Abstract
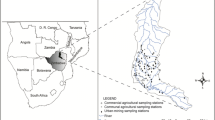
Patterns of epilithic diatom species distribution in relation to environmental variables from 12 sampling sites on the main stream and some of its tributaries in the Nilüfer Stream Basin were determined using multivariate statistical techniques. The stream basin has been heavily influenced by anthropogenic effects. The upper part of the basin that is distant from pollution sources mostly has a spring water quality, while the lower part where the stream flows through the urban area and receives domestic and industrial wastewater has a quite low quality. Ordination techniques using both diatom taxa and 21 environmental variables revealed non- to slightly polluted upper basin sites and highly polluted lower basin sites along the stream. The results showed that the stream catchment is polluted gradually from upstream to downstream and that most of the downstream sites have very low water quality especially in summer months. A total of 134 epilithic diatom taxa belonging to 50 genera were recorded for 12 sample sites. Partial CCA results indicated that water temperature (T), discharge (Q), and total phosphorus (TP) were the most important variables affecting the distribution of diatom species. Unpolluted or slightly polluted upper basin sites were dominated by Achnanthidium minutissimum, Cocconeis placentula var. euglypta, Gomphonema olivaceum, and Navicula tripunctata. Highly polluted lower basin sites were characterized by high levels of organic and inorganic matters and low dissolved oxygen (DO) values. Species widespread in the highly polluted lower basin sites such as Nitzschia umbonata, Nitzschia amphibia, Nitzschia capitellata, Nitzschia palea, Nitzschia paleacea, Luticola mutica, and Stephanodiscus niagarae were mostly related to pollution indicator variables such as ammonium nitrogen (NH4 +–N), sodium (Na+), total phosphorus (TP), and total organic matter (TOM).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbaş, A. (2014). Türkiye Üzerindeki Önemli Kurak Yıllar (Important drought years over Turkey). Coğrafi Bilimler Dergisi CBD, 12(2), 101–118.
Albek, M., & Albek, E. (2009). Stream temperature trends in Turkey. Clean, 37(2), 142–149.
Anonymous (2007). Drought action plan. Bursa Special Provincial Administration (in Turkish).
Anonymous (2014). Preparation of watershed protection action plans–Susurluk Basin. TÜBİTAK Marmara Research Center Report (in Turkish). Resource document. Republic of Turkey Ministry of Environment and Urbanisation, Directorate General of Environmental Management. http://www.cygm.gov.tr/CYGM/AnaSayfa/SuToprakYonetimi/HavzaKoruma.aspx?sflang=tr. Accessed 08 March 2017.
Anonymous (2016). Nilüfer Stream subbasin water quality action plan (in Turkish). Resource document. Republic of Turkey. Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs. General Directorate of Water Management. http://www2.ormansu.gov.tr/osb/Libraries/Dok%C3%BCmanlar/Nil%C3%BCfer%C3%87ay%C4%B1AltHavzas%C4%B1SuKalitesiEylemPlan%C4%B1_rev__24_05_16_1.sflb.ashx. Accessed 06 March 2017.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Aydınalp, C., FitzPatrick, E. A., & Cresser, M. S. (2005). Heavy metal pollution in some soil and water resources of Bursa Province, Turkey. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 36, 1691–1716.
Aysel, V. (2005). Check-list of the freshwater algae of Turkey. J Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment, 11, 1–124.
Battarbee, R. W., Jones, V. J., Flower, R. J., Cameron, N. G., Bennion, H., Carvalho, L., & Juggins, S. (2001). Diatoms. In J. P. Smol, H. J. B. Birks, & W. M. Last (Eds.), Tracking environmental change using lake sediments, volume 3 terrestrial, algal, and siliceous indicators (pp. 155–202). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bere, T., & Tundisi, J. G. (2010). Epipsammic diatoms in streams influenced by urban pollution, São Carlos, SP. Brazil. Braz. J. Biol., 70(4), 921–930.
Bere, T., & Tundisi, J. G. (2011). Influence of ionic strength and conductivity on benthic diatom communities in a tropical river (Monjolinho), São Carlos-SP, Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 661, 261–276.
Borcard, D., Legendre, P., & Drapeau, P. (1992). Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology, 73(3), 1045–1055.
