Abstract
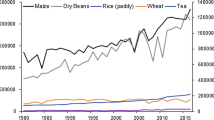
Agricultural drought risk analysis is useful for reducing probable drought risk in the background of global warming. This study aims to identify spatiotemporal characteristics of drought and drought disaster risk in the summer maize growth period under climate change condition. In this research, we use daily datasets from 79 meteorological stations and the maize yield data in the Huang-Huai-Hai (HHH) plain, eastern China during the period 1960–2015. The drought disaster risk index (DDRI) model was applied to assess the drought disaster risk. The maize drought disaster risk maps were drawn under current and future climate change conditions. The results showed that the high DDRI was distributed in northern region and low DDRI was distributed in most of southern region in the HHH plain. During the summer maize growth period, the DDRI decreased gradually from the northern to southern region. The results also exhibited that under the RCP4.5 (Representative Concentration Pathway 4.5) scenario, about one half of the HHH plain belonged to the slight and sub-slight DDRI region in the future 80 years. Overall, our results demonstrated that the DDRI model provided an accurate assessment in both spatial and temporal scales and had a theoretical guidance for improving the adaptation of crop production. Elevating maize drought risk management helps to lessen the anticipated risk to crop production in the HHH plain under the context of climate change.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghakouchak, A., Farahmand, A., Melton, F. S., Teixeira, J., Anderson, M. C., Wardlow, B. D., & Hain, C. R. (2015). Remote sensing of drought: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Reviews of Geophysics, 53(2), 452–480. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014RG000456
Agutu, N. O., Awange, J. L., Zerihun, A., Ndehedehe, C. E., Kuhn, M., & Fukuda, Y. (2017). Assessing multi-satellite remote sensing, reanalysis, and land surface models’ products in characterizing agricultural drought in East Africa. Remote Sensing of Environment, 194, 287–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.03.041
Breshears, D. D., Cobb, N. S., Rich, P. M., Price, K. P., Allen, C. D., Balice, R. G., Romme, W. H., Kastens, J. H., Floyd, M. L., Belnap, J., Anderson, J. J., Myers, O. B., & Meyer, C. W. (2005). Regional vegetation die-off in response to global-change-type drought. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 15144–15148. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0505734102
Chen, H. P., Sun, J. Q., & Chen, X. L. (2013). Future changes of drought and flood events in China under a global warming scenario. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 6(1), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2013.11447051
Chen, J., Tang, C., Sakura, Y., Yu, J., & Fukushima, Y. (2005). Nitrate pollution from agriculture in different hydrogeological zones of the regional groundwater flow system in the North China Plain. Hydrogeology Journal, 13(3), 481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0321-9
Chen, J., Wang, C. Z., Jiang, H., Mao, L. X., & Yu, Z. R. (2011). Estimating soil moisture using Temperature-Vegetation Dryness Index (TVDI) in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(4), 1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903527421
Chiogna, G., Skrobanek, P., Narany, T. S., Ludwig, R., & Stumpp, C. (2018). Effects of the 2017 drought on isotopic and geochemical gradients in the Adige catchment, Italy. Sciences of the Total Environment, 645, 924–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.176
Devos, Y., Ortiz-García, S., Hokanson, K. E., & Raybould, A. (2018). Teosinte and maize teosinte hybrid plants in Europe—environmental risk assessment and management implications for genetically modified maize. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 259, 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.02.032
Du, L., Tian, Q., Yu, T., Meng, Q., Jancso, T., Udvardy, P., & Huang, Y. (2013). A comprehensive drought monitoring method integrating MODIS and TRMM data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 23(1), 245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2012.09.010
Guo, E., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, R., & Li, D. (2017). Assessing spatiotemporal variation of drought and its impact on maize yield in Northeast China. Journal of Hydrology, 553, 231–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.07.060
Hao, Z., & AghaKouchak, A. (2014). A nonparametric multivariate multi-index drought monitoring framework. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 15, 89–101. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-12-0160.1
Hu, Z. H., Wu, Z. R., Islam, A. R. M. T., You, X. Y., Liu, C., Li, Q., & Zhang, X. S. (2021). Spatiotemporal characteristics and risk assessment of agricultural drought disasters during the winter wheat-growing season on the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 143, 1393–1407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03506-8
IPCC. (2014). Climate Change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part B: Regional aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
Islam, A. R. M. T., Shen, S. H., Hu, Z. H., & Rahman, M. A. (2017). Drought hazard evaluation in Boro paddy cultivated areas of western Bangladesh at current and future climate change conditions. Advances in Meteorology, 2017, 3514381. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3514381
Islam, A. R. M. T., Tasnuva, A., Sarker, S. C., Rahman, M. M., Mondal, M. S. H., & Islam, M. M. U. (2014). Drought in Northern Bangladesh: Social, agroecological impact and local perception. International Journal of Ecosystem, 4(3), 150–158. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ije.20140403.07
Jayanthi, H., Husak, G. J., Funk, C., Magadzire, T., Chavula, A., & Verdin, J. P. (2013). Modeling rain-fed maize vulnerability to droughts using the standardized precipitation index from satellite estimated rainfall—Southern Malawi case study. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 4, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2013.02.001
Jia, H., Wang, J., Cao, C., Pan, D., & Shi, P. (2012). Maize drought disaster risk assessment of China based on EPIC model. International Journal of Digital Earth, 5(6), 488–515. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2011.590535
Keating, B. A., & Meinke, H. (1998). Assessing exceptional drought with a cropping systems simulator: A case study for grain production in Northeast Australia. Agricultural Systems, 57, 315–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-521X(98)00021-3
Li, Y., Huang, H., Ju, H., Lin, E., Xiong, W., Han, X., Wang, H., Peng, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Cao, Y., & Hu, W. (2015). Assessing vulnerability and adaptive capacity to potential drought for winter-wheat under the RCP 8.5 scenario in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 209, 125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.03.033
Liu, X. F., Wang, S. X., Zhou, Y., Wang, F. T., Yang, G., & Liu, W. L. (2015). Spatial analysis of meteorological drought return periods in China using Copulas. Natural Hazards, 80(1), 367–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1972-7
Mckee, T. B., Doesken, N. J., & Kleist, J. (1993). The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In American Meteorological Society, Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology. Boston.
