Abstract
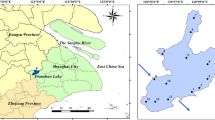
The estimation of chlorophyll-a concentrations (Chla) in lakes using remote sensing is convenient, but its use remains challenging in large eutrophic water bodies due to the great spatial and temporal variations of its optical properties. Combining the sampling location and date information with Chla data, this study divided the lake water into three types, I, II and III, and then built an optimal Chla estimation model for each type based on 11 datasets collected from 2004 to 2012 in Taihu Lake, China. The resultant model expression is Chla = exp (ax2 + bx + c), where x is R701/R677, (1/R686–1/R695) × R710 and (R690/R550–R675/R700) / (R690/R550 + R675/R700). For the Chla ranging from 2 to 192 mg/m3, the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of the new model decreased up to 5.1 mg/m3 compared to that of previous band combination models, such as band ratio, three-band and four-band models when directly validated. The RMSE of the re-parametrization model (the lowest RMSE < 12 mg/m3) is also lower than for those models (the lowest RMSE > 16 mg/m3), indicating that the Chla estimation model that considers the spatial and temporal variations has a better performance and validation accuracy and therefore is more effective for remote sensing monitoring of water quality.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., Stone, C.J. (1984). Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth, Belmont, CA.
Bricaud, A., Babin, M., Morel, A., & Claustre, H. (1995). Variability in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: Analysis and parameterization. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 100(C7), 13321–13332.
Cannizzaro, J. P., & Carder, K. L. (2006). Estimating cldorophyll a concentrations from remote·sensing reflectance in optically shallow waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 101(1), 13–24.
Cheng, C. M., Wei, Y. C., Lv, G. N., & Yuan, Z. J. (2013a). Remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid water using a spectral index: A case study in Taihu Lake, China. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 7(1), 073465–073465.
Cheng, C. M., Wei, Y. C., & Wang, G. X. (2013b). Using spectral smoothing method to improve the validation precision of the Chlorophyll-a estimation model in turbidity water. Remote Sensing of Technology and Application, 28(6), 941–948.
Dall'Olmo, G., Gitelson, A. A., & Rundquist, D. C. (2003). Towards a unified approach for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in both terrestrial vegetation and turbid productive waters. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(18), 1938.
Dierberg, F. E., & Carriker, N. E. (1994). Field testing two instruments for remotely sensing water quality in the Tennessee Valley. Environmental Science & Technology, 28(1), 16–25.
Fan, H., Huang, H. J., & Tang, J. W. (2007). Spectral signature of waters in Huanghe estuary and estimation of suspended sediment concentration from remote sensing data. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 32(7), 601–604.
Fraser, R. N. (1998). Hyperspectral remote sensing of turbidity and chlorophyll a among Nebraska Sand Hills lakes. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(8), 1579–1589.
George, D. G. (1997). The airborne remote sensing of phytoplankton chlorophyll in the lakes and tarns of the English Lake District. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 18(9), 1961–1975.
Gilerson, A. A., Gitelson, A. A., Zhou, J., Gurlin, D., Moses, W., Ioannou, I., & Ahmed, S. A. (2010). Algorithms for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in coastal and inland waters using red and near infrared bands. Optics Express, 18, 24109–24125.
Gitelson, A. A. (1992). The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3367–3373.
Gitelson, A. A., Dall'Olmo, G., Moses, W., Rundquist, D. C., Barrow, T., Fisher, T. R., Gurlin, D., & Holz, J. (2008). A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(9), 3582–3593.
Gitelson, A. A., Schalles, J. F., & Hladik, C. M. (2007). Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in turbid, productive estuaries: Chesapeake Bay case study. Remote Sensing of Environment, 109(4), 464–472.
Glardino, C., Candianl, G., & Zilioli, E. (2005). Detecting chlorophyll-a in Lake Garda using TOA MERIS radiances. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 71(9), 1045–1051.
Gong, S. Q., Huang, J. Z., Li, Y. M., & Wei, Y. C. (2005). Integrated fuzzy evaluation of water eutrophication based on GIS in the Taihu Lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 26(5), 34–37.
Gower, J., King, S., Borstad, G., & Brown, L. (2005). Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the MERIS imaging spectrometer. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(9), 2005–2012.
