Abstract
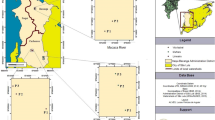
Thirty-four water samples were collected all along the course of River Yautepec, Morelos State, Central Mexico, in three different zones based on the physical and anthropogenic setting. In situ measurements of physical characteristics (temperature, pH, conductivity, and turbidity) were also performed at each sampling station. Likewise, total/dissolved metal concentrations (Fe, Mn, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Cd, As, and Pb) were determined using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Located in a peri-urban and volcanic zone of Central Mexico, the river system presented impacts of both natural and anthropogenic activities. Results revealed differences in pH values (6.7–8.23) in all the three zones probably due to the influences of volcanic ash and local geological formations, whereas conductivity levels (635–1098 μs/cm) were high indicating the effect of agricultural and industrial activities. The relative order of the concentrations of metals in both the total and dissolved fractions was observed to be in the following order: zone I, Fe > Zn > Mn > Cu > Pb > Ni > Cr > As > Cd > Hg; zone II, Fe > Zn > Pb > Ni > Mn > Cu > Cr > Cd > As > Hg; zone III, Fe > Pb > Zn > Mn > Ni > Cu > As > Cd > Cr > Hg. Calculated heavy metal evaluation index (HEI) values indicated less contamination. However, concentrations of Fe and Pb were observed to be higher than the permissible limits set forth by the Mexican government for human consumption. Henceforth, the prerequisite for maintaining and improving the health of a river system depends on continuous long-term monitoring of the dynamic ecosystem for sustainable management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Satar, A. M. (2005). Water quality assessment of River Nile from Idfo to Cairo. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 31(2), 200–223.
Ackay, H., Oguz, A., & Karapire, C. (2003). Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments. Water Research, 37, 813–822.
Addabbo, M. D., Sulpizio, R., Guidi, M., Capitani, G., Mantecca, P., & Zanchetta, G. (2015). Ash leachates from some recent eruptions of Mount Etna (Italy) and Popocatepetl (Mexico) volcanoes and their impact on amphibian living freshwater organisms. Biogeoscienes, 12, 7087–7106.
Agustín-Flores, J., Siebe, C., & Marie, N. G. (2011). Geology and geochemistry of Pelagatos, Cerro del Agua, and Dos Cerros monogenetic volcanoes in the sierra Chichinautzin Volcanic Field, south of Mexico City. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 201, 143–162.
Ahmed, M. K., Baki, M. A., Islam, M. S., Kundu, G. K., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., Sarkar, S. K., & Hossain, M. M. (2015). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in tropical fish and shell fish collected from the river Buriganga, Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(20), 15880–15890.
Ajah, K. C., Ademiluyi, J., & Nnaji, C. C. (2015). Spatiality, seasonality and ecological risks of heavy metals in the vicinity of a degenerate municipal central dumpsite in Enugu, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 13, 15.
Alfayate, B. J. M., González, D. N., Orozco, B. C., Pérez, S. A., & Rodríguez, V. F. J. (2008). Problemas resueltos de contaminación ambiental. Cuestiones y problemas resueltos. Madrid: International Thomson.
Barkatt, A., Pulvirenti, A. L., Adel-Hadadi, M. A., Viragh, C., Senftle, F. E., Thorpe, A. N., & Grant, J. R. (2009). Composition and particle size of superparamagnetic corrosion products in tap water. Water Research, 43, 3319–3325.
Buchet, J. P., & Lison, D. (2000). Clues and uncertainties in the risk assessment of arsenic in drinking water. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 38, 81–85.
Cáceres, D. D., Pino, P., Montesinos, N., Atalah, E., Amigo, H., & Loomis, D. (2005). Exposure to inorganic arsenic in drinking wáter and total urinary arsenic concentration in a Chilean population. Environmental Research, 98(2), 151–159.
Callender, E. (2005). Heavy metals in the environment - historical trends. In B. S. Lollar (Ed.), Treatise on geochemistry - volume 9 (pp. 67–105). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Chen, W., Chang, A. C., & Wu, L. (2007). Assessing long-term environmental risks of trace elements in phosphate fertilizers. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67, 48–58.
Cheng, H., Zhou, T., Li, Q., Lu, L., & Lin, C. (2014). Anthropogenic chromium emissions in China from 1990 to 2009. PLoS One, 9(2), e87753.
CONAGUA (Comisión Nacional del Agua). (2012). Atlas del agua en Mexico. Mexico: SEMARNAT.
