methodology for assessing water quality based on its use. Results classify the water quality in the studied reservoirs as good, while river water was rated for public use, as marginal to very poor. No statistical significant differences in the quality of water between the rainy (June–October) and dry (November–May) seasons were found. However, tendency shows that in the rainy season the water quality was lower, mainly attributed to agricultural runoffs and bank erosion. The main contamination problem was the presence of fecal coliforms in high concentrations, which is associated to the high population density in the area, low sanitation efficiency, and multiple non-point discharges.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used for the determination of water quality in the study area is publicly available at http://sina.conagua.gob.mx/sina/index.php and https://laboratorios.conagua.gob.mx:8446/LABORATORIOS/Pages/Laboratorios.aspx.
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Water quality indices. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-54304-2.00001-4
Addinsoft. (2020). XLSTAT statistical and data analysis solution. Software. Addinsoft Inc. Nueva York, USA. https://www.xlstat.com
Bilgin, A. (2018). Evaluation of surface water quality by using Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) method and discriminant analysis method: A case study Coruh River Basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(9), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6927-5
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index—Do we dare? Water and Sewage Works, 117(10), 339–343.
Casillas-García, L. F., de Anda, J., Yebra-Montes, C., Shear, H., Díaz-Vázquez, D., & Gradilla-Hernández, M. S. (2021). Development of a specific water quality index for the protection of aquatic life of a highly polluted urban river. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107899
CCME. (2017). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. In CCME water quality index user’s manual.
CONAGUA. (2020). Programa Nacional Hídrico 2020–2024. https://www.gob.mx/conagua/documentos/programa-nacional-hidrico-pnh-2020-2024. Accessed 25 Sept 2020.
CONAGUA. (2021a). Ley Federal de Derechos. Diario oficial de la federación, 1–64. https://www.gob.mx/conagua/documentos/ley-federal-de-derechos-2020. Accessed 10 Oct 2021a.
CONAGUA. (2021). Gerencia de Planificación Hídrica, Sistema Nacional de Información del Agua (SINA). http://sina.conagua.gob.mx/sina/index.php. Accessed 6 Sept 2021b.
De La Mora-Orozco, C., Flores-Lopez, H., Rubio-Arias, H., Chavez-Duran, A., & Ochoa-Rivero, J. (2017). Developing a water quality index (WQI) for an irrigation dam. In International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(5), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14050439
de Oliveira, K. L., Ramos, R. L., Oliveira, S. C., & Christofaro, C. (2021). Water quality index and spatio-temporal perspective of a large Brazilian water reservoir. Water Supply, 21(3), 971–982. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.374
García-Rodríguez, G., Sandoval-Rojas, M. E., Corona-Romano, E. R., De Jesús-De la Rosa, R. E., Martínez-Romay, B., García-Gil, E., & García-Gil, E. (2021). Aplicación de dos metodologías para la evaluación de la calidad del agua de cuerpos superficiales destinados a la pesca en el sur del estado de Veracruz. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 37, 89–107. https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.53681
Gikas, G. D., Sylaios, G. K., Tsihrintzis, V. A., Konstantinou, I. K., Albanis, T., & Boskidis, I. (2020). Comparative evaluation of river chemical status based on WFD methodology and CCME water quality index. Science of the Total Environment, 745, 140849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140849
Gitau, M. W., Chen, J., & Ma, Z. (2016). Water quality indices as tools for decision making and management. Water Resources Management, 30(8), 2591–2610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1311-0
Gómez-Álvarez, A., Villalba-Atondo, A., Acosta-Ruíz, G., Catañeda-Olivares, M., & Kamp, D. (2004). Metales pesados en el agua superficial del Río San Pedro durante 1997 y 1999. Revista Internacional De Contaminación Ambiental, 20(1), 5–12.
Gradilla-Hernández, M. S., de Anda, J., Garcia-Gonzalez, A., Montes, C. Y., Barrios-Piña, H., Ruiz-Palomino, P., & Díaz-Vázquez, D. (2020). Assessment of the water quality of a subtropical lake using the NSF-WQI and a newly proposed ecosystem specific water quality index. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(5), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08265-7
Gunda, T., Hess, D., Hornberger, G. M., & Worland, S. (2019). Water security in practice: The quantity-quality-society nexus. Water Security, 6, 100022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasec.2018.100022
Hamlat, A., Guidoum, A., & Koiulala, I. (2017). Status and trends of water quality in the Tafna catchment: A comparative study using water quality indices. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 7(2), 228–245. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.155
Hussien, A. K., Rashwan, I. M. H., & Elshemy, M. (2021). Surface water quality management for drinking use in El-Beheira Governorate. Egypt. Water Environment Research, 93(8), 1428–1444. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1503
IANAS. (2019). Water quality in the Americas. Risks and opportunities. The Inter-American Network of Academies of Sciences (IANAS-IAP): Ciudad de México, Mexico.
