Abstract
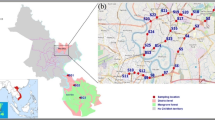
Road dust enriched with heavy metals (HMs) is detrimental to ecosystems and human health in urban environments. In this study, it is to explore the concentrations, spatial distribution, contaminated levels, and source identification of six HMs (lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), cobalt (Co), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni)) based on 130 road dusts in Xinyang urban area. The results indicated that the contents of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Co were higher than the background values in more than 99% of the samples, and their average concentrations were 15.2, 9.2, 8.6, and 6.3 times the background value, respectively. The spatial distribution of high-value areas for Pb, Zn, Cu, Cr, and Ni was more similar, which was associated with traffic density near major roads and population and settlement patterns. Co was relatively different from the five elements, which was distributed in the areas of residence, commerce, and industry. Furthermore, the investigated HMs were clearly polluted, with Pb, Zn, Cu, and Co indicating high levels of contamination, while Cr and Ni were moderately polluted. The comprehensive pollution of the six HMs was mostly moderate to heavy in this study. Moreover, three sources of HMs designated by correlation analysis (CA) and principal component analysis (PCA) were mixed traffic emissions and industrial waste for Cu and Cr; automotive emissions for Pb, Ni, and Zn; and mixed domestic waste and industrial activities for Co, with contributions of 42.3%, 46.4%, and 11.3% via the principal component analysis-multiple linear regression (PCA-MLR) model. The multi-factor index for pollution assessment combined with source identification is extremely effective and practical for providing reliable data support and a theoretical reference for pollution monitoring and governance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adamiec, E. (2017). Chemical fractionation and mobility of traffic-related elements in road environments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(6), 1457–1468.
Aguilera, A., Bautista, F., Gutierrez-Ruiz, M., Ceniceros-Gomez, A. E., Cejudo, R., & Goguitchaichvili, A. (2021). Heavy metal pollution of street dust in the largest city of Mexico, sources and health risk assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08993-4
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). The investigation of metal concentrations in street dust samples in Aqaba city. Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(3), 197–207.
Aminiyan, M. M., Baalousha, M., Mousavi, R., Aminiyan, F. M., Hosseini, H., & Heydariyan, A. (2018). The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: A case study in Rafsanjan, SE Iran. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(14), 13382–13395.
Angulo, E. (1996). The Tomlinson Pollution Load Index applied to heavy metal, ‘Mussel-Watch’ data: A useful index to assess coastal pollution. Science of the Total Environment, 187(1), 19–56.
Bourliva, A., Kantiranis, N., Papadopoulou, L., Aidona, E., Christophoridis, C., Kollias, P., Evgenakis, M., & Fytianos, K. (2018). Seasonal and spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in road dusts of Thessaloniki city, Greece: A one-year monitoring period. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 417–427.
Bryanin, S. V., & Sorokina, O. A. (2019). Effect of soil properties and environmental factors on chemical compositions of forest soils in the Russian Far East. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(3), 1130–1138.
Charlesworth, S., De Miguel, E., & Ordóñez, A. (2011). A review of the distribution of particulate trace elements in urban terrestrial environments and its application to considerations of risk. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(2), 103–123.
Chen, X., Lu, X., & Yang, G. (2012). Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. CATENA, 98, 73–78.
Chen, X., Lu, X., Li, L. Y., & Yang, G. (2013). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an second ring road. NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68(7), 1979–1988.
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre). (1990). The Soil Element Background Value in China. China Environmental Science Press.
Cowan, N., Blair, D., Malcolm, H., & Graham, M. (2021). A survey of heavy metal contents of rural and urban roadside dusts: Comparisons at low, medium and high traffic sites in Central Scotland. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(6), 7365–7378.
Cui, X., Wang, X., & Liu, B. (2020). The characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface dust in Tangshan, a heavily industrialized city in North China, and an assessment of associated health risks. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106432
Delibašić, Š, Đokić-Kahvedžić, N., Karić, M., Keskin, I., Velispahić, A., Huremović, J., Herceg, K., Selimović, A., Silajdžić, S., Žero, S., Gojak-Salimović, S., Partić, A., & Pašalić, A. (2020). Health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in street dust of federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 27(5), 1296–1308.