BWSA (2002). BWSA (Bursa Water and Sewerage Administration) Wastewater Discharge Legislation. Bursa, Turkey (in Turkish).
BWSA (2017a). Doğancı Dam. Resource document. http://www.buski.gov.tr/tr/icerik/doganci_baraji_565. Accessed 06 March 2017.
BWSA (2017b). Bursa East Wastewater Treatment Plant. Resource document. http://www.buski.gov.tr/tr/icerik/dogu_atik_su_aritma_tesisi_575. Accessed 06 March 2017.
Camargo, J. A., & Jiménez, A. (2007). Ecological responses of epilithic diatoms and aquatic macrophytes to fish farm pollution in a Spanish river. Anales del Jardín Botánico de Madrid, 64(2), 213–219.
Dere, Ş., Dalkıran, N., Karacaoğlu, D., Elmacı, A., Dülger, B., & Şentürk, E. (2006). Relationships among epipelic diatom taxa, bacterial abundances and water quality in a highly polluted stream catchment, Bursa-Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 112, 1–22.
Dere, Ş., Karacaoğlu, D., & Dalkıran, N. (2003). A study on the epilithic algae of the Nilüfer Stream (Bursa). Cumhuriyet Üniversitesi Fen Edebiyat Fak Fen Bilimleri Dergisi, 28(3), 35–51.
Dodds, W. K., Smith, V. H., & Lohman, K. (2002). Nitrogen and phosphorus relationships to benthic algal biomass in temperate streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 59(5), 865–874.
Felisberto, S. A., Leandrini, J. A., & Rodrigues, L. (2011). Effects of nutrients enrichment on algal communities: an experimental in mesocosms approach. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 23(2), 128–137.
Gasse, F., Juggins, S., & Khelifa, L. B. (1995). Diatom-based transfer functions for inferring past hydrochemical characteristics of African lakes. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 117, 31–54.
Grimm, N. B., & Fisher, S. G. (1986). Nitrogen limitation potential of Arizona streams and rivers. Journal of the Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science, 21(1), 31–43.
Güleryüz, G., Arslan, H., Çelik, C., Güçer, Ş., & Kendall, M. (2008). Heavy metal content of plant species along Nilüfer Stream in industrialized Bursa City, Turkey. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 195(1), 275–284.
Hill, M. O., & Gauch, H. G. (1980). Detrended correspondence analysis: an improved ordination technique. Vegetatio, 42, 47–58.
Hope, A. C. A. (1968). A simplified Monte Carlo significance test procedure. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B (Methodological), 30(3), 582–598.
Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Vollertsen, J., & Nielsen, A. H. (2010). Urban and highway stormwater pollution. Concepts and Engineering. Taylor & Francis Group. Boca Raton, London, New York: CRC Press.
Jones, V. J., & Juggins, S. (1995). The construction of diatom based chlorophyll transfer function and its application at three lakes on Signy Island (maritime Antarctic) subject to differing degrees of nutrient enrichment. Freshwater Biology, 34, 433–445.
Jüttner, I., Sharma, S., Dahal, B. M., Ormerod, S. J., Chimonides, P. J., & Cox, E. J. (2003). Diatoms as indicators of stream quality in the Kathmandu Valley and middle hills of Nepal and India. Freshwater Biology, 48(11), 2065–2084.
Karaca, G., & Taşdemir, Y. (2014). Temporal and spatial variations in PAH concentrations in the sediment from the Nilüfer Creek in Bursa, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 49, 900–912.
Karaer, F., & Küçükballı, A. (2006). Monitoring of water quality and assessment of organic pollution load in the Nilüfer Stream, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 114, 391–417.
Kelly, M. G., & Whitton, B. A. (1998). Biological monitoring of eutrophication in rivers. Hydrobiologia, 384, 55–67.
Kelly, M.G., Adams, C., Graves, A.C., Jamieson, J., Krokowski, J., Lycett, E.B., Murray-Bligh, J., Pritchard, S., & Wilkins, C. (2001). The trophic diatom index: a user’s manual. Revised Edition. R&D Technical Report E2/TR2. Bristol: Environment Agency.
