Abstract
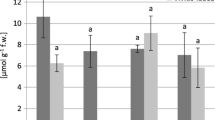
In a specific area of the Krušné Hory Mts. (Ore Mountains), Czech Republic, branches and leaves of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) were collected during the growing seasons in 2010–2016 on the low-pH soil (2.77–3.62) with a high total content of manganese (490–6277 mg kg−1 dwt.). Mn content in leaves occurred in a wide range (274–11,159 mg kg−1) and was markedly increased during the growing season with the exception of year 2015, when the leaves dried out early due to the precipitation deficit. New leaves exhibited the Mn content corresponding to the beginning of the growing season. Mn content in branches was comparable both in the years of collection (including 2015) and in the respective growing seasons (2062–3885 mg kg−1). The content of manganese in bilberry leaves was dependent on the cumulated amount of precipitation (p < 10−6; r2 = 0.4962) and on the cumulated amount of water in the soil captured in lysimeters (p = 0.00003; r2 = 0.4520).
Hyperaccumulation of manganese in bilberry was confirmed as well as its continuous increase during the vegetation seasons. The manganese content in leaves of bilberry showed positive correlation with soil moisture. For the assessment of bilberry condition (nutrition), the collection of samples should be made towards the end of the growing season, closely before the onset of senescence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environment: biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risk of metal. (Second ed., Trace elements in the terrestrial environment, 2nd edition., 867 pp.). New York, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Verlag, 867 pp.
Baker, A. J. M. (1981). Accumulators and excluders - strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 3(1–4), 643–654.
Baker, A. J. M., & Brooks, R. R. (1989). Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements - a review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery, 1, 81–126.
Bergmann, W. (1988). Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen. (Entstehung, visuelle und analytische Diagnose). Jena: VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, p. 223 pp.
Białońska, D., Zobel, A. M., Kuraś, M., Tykarska, T., & Sawicka-Kapusta, K. (2007). Phenolic compounds and cell structure in bilberry leaves affected by emissions from a Zn–Pb smelter. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 181, 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9284-x.
Coudon, C., & Gégout, J.-C. (2007). Quantitative prediction of the distribution and abundance of Vaccinium myrtillus with climatic and edaphic factors. Journal of Vegetation Science, 18(4), 517–524.
Mora, M. L., Rosas, A., Ribera, A., & Rengel, Z. (2009). Differential tolerance to Mn toxicity in perennial ryegrass genotypes: involvement of antioxidative enzymes and root exudation of carboxylates. Plant and Soil, 320(1–2), 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9872-1.
Fernando, D. R., & Lynch, J. P. (2015). Manganese phytotoxicity: new light on an old problem. Annals of Botany, 116(3), 313–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcv111.
Fernando, D. R., Baker, A. J. M., & Woodrow, I. E. (2009a). Physiological responses in Macadamia integrifolia on exposure to manganese treatment. Australian Journal of Botany, 57(5), 406–413. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT09077.
Fernando, D. R., Guymer, G., Reeves, R. D., Woodrow, I. E., Baker, A. J. M., & Batianoff, G. N. (2009b). Foliar Mn accumulation in eastern Australian herbarium specimens: prospecting for ‘new’ Mn hyperaccumulators and potential applications in taxonomy. Annals of Botany, 103(6), 931–939. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp013.
Fiala, P., Reininger, D., Samek, T., Němec, P., & Sušil, A. (2013). A survey of nutrition forest in the Czech Republic, 1996-2011. Brno: Central Institute for Supervising and Testing in Agriculture 150 pp.
Führs, H., Specht, A., Erban, A., Kopka, J., & Horst, W. J. (2012). Functional associations between the metabolome and manganese tolerance in Vigna unguiculata. Journal of Experimental Botany, 63(1), 329–340. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err276.
Heenan, D. P., & Campbell, C. L. (1980). Growth, yield components and seed composition of two soybean cultivars as affected by manganese supply. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 31(3), 471–476. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9800471.
Horiguchi, T. (1987). Mechanism of manganese toxicity and tolerance of plants. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 33(4), 595–606.
Hrdlička, P., & Kula, E. (2004). Changes in the chemical content of birch (Betula pendula Roth) leaves in the air polluted Krusne hory mountains. Trees - Structure and Function, 18(2), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-003-0301-z.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2004). Soil–plant transfer of trace elements-an environmental issue. Geoderma, 122, 143–149.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soil and plants (Fourth ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press 520 pp.