Dong, S., Zhang, S., Wang, L., Ma, G., Lu, X., & Li, X. (2020). Concentrations, speciation, and bioavailability of heavy metals in street dust as well as relationships with physiochemcal properties: A case study of Jinan City in East China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(28), 35724–35737.
Fan, X., Lu, X., Liu, H., & Qin, Q. (2020). Pollution and source analysis of heavy metal in surface dust from Xi’an university campuses. Environmental Science, 41(8), 3556–3562.
Fang, F. M., Lin, Y. S., Wang, H. D., & Xie, H. F. (2011). Source, exposure characteristics and its environmental effect of heavy metals in urban surface dust. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(23), 7301–7310.
Håkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sediment ecological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Han, Y., Liu, X., Zhao, G., Lü, B., & Chen, Q. (2021). Magnetic monitoring of topsoil and street dust in Xinyang (China) and their environmental implications. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment ,193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09407-1
Hou, S., Zheng, N., Tang, L., Ji, X., Li, Y., & Hua, X. (2019). Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environment International, 128, 430–437.
Huang, B., Zhou, Y., Chang, W., Li, Z., & Zeng, H. (2019). Differential characteristics of heavy metal pollution in road dust and its ecological risk in different function areas of Shenzhen city. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(12), 2398–2408.
Jadoon, W. A., Abdel-Dayem, S., Saqib, Z., Takeda, K., Sakugawa, H., Hussain, M., Shah, G. M., Rehman, W., & Syed, J. H. (2020). Heavy metals in urban dusts from Alexandria and Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt: Implications for human health. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(2), 2007–2018.
Jahandari, A. (2020). Pollution status and human health risk assessments of selected heavy metals in urban dust of 16 cities in Iran. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(18), 23094–23107.
Jose, J., & Srimuruganandam, B. (2020). Investigation of road dust characteristics and its associated health risks from an urban environment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(9), 2819–2840.
Kara, M. (2020). Assessment of sources and pollution state of trace and toxic elements in street dust in a metropolitan city. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(10), 3213–3229.
Kreider, M. L., Panko, J. M., McAtee, B. L., Sweet, L. I., & Finley, B. L. (2010). Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Science of the Total Environment, 408(3), 652–659.
Krupnova, T. G., Rakova, O. V., Gavrilkina, S. V., Antoshkina, E. G., Baranov, E. O., (2020) Road dust trace elements contamination, sources, dispersed composition, and human health risk in Chelyabinsk Russia. Chemosphere 261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127799
Larsen, R. K., & Baker, J. E. (2003). Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere: A comparison of three methods. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(9), 1873–1881.
Li, H.-H., Chen, L.-J., Yu, L., Guo, Z.-B., Shan, C.-Q., Lin, J.-Q., Gu, Y.-G., Yang, Z.-B., Yang, Y.-X., Shao, J.-R., Zhu, X.-M., & Cheng, Z. (2017). Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Science of the Total Environment, 586, 1076–1084.
Lu, X., Shi, D., Yin, N., Pan, H., & Smith, P. (2017). Risk assessment of heavy metals in finer than 63-μm dust particles from various functional areas in Xi’an. China. Air Quality Atmosphere and Health, 10(7), 907–915.
Lu, X., Wang, L., Li, L. Y., Lei, K., Huang, L., & Kang, D. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1–3), 744–749.
Malik, R. N., Jadoon, W. A., & Husain, S. Z. (2010). Metal contamination of surface soils of industrial city Sialkot, Pakistan: A multivariate and GIS approach. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32(3), 179–191.
Manno, E., Varrica, D., & Dongarrà, G. (2006). Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an urban area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela. Sicily. Atmospheric Environment, 40(30), 5929–5941.