Niemeyer, S., & Vogt, J. V. (1998). Towards monitoring drought conditions in Sicily using an energy balance approach. Proc 7th ICCTA, pp. 459–466. Florence, Italy.
Palmer, W. C. (1965). Meteorological Drought. Research Paper No. 45. Washington, DC: US Department of Commerce Weather Bureau.
Potopová, V., Štěpánek, P., Možný, M., Türkotta, L., & Soukup, J. (2015). Performance of the standardised precipitation evapotranspiration index at various lags for agricultural drought risk assessment in the Czech Republic. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 202, 26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.11.022
Pulwarty, R. S., & Sivakumar, M. V. K. (2014). Information systems in a changing climate: Early warnings and drought risk management. Weather and Climate Extremes, 3, 14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2014.03.005
Rahman, M. S., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2019). Are precipitation concentration and intensity changing in Bangladesh overtimes? Analysis of the possible causes of changes in precipitation systems. Science of the Total Environment, 690, 370–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.529
Shi, W. J., Tao, F. L., & Liu, J. Y. (2014). Regional temperature change over the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China: The roles of irrigation versus urbanization. International Journal of Climatology, 34, 1181–1195. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3755
Sun, Z., Zhu, X., Pan, Y., Zhang, J., & Liu, X. (2018). Drought evaluation using the GRACE terrestrial water storage deficit over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 634, 727–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.292
Vicente-Serrano, S. M., & Beguer ́ıa, S., & Lo ́pez-Moreno, J. I. . (2010). A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. Journal of Climate, 23(7), 1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Wang, L., Chen, W., & Zhou, W. (2014). Assessment of future drought in Southwest China based on CMIP5 multimodel projections. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 31(5), 1035–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-3223-3
Wilhite, D. A. (2000). Drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions. In D. A. Wilhite (Eds.), Drought: a global assessment (pp. 3–18). Routledge. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/droughtfacpub/69
Wisner, B. (2000). Risk: Natural hazards, people’s vulnerability and disasters. Routledge.
Wu, X., Wang, P., Huo, Z., Wu, D., & Yang, J. (2018). Crop Drought Identification Index for winter wheat based on evapotranspiration in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 263, 18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.05.001
Yang, J. Y., Mei, X. R., Huo, Z. G., Yan, C. R., Ju, H., Zhao, F. H., & Liu, Q. (2015). Water consumption in summer maize and winter wheat cropping system based on SEBAL model in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(10), 2065–2076. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60951-5
Zhang, F., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, E., Wang, R., & Li, D. (2019). Dynamic drought risk assessment for maize based on crop simulation model and multi-source drought indices. Journal of Cleaner Production, 233, 100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.051
Zhang, Q., & Hu, Z. (2018). Assessment of drought during corn growing season in Northeast China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 133(3–4), 1315–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2469-6
Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., & Wang, C. (2016). Risk assessment of drought disaster in typical area of corn cultivation in China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 128(3–4), 533–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1723-4.
Zhang, X., Wei, C. H., Obringer, R., Li, D. R., Chen, N. C., & Niyogi, D. (2017). Gauging the severity of the 2012 Midwestern U.S. drought for agriculture. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080767
Zinat, M. R. M., Salam, R., Badhan, M. A., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2020). Appraising drought hazard during Boro rice growing period in western Bangladesh. International Journal of Biometeorology, 64, 1687–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01949-2
Zipper, S. C., Qiu, J., & Kucharik, C. J. (2016). Drought effects on us maize and soybean production: Spatiotemporal patterns and historical changes. Environmental Research Letters, 11, 094021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/9/094021
Acknowledgements
This study is jointly supported by the Special Scientific Research Fund of Meteorological Public Welfare Profession of China (GYHY201506001-06), and the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2019YFD1002202).
Funding
This study is jointly supported by the Special Scientific Research Fund of Meteorological Public Welfare Profession of China (GYHY201506001-06), and the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2019YFD1002202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH Hu and ARM Towfiqul Islam designed the study. ZR Wu, YX Zhang, and CC Pan analyzed data. ZH Hu and ZR Wu wrote original draft. ZH Hu, ARM Towfiqul Islam, and Q Li revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Wu, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Risk assessment of drought disaster in summer maize cultivated areas of the Huang-Huai-Hai plain, eastern China. Environ Monit Assess 193, 441 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09224-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09224-6