Kandziora-Ciupa, M., Ciepal, R., Nadgórska-Socha, A., & Barczyk, G. (2013). A comparative study of heavy metal accumulation and antioxidant responses in Vaccinium myrtillus L. leaves in polluted and non-polluted areas. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(7), 4920–4932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1461-4.
Kitao, M., Lei, T. T., Nakamura, T., & Koike, T. (2001). Manganese toxicity as indicated by visible foliar symptoms of Japanese white birch (Betula platyphylla var. japonica). Environmental Pollution, 111(1), 89–94.
Korcak, R. F. (1989). Variation in nutrient requirements of blueberries and other calcifuges. Hort Science, 24, 573–578.
Kukla, J., & Kuklová, M. (2008). Growth of Vaccinium myrtillus L. (Ericaceae) in spruce forests damaged by air pollution. Polish Journal of Ecology, 56(1), 149–155.
Kula, E., Hrdlička, P., Hedbávný, J., & Švec, P. (2012). Various content of manganese in selected forest tree species and plants in the undergrowth. Beskydy, 5(1), 19–26.
Kula, E., Martinek, P., Chromcova, L., & Hedbavny, J. (2014). Development of Lymantria dispar affected by manganese in food. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(20), 11987–11997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3075-5.
Laboratory-Morava. (2010). Standardized internal laboratory methods for chemical analyses soil and plant (p. 30). Studénka: Laboratory Morava, Inc., accredited laboratory.
Lazorík, M., & Kula, E. (2015). Impact of weather and habitat on the occurrence of centipedes, millipedes and terrestrial isopods in mountain spruce forests. Folia Oecologica, 42(2), 103–112.
Liu, P., Tang, X., Gong, C., & Xu, G. (2010). Manganese tolerance and accumulation in six Mn hyperaccumulators or accumulators. Plant and Soil, 335(1–2), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0427-x.
Marschner, H. (2006). Mineral nutrition of higher plants (Second ed.). Amsterdam: Academic Press 890 pp.
Memon, A. R., & Yatazawa, M. (1982). Chemical nature of manganese in the leaves of manganese accumulator plants. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 28(3), 401–412.
Memon, A. R., & Yatazawa, M. (1984). Nature of manganese complexes in manganese accumulator plant – Acanthopanax sciadophylloides. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 7(6), 961–974.
Memon, A. R., Chino, M., Hidaka, H., Hara, K., & Yatazawa, M. (1981). Manganese toxicity in field grown tea plants and the microdistribution of manganese in the leaf tissues as revealed by electron probe X-ray micrography. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 27(3), 317–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1981.10431286.
Mengel, K., & Kirkby, E. A. (2001). Principles of plant nutrition (5rd ed.). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers 593 pp.
Migocka, M., & Klobus, G. (2007). The properties of the Mn, Ni and Pb trasport operating at plasma membranes of cucumber roots. Physiologia Plantarum, 129(3), 578–587. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00842.x.
Mikkonen, H., & Huttunen, S. (1981). Dwarf shrubs as bioindicator. Silva Fennica, 15(4), 475–480.
Moroni, J. S., Scott, B. J., & Wratten, N. (2003). Differential tolerance of high manganese among rapeseed genotypes. Plant and Soil, 253(2), 507–519.
Mróz, L., & Demczuk, M. (2010). Contents of phenolics and chemical elements in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) leaves from copper smelter area (SW Poland). Polish Journal of Ecology, 58(3), 475–486.
Parzych, A. (2014). The heavy metal content of soil and shoots of Vaccinium myrtillus L. in the Słowiński National Park. Forest Research Papers, 75(3), 217–224. https://doi.org/10.2478/frp-2014-0020.
Parzych, A. (2016). Accumulation and distribution of nutrients in shoots of Vaccinium vitis−idaea L. and Vaccinium myrtillus L. Sylwan, 160(1), 40–48.
Peng, K., Luo, C., You, W., Lian, C., Li, X., & Shen, Z. (2008). Manganese uptake and interactions with cadmium in the hyperaccumulator—Phytolacca Americana L. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1–3), 674–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.080.
Pittman, J. K. (2005). Managing the manganese: molecular mechanisms of manganese transport and homestasis. New Phytologist, 167(3), 733–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01453.x.
Pokladníková, H., Rožnovský, J., & Mužíková, B. (2008) Selected agro-climatic characteristics of the Czech Republic on the basis of climatic data in the grid 10 km. In J. Rožnovský, & T. Litschmann (Eds.), Bioclimatological aspects of the evaluation process in the country, Mikulov, Czech Republic, (pp. 1–8).