Jiménez Cisneros, B. E. (2007). Información y calidad de agua en México. Trayectorias, 9(24), 45–56.
Kachroud, M., Trolard, F., Kefi, M., Jebari, S., & Bourrié, G. (2019). Water quality indices: Challenges and application limits in the literature. Water, 11(2), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020361
Lopes, O. F., de Jesus, R. M., de Sousa, L. F., Rocha, F. A., da Silva, D. M. L., Amorim, A. F., da Silva, V. H. C., & Navoni, J. A. (2021). Comparison between water quality indices in watersheds of the Southern Bahia (Brazil) with different land use. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 12944–12959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10941-7
Lumb, A., Sharma, T. C., & Bibeault, J. -F. (2011). A review of genesis and evolution of water quality index (WQI) and some future directions. Water Quality, Exposure and Health, 3(1), 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-011-0040-0
McClelland, N. I. (1974). Water quality index application in the Kansas River Basin (Vol. 74, No. 1). US Environmental Protection Agency-Region VII
Muñoz-Nava, H., Suárez-Sánchez, J., Valencia-Quintana, R., & Gaspar-Vázquez, K. (2018). Influence of dry and rainy seasons on physicochemical parameters and water quality index, Zahuapan River, Mexico. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 8(8), 1–9.
Musálem-Castillejos, K., Laino-Guanes, R., Bello-Mendoza, R., González-Espinosa, M., & Ramírez-Marcial, N. (2018). Water quality of the Grijalva river on the Chiapas-Tabasco border. Ecosistemas y recursos agropecuarios, 5(13), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.19136/era.a5n13.1334
Poonam, T., Tanushree, B., & Sukalyan, C. (2013). Water quality indices—Important tools for water quality assessment: A review. International Journal of Advances in Chemistry, 1(1), 15–28.
Ranjbar Jafarabadi, A., Masoodi, M., Sharifiniya, M., & Riyahi Bakhtiyari, A. (2016). Integrated river quality management by CCME WQI as an effective tool to characterize surface water source pollution (case study: Karun River, Iran). Pollution, 2(3), 313–330. https://doi.org/10.7508/pj.2016.03.006
Safieh, J., Rebwar, D., Hamed, M. H., Saeed, M. A. H., & Forough, J. (2020). Investigation of water quality in wet and dry seasons under climate change. Ukrainian Journal of Ecology, 10(5), 94–104. https://www.ujecology.com/articles/investigation-of-water-quality-in-wet-and-dry-seasons-under-climate-change.pdf
Şener, Ş, Şener, E., & Davraz, A. (2017). Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Science of the Total Environment, 584, 131–144.
SEMARNAT. (2013). Ordenamiento ecológico del territorio del municipio de Durango. In Resumen ejecutivo. http://api-transparencia.durangocapital.gob.mx/?action=preview&uid=11ae7bbc40d97d9fdf8f375606198ebb&key=2fe548d5ae881ccfbe2be3f5429d7852. Accessed 1 Sept 2020.
SEMARNAT. (2019a). Criterios de calidad del agua. https://apps1.semarnat.gob.mx:8443/dgeia/informe_2008/compendio_2008/compendio2008/10.100.8.236_8080/ibi_apps/WFServleta0c5.html. Accessed 6 Sept 2020.
SEMARNAT. (2019b). Indicadores de calidad del agua. https://apps1.semarnat.gob.mx:8443/dgeia/compendio_2013/dgeiawf.semarnat.gob.mx_8080/ibi_apps/WFServlet28b9.html. Accessed 6 Sept 2020.
Sutadian, A. D., Muttil, N., Yilmaz, A. G., & Perera, B. J. C. (2016). Development of river water quality indices—A review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5050-0
Uddin, M. G., Nash, S., & Olbert, A. I. (2020). A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecological Indicators, 122, 107218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107218
World Health Organization. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chronicle, 38(4), 104–108.
Zotou, I., Tsihrintzis, V. A., & Gikas, G. D. (2020). Water quality evaluation of a lacustrine water body in the Mediterranean based on different water quality index (WQI) methodologies. Journal of Environmental Science and Health—Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 55(5), 537–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2019.1710956.
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous reviewers for insightful comments that helped to improve the manuscript.
Funding
A.P. Gaytán-Alarcón received a scholarship from CONACYT for her doctoral studies. No other funds, grants, or additional support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaytán-Alarcón, A.P., González-Elizondo, M.S., Sánchez-Ortíz, E. et al. Comparative assessment of water quality indices—a case study to evaluate water quality for drinking water supply and irrigation in Northern Mexico. Environ Monit Assess 194, 588 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10198-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10198-2