Han, L. H., & Rundquist, D. C. (1997). Comparison of NIR/RED ratio and first derivative of reflectance in estimating algal-chlorophyll concentration: A case study in a turbid reservoir. Remote Sensing of Environment, 62(3), 253–261.
Johson, R. W., & Harris, R. C. (1980). Remote sensing for water quality and biological measurements in coastal waters. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 46, 77–85.
Kallio, K., Kutser, T., & Hannonena, T. (2001). Retrieval of water quality from airborne imaging spectrometry of various Lake types in different seasons. The Science of the Total Environment, 268(1–3), 59–77.
Le, C. F., Li, Y. M., Sun, D. Y., & Wang, H. J. (2007). Research on chlorophyll concentration retrieval models of Taihu Lake based on seasonal difference. Journal of Remote Sening-Beijing, 11(4), 473.
Le, C. F., Li, Y. M., Zha, Y., Sun, D. Y., Huang, C., & Lu, H. (2009). A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: The case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(6), 1175–1182.
Li, F., Xu, J. P., Ma, R. H., Duan, H. T., & Zhang, B. (2011). Chlorophyll-a retrieval in inland waters based on a regional three-band model. Remote Sensing-Beijing, 15(6), 1156–1170.
Li, Y. M., Huang, J. Z., Wei, Y. C., & lu, W. N. (2006). Inversing chlorophyll concentration of Taihu Lake by analytic model. Journal of Remote Sening-Beijing, 10(2), 169.
Li, Y. P., Yan, Y., & Han, G. Y. (2005). Temporal-spatial correlation analysis of water quality for Taihu Lake. JournaI of Hohai University(NaturaI Sciences), 33(5), 505–508.
Liu, R. M., Wang, X. J., Wang, C. H., Jiang, Y. C., & Zhou, X. W. (2001). Application of geo-statistics in studying spatial distribution of chlorophyll a in lakes. Agro-environment Protection, 20(5), 308–310.
Liu, X. F., Duan, H. T., & Ma, R. H. (2010). The spatial heterogeneity of water quality variables in Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Lake Sciences, 22, 367–374.
Lorenzen, C. J. (1966). A method for the continuous measurement of in-vivo chlorophyll concentration. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts. Elsevier, 13(2), 223–227.
Ma, R. H., & Dai, J. F. (2005). Chlorophyll-a concentration estimation with field spectra of water body near Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake. Journal of Remote Sening-Beijing, 9(1), 78–86.
Ma, R. H., Tang, J. W., & Dai, J. F. (2006). Bio-optical model with optimal parameter suitable for Taihu Lake in water colour remote sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(19), 4305–4328.
Matthews, M. W. (2011). A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near-coastal transitional waters. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(21), 6855–6899.
Matthews, M. W., Bernard, S., & Robertson, L. (2012). An algorithm for detecting trophic status (chlorophyll-a), cyanobacterial-dominance,surface scums and floating vegetation in inland and coastal waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 637–652.
Mishra, S., & Mishra, D. R. (2012). Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 117, 394–406.
Moses, W. J., Gitelson, A. A., Berdnikov, S., & V, P. (2009). Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case II waters using MODIS and MERIS data-successes and challenges. Environmental Research Letters, 4(4), 045005.
Mueller, J.L., Fargion, G.S., McClain, C.R., & et al. (2003). NASA/TM–2003–ocean optics protocols for satellite ocean color sensor validation. In Revision 4, Volume III: Radiometric measurements and data analysis protocols.
Myers, R. H. (1990). Classical and modern regression with applications (2nd ed.). Belmont: Duxbury Press.
Odermatt, D., Gitelson, A., Brando, V. E., & M, S. (2012). Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 118, 116–126.
Pepe, M., Giardino, C., Borsani, G., Cardoso, A., Chiaudani, G., Premazzi, G., Rodari, E., & Zilioli, E. (2001). Relationship between apparent optical properties and photosynthetic pigments in the sub-alpine Lake Iseo. Science of the Total Environment, 268(1–3), 31–45.
Qin, B. Q., Hu, W. P., & Chen, W. M. (2004). Water environment evolution process and mechanism of Taihu Lake. Beijing: Science Press.
Reynolds, C. S. (1984). The ecology of fresh water phytoplankton. London: Cambridge Univ Press.