Kelly, M. G., Cazaubon, A., Coring, E., Dell’Uomo, A., Ector, L., Goldsmith, B., Guach, H., Hürlimann, J., Jarlman, A., Kawecka, B., et al. (1998). Recommendations for the routine sampling of diatoms for water quality assessments in Europe. Journal of Applied Phycology, 10, 215–224.
Kinouchi, T., Yagi, H., & Miyamoto, M. (2007). Increase in stream temperature related to anthropogenic heat input from urban wastewater. Journal of Hydrology, 335, 78–88.
Krammer, K., & Lange-Bertalot, H. (1991a). Bacillariophyceae 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Band 2/3. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag (in German).
Krammer, K., & Lange-Bertalot, H. (1991b). Bacillariophyceae 4. Teil: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Ergänzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae) und Gomphonema. Gesamtliteraturverzeichnis. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Band 2/4. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag (in German).
Krammer, K., & Lange-Bertalot, H. (1997a). Bacillariophyceae 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Band 2/1. Heidelberg Berlin: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag (in German).
Krammer, K., & Lange-Bertalot, H. (1997b). Bacillariophyceae 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Band 2/2. Heidelberg Berlin: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag (in German).
Lamberti, G. A., Gregory, S. V., Ashkenas, L. R., Wildman, R. C., & Moore, K. M. S. (1991). Stream ecosystem recovery following a catastrophic debris flow. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 48, 196–208.
LeBlanc, R. T., Brown, R. D., & FitzGibbon, J. E. (1997). Modeling the effects of land use change on the water temperature in unregulated urban streams. Journal of Environmental Management, 49(4), 445–469.
Leira, M., & Sabater, S. (2005). Diatom assemblages distribution in catalan rivers, NE Spain, in relation to chemical and physiographical factors. Water Research, 39, 73–82.
Leland, H. V., & Porter, S. D. (2000). Distribution of benthic algae in the upper Illinois River Basin in relation with to geology and land use. Freshwater Biology, 44, 279–301.
Lewis, B. R., Jüttner, I., Reynolds, B., & Ormerod, S. J. (2007). Comparative assessment of stream acidity using diatoms and macroinvertebrates: implications for river management and conservation. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 17(5), 502–519.
Lotter, A. F., Birks, H. J. B., Hofmann, W., & Marchetto, A. (1997). Modern diatom, cladocera, chironomid, and chrysophyte cyst assemblages as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in the Alps. I. Climate. Journal of Paleolimnology, 18, 395–420.
Medley, C. N., & Clements, W. H. (1998). Responses of diatom communities to heavy metals in streams: The influence of longitudinal variation. Ecological Applications, 8(3), 631–644.
Michelutti, N., Douglas, M. S. V., & Smol, J. P. (2003). Diatom response to recent climatic change in a high arctic lake (Char Lake, Cornwallis Island, Nunavut). Global and Planetary Change, 38(3–4), 257–271.
Økland, R. H. (1999). On the variation explained by ordination and constrained ordination axes. Journal of Vegetation Science, 10(1), 131–136.
Ölmez, G. (2014). Yerüstü Su Kaynaklarında Su Kalitesinin İyileştirilmesi İçin Çevresel Hedeflerin Belirlenmesi. Uzmanlık Tezi. Republic of Turkey. Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs. General Directorate of Water Management. Ankara. http://suyonetimi.ormansu.gov.tr/Libraries/su/G%C3%9CLNUR_%C3%96LMEZ_2.sflb.ashx. Accessed 15 Feb 2017.
Patrick, R., & Reimer, C. W. (1966). The diatoms of the United States. Vol.I. Monograph 13. USA: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia.
Patrick, R., & Reimer, C. W. (1975). The diatoms of the United States. Vol.II., Part 1, Monograph 13. USA: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia.
Redfield, A. C. (1958). The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Scientist, 46(3), 205–221.
Rovira, L., Trobajo, R., & Ibáñez, C. (2009). Periphytic diatom community in a Mediterranean salt wedge estuary: the Ebro Estuary (NE Iberian Peninsula). Acta Botanica Croatica, 68(2), 285–300.
Sawai, Y., Horton, B. P., & Nagumo, T. (2004). The development of a diatom-based transfer function along the Pacific coast of eastern Hokkaido, northern Japan—an aid in paleoseismic studies of the Kuril subduction zone. Quaternary Science Reviews, 23, 2467–2483.