Men, C., Liu, R., Xu, L., Wang, Q., Guo, L., Miao, Y., & Shen, Z. (2020) Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121763
Miguel, E., Llamas, J., Chacón, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Røyset, O., & Vadset, M. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: Unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31(17), 2733–2740.
Moradi, Q., Mirzaei, R., Alipour, M., Bay, A., Ghaderpoori, M., Asadi, A., Fakhri, Y., Sorooshian, A., & Mousavi Khaneghah, A. (2020). The concentration, characteristics, and probabilistic health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in street dust: A case study of Kashan, Iran. Toxin Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2020.1728336
Nematollahi, M. J., Dehdaran, S., Moore, F., & Keshavarzi, B. (2021). Potentially toxic elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in street dust of Yazd, a central capital city in Iran: Contamination level, source identification, and ecological-health risk assessment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(1), 485–519.
Othman, M., & Latif, M. T. (2020). Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessments of urban road dust in Kuala Lumpur City. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(10), 11227–11245.
Pan, H., Lu, X., & Lei, K. (2017). A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: Contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 1361–1369.
Phil-Eze, P. O. (2010). Variability of soil properties related to vegetation cover in a tropical rainforest landscape. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 3(7), 177–184.
Rajaram, B. S., Suryawanshi, P. V., Bhanarkar, A. D., & Rao, C. V. C. (2014). Heavy metals contamination in road dust in Delhi city. India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(10), 3929–3938.
Sadeghdoust, F., Ghanavati, N., Nazarpour, A., Babaenejad, T., & Watts, M. J. (2020). Hazard, ecological, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust in Dezful Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05915-5
Shahab, A., Zhang, H., Ullah, H., Rashid, A., Rad, S., Li, J., & Xiao, H. (2020). Pollution characteristics and toxicity of potentially toxic elements in road dust of a tourist city, Guilin, China: Ecological and health risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115419
Shi, D., & Lu, X. (2018). Contamination levels levels and source source analysis analysis of heavy heavy metals metals in the finer finer particles particles of urban urban road road dust dust from Xi’an. China. Environmental Science, 39(7), 3126–3133.
Song, Y., Ji, J., Yang, Z., Yuan, X., Mao, C., Frost, R. L., & Ayoko, G. A. (2011). Geochemical behavior assessment and apportionment of heavy metal contaminants in the bottom sediments of lower reach of Changjiang River. CATENA, 85(1), 73–81.
Song, Y., Lu, X., Zhou, X., & Ge, Z. (2020). Source Identification identification and pollution pollution characteristics characteristics of heavy heavy metals metals in suspended suspended particles particles of urban urban road road dust dust from Xingtai City. Environmental Science, 41(7), 3130–3135.
Srithawirat, T., & Latif, M. T. (2015). Concentration of selected heavy metals in the surface dust of residential buildings in Phitsanulok. Thailand. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(3), 2701–2706.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Tang, Z., Chai, M., Cheng, J., Jin, J., Yang, Y., Nie, Z., Huang, Q., & Li, Y. (2017). Contamination and health risks of heavy metals in street dust from a coalmining city in eastern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 83–91.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2), 241–265.
Tian, H., Yang, L., Xia, Z., Ning, S., & Wei, C. (2018). Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in road sediments of Lintong District. Xi’an. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(2), 276–281.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1–4), 566–575.
Wang, B., Xia, D., Yu, Y., Jia, J., & Xu, S. (2012). Magnetic records of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoil in Lanzhou. China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(3), 384–395.
Wang, H., Cai, L. Qs Wang, G Hu, & Chen, L. (2021b) A comprehensive exploration of risk assessment and source quantification of potentially toxic elements in road dust: A case study from a large Cu smelter in central China CATENA 196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104930
Wang, G., Zhang, S., Xiao, L., Zhong, Q., Li, L., Xu, G., Deng, O., & Pu, Y. (2017b). Heavy metals in soils from a typical industrial area in Sichuan, China: Spatial distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(20), 16618–16630.