CONAGUA (Comisión Nacional del Agua). (2015). Actualización de la disponibilidad media anual del agua en el acuífero Cuautla-Yautepec (1702), Estado de Morelos. CONAGUA Publishing Web. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/103146/DR_1702.pdf.
CONAGUA (Comisión Nacional del Agua). (2017). Estadística del Agua en México 2017. Mexico: SEMARNAT.
Edet, A. E., & Offiong, O. E. (2002). Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination for monitoring. A case study from Akpabuyo-Odukpani area, Lower cross River Basin (Southeastern Nigeria). GeoJournal, 57, 295–304.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). (2009). Method 3010, acid digestion of aqueous samples and extracts for total metals for analysis by FLAA or ICP spectroscopy. Washington: Environmental Protection Agency.
Faroon, O., Ashizawa, A., Wright, S., et al. (2012). Production, import/export, use, and disposal. In Toxicological profile for cadmium. Atlanta (GA): Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US); 2012 Sep. 5.
Fickel, M., & Delgado, G. H. (2017). On the use of different spectral windows in DOAS evaluations: effects on the estimation of SO2 emission rate and mixing ratios during strong emission of Popocatépetl volcano. Chemical Geology, 462, 67–73.
Garneau, C., Sauvage, S., Sánchez-Pérez, J. M., Lofts, S., Brito, D., Neves, R., & Probst, A. (2017). Modelling trace metal transfer in large rivers under dynamic hydrology: a coupled hydrodynamic and chemical equilibrium model. Environmental Modelling & Software, 89, 77–96.
Giménez, M. C., Blanes, P. S., Buchhamer, E. E., Osicka, R. M., Morisio, Y., & Farías, S. S. (2013). Assessment of heavy metal concentrations in arsenic contaminated groundwater of the Chaco Plain, Argentina. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 1–12.
Godt, J., Scheidig, F., Grosse-Siestrup, C., Esche, V., Brandenburg, P., Reich, A., & Groneberg, D. A. (2006). The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (London, England), 1, 22.
Goher, M. E., Hassan, A. M., Abdel Moniem, I. A., Fahmy, A. H., & El-Sayed, S. M. (2014). Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 40, 225–233.
Gupta, A., Rai, D. K., Pandey, R. S., & Sharma, B. (2009). Analysis of some heavy metals in the riverine water, sediment and fish from river Ganges at Allahabad. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 157, 449–458.
Huang, X., Sillanpää, M., Duo, B., & Gjessing, E. T. (2008). Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: metal contents of four selected rivers. Environmental Pollution, 156, 270–277.
INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografia). (2017). Anuario Estadístico y Geográfico de Morelos 2017. México: INEGI.
Jia, H., Wang, S., Wei, M., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Scenario analysis of water pollution control in the typical peri-urban river using a coupled hydrodynamic water quality model. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 5(2), 255–265.
Jiao, W., Chen, W., Chang, A. C., & Page, A. L. (2012). Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: a review. Environmental Pollution, 168, 44–53.
Jiménez, C. B. E. (2001). La contaminación ambiental en México: causas, efectos y tecnología apropiada. México: Limusa.
Jung, K. Y., Lee, K.-L., Im, T. H., Lee, I. J., Kim, S., Han, K.-Y., et al. (2016). Evaluation of water quality for the Nakdong River watershed using multivariate analysis. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 5, 67–82.
Kalpakjian, S., & Schmid, S. R. (2002). Manufactura, ingeniería y tecnología. México: Pearson Educación de México.
Karbassi, A. R., Torabi, F., Ghazban, F., & Ardestani, M. (2011). Association of trace metals with various sedimentary phases in dam reservoirs. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 8(4), 841–852.
Kibria, G., Lau, T. C., & Wu, R. (2012). Innovative ‘artificial mussels’ technology for assessing spatial and temporal distribution of metals in Goulburn–Murray catchments waterways, Victoria, Australia: effects of climate variability (dry vs. wet years). Environmental International, 50, 38–46.
Mancilla-Villa, O. R., Ortega-Escobar, H. M., Ramírez-Ayala, C., Uscanga-Montera, E., Ramos-Bello, R., & Reyes-Ortigoza, A. L. (2012). Metales pesados totales y arsénico en el agua para riego de Puebla y Veracruz, México. Revista Internacional de Contaminacion Ambiental, 28(1), 39–48.