Reeves, R. D. (2006). Hyperaccumulation of trace elements by plants. In J.-L. Morel, G. Echevarria, & N. Goncharova (Eds.), Phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils (pp. 25–52, Nato Science, Vol. 68). Berlin: Springer.
Reimann, C., Koller, F., Frengstad, B., Kashulina, G., Niskavaara, H., & Englmaier, P. (2001a). Comparison of the element composition in several plant species and their substrate from a 1 500 00-km2 area in Northern Europe. The Science of the Total Environment, 278, 87–112.
Reimann, C., Koller, F., Kashulina, G., Niskavaara, H., & Englmaier, P. (2001b). Influence of extreme pollution on the inorganic chemical composition of some plants. Environmental Poluttion, 115, 239–252.
Salemaa, M., Derome, J., Helmisaari, H.-S., Nieminen, T., & Vanha-Majamaa, I. (2004). Element accumulation in boreal bryophytes, lichens and vascular plants exposed to heavy metal and sulfur deposition in Finland. Science of the Total Environment, 324(1–3), 141–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.10.025.
SEPAS. (2010). Environmental quality criteria for forest landscapes. Stockholm: Swedish Environmental Protection Agency 18 pp.
Sheppard, S. C. (1991). A field and literature survey, with interpretation, of element concentration in blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium). Canadian Journal of Botany, 69, 63–77, doi:alt ISSN 1916-2790.
Sims, T. J. (2000). Soil test phosphorus: Mehlich 3. In G. M. Pierzynski (Ed.), Methods of phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters (Vol. Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin No. # 396, pp. 17–19). Kansas State University: Department of Agronomy, 2004 Throckmorton Plant Sciences Ctr.
Slodičák, M., Balcar, V., Novák, J., & Šrámek, V. (2008). Forestry management in the Krušné hory Mts (Vol. 03). Hradec Kralove: Grant Agency of the Forests of the Czech Republic 480 pp.
Sobíšek, B., Munzar, J., Krška, K., et al. (1993). Meteorological dictionary interpretation & terminology (p. 594). Academia: Prague.
StatSoft Inc. (2012). STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 12.
Taulavuori, K., Laine, K., & Taulavuori, E. (2013). Experimental studies on Vaccinium myrtillus and Vaccinium vitis-idaea in relation to air pollution and global change at northern high latitudes: a review. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 87, 191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.10.002.
Uhlig, C., & Junttila, O. (2001). Airborne heavy metal pollution and its effects on foliar elemental composition of Empetrum hermaphroditum and Vaccinium myrtillus in Sor-Varanger, northern Norway. Environmental Poluttion, 114, 461–469.
Uhlig, C., Salemaa, M., Vanha-Majamaa, I., & Derome, J. (2001). Element distribution in Empetrum nigrum microsites at heavy metal contaminated sites in Harjavalta, western Finland. Environmetal Pollution, 112(3), 435–442.
UN-ECE (2016). Manual on methods and criteria for harmonized sampling, assessment, monitoring and analysis of the effects of air pollution on forest. In Sampling and analysis of needles and leaves (Vol. part XII, pp. 1–19). Eberswalde, Germany: UN ECE.
Xu, X., Shi, J., Chen, Y., Chen, X., Wang, H., & Perera, A. (2006). Distribution and mobility of manganese in the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Plant and Soil, 285(1–2), 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9018-2.
Reeves, R. D., Baker, A. J. M., Lin, Q., & Fernando, D. R. (2004). Manganese uptake and accumulation by the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Environmental Pollution, 131, 393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.03.011.
Xue, S., Zhu, F., Wu, C., Lei, J., Hartley, W., & Pan, W. (2016). Effects of manganese on the microstructures of Chenopodium ambrosioides L., a manganese tolerant plant. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18(7), 710–719. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2015.1131233.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Students Grant Agency, J.E. Purkyně University in Ústí nad Labem, within Project 44201 15 007501: “Accumulation of manganese in the leaves of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) in the growing season and interaction with the manganese load in the soil.” The research was supported by the companies Nadace ČEZ, a.s. Prague; Netex s.r.o. Děčín; and Lafarge cement a.s., Čížkovice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kula, E., Wildová, E. & Hrdlička, P. Accumulation and dynamics of manganese content in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.). Environ Monit Assess 190, 224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6604-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6604-8