Schönfelder, I., Gelbrecht, J., Schönfelder, J., & Steinberg, C. E. W. (2002). Relationships between littoral diatoms and their chemical environment in northeastern German lakes and rivers. Journal of Phycology, 38, 66–89.
Sládeček, V. (1986). Diatoms as indicators of organic pollution. Acta hydrochim et hydrobiol, 14(5), 555–566.
Sonneman, J. A., Walsh, C. J., Breen, P. F., & Sharpe, A. K. (2001). Effects of urbanisation on streams of the Melbourne Region, Victoria, Australia. II. Benthic diatom communities. Freshwater Biology, 46, 553–565.
Şiltu, E. (2014). Nilüfer Çayı Alt Havzası İçin Alıcı Ortam Bazlı Deşarj Standartlarının Hesaplanması. Republic of Turkey. Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs. General Directorate of Water Management. Ankara. http://suyonetimi.ormansu.gov.tr/AnaSayfa/Yayinlarimiz/sygmsunumarsiv/sukalitesi_sunumlari.aspx?sflang=tr. Accessed 15 Feb 2017.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1986). Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology, 67(5), 1167–1179.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1988a). CANOCO—a FORTRAN programme for canonical community ordination by [partial][ detrended] [canonical] correspondence analysis, principal components analysis and redundancy analysis (version 2.1). Technical report LWA8802. Agricultural Mathematics Group: Wageningen.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1988b). Partial canonical correspondence analysis. In H. H. Bock (Ed.), Classification and related methods of data analysis (pp. 551–558). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1995). Ordination. In R. H. G. Jongman, C. J. F. ter Braak, O. F. R. van Tongeren (Eds.), Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology (pp. 91–173) (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
ter Braak, C. J. F., & Prentice, I. C. (1988). A theory of gradient analysis. Advances in Ecological Research, 18, 271–317.
ter Braak, C. J. F., & Šmilauer, P. (2002). CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Ithaca: Microcomputer Power.
ter Braak, C. J. F., & Verdonschot, P. F. M. (1995). Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Sciences, 57(3), 255–289.
Üstün, G. E. (2011). The assessment of heavy metal contamination in the waters of the Nilüfer Stream in Bursa. Ekoloji, 20(81), 61–66.
Üstün, G. E., Karaer, F. & Solmaz, S. K. A. (2008). Assessment of the useability of Nilüfer Stream for irrigation. Water consumption, treatment, reuse symposium. September 3-5, 2008, İznik, Bursa. Proceeding Book (pp. 97–103) (in Turkish).
Van Dam, H., Mertens, A., & Sinkeldam, J. (1994). A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from the Netherlands. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology, 28(1), 117–133.
Weckström, J., & Korhola, A. (2001). Patterns in the distribution, composition and diversity of diatom assemblages in relation to ecoclimatic factors in Arctic Lapland. Journal of Biogeography, 28, 31–45.
Weilhoefer, C. L., & Pan, Y. (2007). Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in wetlands in the Willamette Valley, Oregon, USA. Wetlands, 27(3), 668–682.
Yılmaz, A., Özer, U., Torunoğlu, T., & Aksoy, S. (1998). Evalution of heavy metal contents, polyaromatic petroleum hydrocarbons and some inorganic pollutants in the south Marmara Rivers, Turkey. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 7(5), 269–276.
Yolcu, İ. D., Karaer, F., Işığıçok, E., & Albek, E. A. (2012). Statistical analysis of Bursa Nilüfer Creek’s water quality parameters for period of 2002–2010. Journal of Environmental Protection, 3, 956–965.
Zong, Y., & Horton, B. P. (1999). Diatom-based tidal-level transfer functions as an aid in reconstructing Quaternary history of sea-level movements in the UK. Journal of Quaternary Science, 14(2), 153–167.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Engin Şentürk, Şenay Kara, and İlhami Kaş from the State Hydraulic Works 1st Regional Directorate for their help in the field and in the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karacaoğlu, D., Dalkıran, N. Epilithic diatom assemblages and their relationships with environmental variables in the Nilüfer Stream Basin, Bursa, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 189, 227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5929-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5929-z