Wang, H., Shen, C., Kang, Y., Deng, Q., & Lin, X. (2020a). Spatial distribution of pollution characteristics and human health risk assessment of exposure to heavy elements in road dust from different functional areas of Zhengzhou. China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(21), 26650–26667.
Wang, L., Tao, W., Smardon, R. C., Xu, X., & Lu, X. (2017a). Speciation, sources, and risk assessment of heavy metals in suburban vegetable garden soil in Xianyang City, Northwest China. Frontiers of Earth Science, 12(2), 397–407. Wang, J., Huang, Y., & Cheng, X. (2021a). Status, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment of potentially harmful element from road dust in steel industry city, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 14(4), 1–9.
Wang, S., Cai, L. M., Wen, H. H., Luo, J., Wang, Q. S., & Liu, X. (2019). Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 655, 92–101.
Wang, X., Liu, E., Lin, Q., Liu, L, Yuan, H. Li, Z. (2020b). Occurrence, sources and health risks of toxic metal (loid)s in road dust from a mega city (Nanjing) in China Environmental Pollution, 263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114518
Xia, D., Wang, B., Yu, Y., Jia, J., Nie, Y., Wang, X., & Xu, S. (2014). Combination of magnetic parameters and heavy metals to discriminate soil-contamination sources in Yinchuan — A typical oasis city of Northwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 485, 83–92.
Xiao, Q., Zong, Y., Malik, Z., & Lu, S. (2019). Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 26(5), 1359–1378.
Ye, C., Li, S., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2011). Assessing soil heavy metal pollution in the water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 191(1–3), 366–372.
Yesilkanat, C. M., Kobya, Y., (2021). Spatial characteristics of ecological and health risks of toxic heavy metal pollution from road dust in the Black Sea coast of Turkey Geoderma Regional, 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2021.e00388
Yu, B., Lu, X., Fan, X., Fan, P., Zuo, L., Yang, Y., & Wang, L. (2021). Analyzing environmental risk, source and spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in dust of residential area in Xi'an urban area China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111679
Zeng, J., Han, G. K. (2020 )Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment, northeast Thailand Journal of Cleaner Production 265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121898
Zhang, P., Qin, C., Hong, X., Kang, G., Qin, M., Yang, D., Pang, B., Li, Y., He, J., & Dick, R. P. (2018). Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 1136–1147.
Zhang, S., Wang, L., Zhang, W., Wang, L., Shi, X., Lu, X., & Li, X. (2019). Pollution assessment and source apportionment of trace metals in urban topsoil of Xi’an City in Northwest China. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(4), 575–586.
Zhang, Y., Wu, D., Wang, C., Fu, X., & Wu, G. (2020). Impact of coal power generation on the characteristics and risk of heavy metal pollution in nearby soil. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/20964129.2020.1787092.
Zhao, G., Han, Y., Yan, J., Jiang, L., & Xiang, M. (2015). Studies on the characteristic of four seasons variation in Xinyang City. Journal of Xinyang Normal University Natural Science Edition, 28(4), 529–532.
Zhao, G., Zhang, R., Han, Y., Lü, B., Meng, Y., Wang, S., & Wang, N. (2020). Identifying environmental pollution recorded in street dust using the magnetic method: A case study from central eastern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(28), 34966–34977.
Zhao, N., Lu, X., Chao, S., & Xu, X. (2014). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in less than 100 μm particles of street dust from Xining. China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(5), 2319–2327.
Funding
This research was supported by the intercollegiate Key Scientific Research Projects of Henan Province (Grant No. 22A610012), the Scientific Research Foundation of Graduate School of Xinyang Normal University (Grant No. 2020KYJJ07), the Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU, the State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, CAS (Grant No. SKLLQG2039), and the Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Water and Soil Conservation and Environmental Protection (Grant No. STKF-201928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Zhang, R., Han, Y. et al. Pollution characteristics, spatial distribution, and source identification of heavy metals in road dust in a central eastern city in China: a comprehensive survey. Environ Monit Assess 193, 796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09584-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09584-z