Márquez, A., Verma, S. P., Anguita, F., Oyarzun, R., & Brandle, J. L. (1999). Tectonics and volcanism of Sierra Chichinautzin: extensión at the front of the Central Trans-Mexican Volcanic belt. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 93, 125–150.
Mohammed, A. S., Kapri, A., & Goel, R. (2011). Heavy metal pollution: sources, impact and remedies. In M. S. Khan, A. Zaidi, R. Goel, & J. Musarrat (Eds.), Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils (pp. 1–28). New York: Springer.
Moiseenko, T. I., Gashkina, N. A., Sharova, Y. N., & Kudryavtseva, L. P. (2008). Ecotoxicological assessment of water quality and ecosystem health: a case study of the Volga River. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 71(3), 837–850.
Molina, G. R. S., Böhnel, H. N., & Hernández, T. (2003). Paleomagnetism of the Cretaceous Morelos and Mezcala Formations, southern Mexico. Tectonophysics, 361, 301–317.
Moore, G., & Carmichael, I. S. E. (1998). The hydrous phase equilibria (to 3 kbar) of an andesite and basaltic andesite from western Mexico: constraints on water content and conditions of phenocryst growth. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 130(3–4), 304–319.
Morrison, J. M., Goldhaber, M. B., Mislls, C. T., Breit, G. N., Hooper, R. L., et al. (2015). Weathering and transport of chromium and nickel from serpentinites in the Coast Range ophiolite to the Sacramento valley, California, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 61, 72–86.
Mousavi, S. R., Balali-Mood, M., Riahi-Zanjani, B., Yousefzadeh, H., & Sadeghi, M. (2013). Concentrations of mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, arsenic and aluminium in irrigation water wells and wastewaters used for agriculture in Mashhad, North eastern Iran. The International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 4(2), 80–86.
Nasrabadi, T., Ruegner, H., Sirdari, Z. Z., Schwientek, M., & Grathwohl, P. (2016). Using total suspended solids (TSS) and turbidity as proxies for evaluation of metal transport in river water. Applied Geochemistry, 68, 1–9.
Nordstrom, D. K. (2011). Hydrogeochemical processes governing the origin, transport and fate of major and trace elements from mine wastes and mineralized rock to surface waters. Applied Geochemistry, 26(11), 1777–1791.
Nriagu, J. O. (1986). Chemistry of the river Niger II. Trace metals. Science of the Total Environment, 58(1), 89–92.
Oswald, S. U. (2016). Sustainability transition in a vulnerable river basin in Mexico. In B. H. Günter, S. U. Oswald, J. Grin, & J. Scheffran (Eds.), Handbook on sustainability transition and sustainable peace (pp. 675–704). Switzerland: Springer.
Oyem, H. H., Oyem, I. M., & Ezeweali, D. (2014). Temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids and chemical oxygen demand of groundwater in Boji-BojiAgbor/Owa area and immediate suburbs. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8, 444–450.
Pinto, V., & Maheshwari, B. (2014). A framework for assessing river health in peri urban landscapes. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology, 14, 121–131.
Roldán, P. G., & Ramírez, R. J. J. (2008). Fundamentos limnología neotropical. Antioquia: Universidad de Antioquia.
Ruiz-Picos, R. A., Kohlmann, B., Sedeño-Díaz, J. E., & López-López, E. (2017). Assessing ecological impairments in Neotropical rivers of Mexico: calibration and validation of biomonitoring working party. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 14(9), 1835–1852.
Saha, R., Nandi, R., & Saha, B. (2011). Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 64(10), 1782–1806.
Seyler, P. T., & Boaventura, G. R. (2003). Distribution and partition of trace metals in the Amazon basin. Hydrological Processes, 17(7), 1345–1361.
Shamrukh, M., & Abdel-Wahab, A. (2011). Water pollution and riverbank filtration for water supply along River Nile, Egypt. In C. Ray & M. Shamrukh (Eds.), Riverbank filtration for water security in desert countries (pp. 5–28). Quena: Springer.
Shiller, A. M. (1997). Dissolved trace elements in the Mississippi river: seasonal, interannual, and decadal variability. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(20), 4321–4330.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling and Software, 22, 464–475.
SSA (Secretaría de Salud). (1994). Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM 127-SSA1-1994, Salud ambiental, agua para uso y consumo humano-límites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización. México: Diario Oficial de la Federación.