Ruiz-Verdú, A., Simis, S. G., de Hoyos, C., Gons, H. J., & Peña-Martínez, R. (2008). An evaluation of algorithms for the remote sensing of cyanobacterial biomass. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(11), 3996–4008.
Schalles, J. F., Gitelson, A. A., Yacobi, Y. Z., & Kroenke, A. E. (1998). Estimation of chlorophyll a from time series measurements of high spectral resolution reflectance in an eutrophic lake. Journal of Phycology, 34(2), 383–390.
Simis, S. G. H., Peters, S. W. M., & Gons, H. J. (2005). Remote sensing of the cyanobacterial pigment phycocyanin in turbid inland water. Limnology and Oceanography, 50(1), 237–245.
Strömbeck, N., & Pierson, D. C. (2001). The effects of variability in the inherent optical properties on estimations of chlorophyll a by remote sensing in Swedish freshwaters. Science of the Total Environment, 268(1–3), 123–137.
Suzuki, K., Kishino, M., Sasaoka, K., Saitoh, S.-i., & Saino, T. (1998). Chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients and pigments of phytoplankton off Sanriku, Northwestern North Pacific. Journal of Oceanography, 54(5), 517–526.
Vos, W. L., Donze, M., & Bueteveld, H. (1986). On the reflectance spectrum of algae in water: The nature of the peak at 700nm and its shift with varying concentration. Delft: Communications on sanitary engineering and water management.
Wang, Y. H., Ma, R. H., & Deng, Z. D. (2007). Regionalized RS estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in Taihu Lake. JournaI of Hohai University(NaturaI Sciences), 35, 86–91.
Wei, Y. C., Huang, J. Z., Li, Y. M., & Guang, J. (2007). The hyperspectral data monitoring model of chlorophyll-a of summer in Taihu Lake, China. Journal of Remote Sening-Beijing, 11(5), 756–762.
Wei, Y. C., Wang, G. X., & Cheng, C. M. (2010a). Noise removal in spectrum above water surface using kernel regression smoothing. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 33(3), 97–102.
Wei, Y. C., Wang, G. X., & Sun, H. Y. (2010b). A logical problem in the building linear regression model on estimating chlorophyll-a concentration in lake based on the measured spectrum data. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 40(18), 100–110.
Yacobi, Y. Z., Gitelson, A., & Mayo, M. (1995). Remote sensing of chlorophyll in Lake Kinneret using highspectral-resolution radiometer and Landsat TM: Spectral features of reflectance and algorithm development. Journal of Plankton Research, 17(11), 2155–2173.
Yang, T., Zhang, H., Wang, Q., Ma, R. H., & Duan, H. T. (2011). Zoning of Taihu Lake by concentration of suspended substances and transparency based on measured hyper-spectral data. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 27(4), 21–26.
Zhang, J. Y., Lu, M., Ye, l., Song, T., & Shi, J. Z. (2010). Temporal and spatial distributions of blue-green algae density and chlorophyll in summer Meiliang Lake. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 19, 97–100.
Zhang, Y. L. (2005). Biological-optical properties of Lake Taihu and its ecological significance. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Zhang, Y. L., & Qin, B. Q. (2006). Quantitative retrieval of phytoplankton pigment based on water inherent optical properties in Lake Taihu. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 27(12), 2439–2444.
Zimba, P. V., & Gitelson, A. (2006). Remote estimation of chlorophyll concentration in hyper-eutrophic aquatic systems: Model tuning and accuracy optimization. Aquaculture, 256(1–4), 272–286.
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41471283). We would like to express our gratitude to Wang Lei, Zhang Xiaowei, Zhou Yu and Sun Xiaopeng for field work and to Zhang Jing for laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The appendix section lists the typical Chla estimation models before and after the data partition. Figures 12, 13, 14, and 15 present the four models for Type I, II and III based on partitioned data and unpartitioned data; the subfigures in the Z order of each type present scatter plots between the model variable and lnChla, estimated and measured Chla, residuals and predicted Chla, and the QQ plot of residuals, respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Wei, Y., Lv, G. et al. Remote sensing estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in Taihu Lake considering spatial and temporal variations. Environ Monit Assess 191, 84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7106-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7106-4