Stewart, C., Johnston, D. M., Leonard, G. S., Horwell, C. J., Thordarson, T., & Cronin, S. J. (2006). Contamination of water supplies by volcanic ashfall: a literature review and simple impact modelling. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 158, 296–306.
Sundaray, S. K., Nayak, B. B., Kanungo, T. K., & Bhatta, D. (2012). Dynamics and quantification of dissolved heavy metals in the Mahanadi river estuarine system, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1157–1179.
Taquet, N., Meza, H. I., Stremme, W., Bezanilla, A., Grutter, M., Campion, R., Palm, M., & Boulesteix, T. (2017). Continuous measurements of SiF4 and SO2 by thermal emission spectroscopy: insight from a 6-month survey at the Popocatépetl volcano. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 341, 255–268.
Telesca, L., Lovallo, M., & Flores-Marquez, E. L. (2017). Characterization volcanic states at Popocatepetl, Mexico by informational analysis of continuous geomagnetic signal. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 487, 178–184.
Teunissen, K., Abrahamse, A., Leijssen, H., Rietveld, L., & van Dijk, H. (2008). Removal of both dissolved and particulate iron from groundwater. Drinking Water Engineering and Science Discussions, 1, 87–115.
Thompson, T., Fawell, J., Kunikane, S., Jackson, D., Appleyard, S., Callan, P., Bartraman, J., & Kingston, P. (2007). Chemical safety of drinking-water: assessing priorities for risk management. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Tkachenko, A. N., Tkachenko, O. V., Lychagin, M. Y., & Kasimov, N. S. (2017). Heavy metal flows in aquatic systems of the Don and Kuban river delta. Doklady Earth Sciences, 474(1), 587–590.
UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). (2008). Interim review of scientific information on cadmium.
US Environmental Protection Agency, (1994). In: Creed, J. T., Martin, T. D., Lobring, L. B., & O'Dell, J.W (Eds) Method 200.9, Revision 2.2: Determination of Trace Elements by Stabilized Temperature Graphic Furnace Atomic Absorption, 43p.
Varol, M., & Sen, B. (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the Upper Tigris River, Turkey. Catena, 92, 1–10.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Sen, B. (2012). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Tigris River (Turkey) using multivariate statistical techniques—a case study. River Research and Applications, 28, 1428–1438.
Velázquez, M. A., Pimentel, J. L., & Ortega, M. (2011). Estudio de la distribución de boro en fuentes de agua de la cuenca del río Duero, México, utilizando análisis estadístico multivariado. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 27(1), 19–30.
Verrengia, G. N. R., & Kesten, E. M. (1994). Levels of heavy metals in waters from the la Plata river, Argentina: an approach to assess bioavailability. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 52(2), 254–260.
Wang, Y., Chen, P., Cui, R., Si, W., Zhang, Y., & Ji, W. (2009). Heavy metal concentration in water, sediment and tissues of two fish species (Triplohysa pappenheimi, Gobio hwanghensis) from the Lanzhou section of the Yellow. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165(1), 97–102.
Wang, X., Cai, Q., Ye, L., & Qu, X. (2012). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Xiangxi River basin, China. Quaternary International, 282, 137–144.
Wang, Q., Zhang, Q., Wu, Y., & Wang, X. C. (2017). Physicochemical conditions and properties of particles in urban runoff and rivers: implications for runoff pollution. Chemosphere, 173, 318–325.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (fourth ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Zarazua, G., Ávila-Pérez, P., Tejeda, S., Barcelo-Quintal, I., & Mártínez, T. (2006). Analysis of total and dissolved heavy metals in surface water of a Mexican polluted river by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 61, 1180–1184.
Zhang, J., Hua, P., & Krebs, P. (2016). The influences of dissolved organic matter and surfactant on the description of Cu and Zn from road deposited sediment. Chemosphere, 50, 63–70.
Acknowledgements
FRG wishes to thank the financial support through the projects SIP-IPN No. 20170470 and 20180759 by the Secretaria de Investigación y Posgrado of Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN), Ciudad de Mexico. FRG, MPJ, and SBS thank the Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI), CONACyT. FRG and MPJ thank COFAA & EDI of IPN, México. This article is the 98th contribution (partial) from the members (SBS & MPJ) of the Earth System Science Group (ESSG), Chennai, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vargas-Solano, S.V., Rodríguez-González, F., Arenas-Ocampo, M.L. et al. Heavy metals in the volcanic and peri-urban terrain watershed of the River Yautepec, Mexico. Environ Monit Assess 191, 187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7300-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7300-z