Abstract
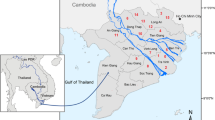
Activity concentrations of radionuclides in water, soil and tuber crops of a major food-producing area in Ghana were investigated. The average gross alpha and beta activities were 0.021 and 0.094 Bq/L, respectively, and are below the guidelines for drinking water and therefore not expected to pose any significant health risk. The average annual effective dose due to ingestion of radionuclide in water ranged from 20.08 to 53.45 μSv/year. The average activity concentration of 238U, 232Th, 40K and 137Cs in the soil from different farmlands in the study area was 23.19, 31.10, 143.78 and 2.88 Bq/kg, respectively, which is lower than world averages. The determined absorbed dose rate for the farmlands ranged from 23.63 to 50.51 nGy/year, which is within worldwide range of 18 to 93 nGy/year. The activity concentration of 238U, 232Th, 40K and 137Cs in cassava ranges from 0.38 to 6.73, 1.82 to 10.32, 17.65 to 41.01 and 0.38 to 1.02 Bq/kg, respectively. Additionally, the activity concentration of 238U, 232Th, 40K and 137Cs in yam also ranges from 0.47 to 4.89, 0.93 to 5.03, 14.19 to 35.07 and 0.34 to 0.89 Bq/kg, respectively. The average concentration ratio for 238U, 232Th and 40K in yam was 0.12, 0.11 and 0.17, respectively, and in cassava was 0.11, 0.12 and 0.2, respectively. None of the radioactivity is expected to cause significant health problems to human beings.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Khadral, S.A., Abdel-Sabour, M.F., Abdel-Fattah, A.T., & Eissa, H.S. (2008). Transfer factor of radioactive Cs and Sr from Egyptian soils to roots and leafs of wheat plant. In IX radiation physics & protection conference (pp. 15–19). Nasr City—Cairo, Egypt: IAEA/INIS. http://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:40092046. Accessed 13 November 2014.
Adu, S., Darko, E., & Awudu, A. (2011). Preliminary study of natural radioactivity in the lake Bosumtwi Basin. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 3(5), 463–468. http://maxwellsci.com/print/rjees/v3-463-468.pdf. Accessed 13 November 2014.
Alam, M. N., Chowdhury, M. I., Ghose, S., & Islam, M. N. (1999). Radiological assessment of drinking water of the Chittagong Region of Bangladesh. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 82, 207–214.
Alharbi, A., & El-Taher, A. (2013). A study on transfer factors of radionuclides from soil to plant. Life Science Journal, 10(2), 532–539.
Amin, M., Uosif, M., Ra, A., Özgül, K., & Belirlenmesi, A. (2011). Specific activity of 226 Ra, 232 Th and 40 K for assessment of radiation hazards from building materials commonly used in upper Egypt. SDU Journal of Science, 6(2), 120–126.
Angelucci, F. (2013). Analysis of incentives and disincentives for cassava in Ghana. Rome: FAO.
Appl, P., Britain, G., Revort, H., Mact, D. O. D. E., Aprile-, V. X. X. I., & Grande, R. (1998). Gross alpha- and beta-activities in surface and ground water of Rio Grande do Norte. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 49(7), 893–898.
Bengtsson, S. B., Eriksson, J., Gärdenäs, A. I., & Rosén, K. (2012). Influence of development stage of spring oilseed rape and spring wheat on interception of wet-deposited radiocaesium and radiostrontium. Atmospheric Environment, 60, 227–233. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.062.
Bozkurt, A., Yorulmaz, N., Kam, E., Karahan, G., & Erdal, A. (2007). Assessment of environmental radioactivity for Sanliurfa region of southeastern Turkey. Radiation Measurements, 42, 1387–1391. doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2007.05.052.
Canu, I. G., Laurent, O., Pires, N., Laurier, D., & Dublineau, I. (2011). Health effects of naturally radioactive water ingestion: the need for enhanced studies. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119, 1676–1680.
Cevik, U., Damla, N., Karahan, G., & Celebi, N. (2006). Natural radioactivity in tap water from eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 118(1), 88–92. doi:10.1093/rpd/nci325.
Darko, G., Faanu, A., Akoto, O., Atta-Agyeman, F., Aikins, M. A., Agyemang, B., & Ibrahim, A. (2014). Assessment of the activity of radionuclides and radiological impacts of consuming underground water in Kumasi, Ghana. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(1), 399–404. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3433-0.
Degerlier, M., & Karahan, G. (2010). Natural radioactivity in various surface waters in Adana, Turkey. Desalination, 261(1–2), 126–130. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.020.
Ehsanpour, E., Abdi, M. R., Mostajaboddavati, M., & Bagheri, H. (2014). 226 Ra, 232 Th and 40 K contents in water samples in part of central deserts in Iran and their potential radiological risk to human population. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12(1), 1–7. doi:10.1186/2052-336X-12-80.
El-Mageed, A. I. A., El-Kamel, A. E. H., Abbady, A. E. B., Harb, S., & Saleh, I. I. (2013). Natural radioactivity of ground and hot spring water in some areas in Yemen. Desalination, 321, 28–31. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.022.
Evensen, J. F., Bjordal, K., Knutsen, B. H., Olsen, D. R., Støre, G., & Tausjø, J. E. (2002). Side effects and quality of life after inadvertent radiation overdosage in brachytherapy of head-and-neck cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 52(4), 944–952. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(01)02726-2.
Faanu, A., Adukpo, O. K., Okoto, R. J. S., Diabor, E., Darko, E. O., Awudu, A. R., et al. (2011a). Determination of radionuclides in underground water sources within the environments of University of Cape Coast. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 3(3), 269–274.
Faanu, A., Ephraim, J. H., & Darko, E. O. (2011b). Assessment of public exposure to naturally occurring radioactive materials from mining and mineral processing activities of Tarkwa Goldmine in Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 180(1–4), 15–29. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10661-010-1769-9. Accessed 9 December 2013.
Faanu, A., Ephraim, J. H., & Darko, E. O. (2010). Assessment of public exposure to naturally occurring radioactive materials from mining and mineral processing activities of Tarkwa Goldmine in Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 180(1-4), 15–29. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1769-9.
Hakam, O. K., Choukri, A., Moutia, Z., Chouak, A., Cherkaoui, R., Reyss, J.-L., & Lferde, M. (2001). Uranium and radium in groundwater and surface water samples in Morocco. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 61(3–6), 653–654. doi:10.1016/S0969-806X(01)00362-0.
Hopke, P. K., Borak, T. B., Doull, J., Cleaver, J. E., & Eckerman, K. F. (2000). Health risks due to radon in drinking water. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(6), 921–926.
IAEA. (2001). Radiation protection and safety of radiation sources: international basic safety standards general safety requirements Part 3 (No. GSR Part 3 (Interim)) (Vol. 3). Vienna. http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/Pub1578_web-57265295.pdf. Accessed 20 April 2014.
IAEA (2005). Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORM IV). In Proceedings of an International Conference held in Szczyrk, Poland, 17-21 May 2004 I.E. TECDOC 1472 : 0609-Radiation protection IAEATECDOC-1472. http://www-pub.iaea.org/books/IAEABooks/7384/Naturally-Occurring-Radioactive-Materials-NORM-IV-Proceedings-of-an-International-Conference-held-in-Szczyrk-Poland-17-21-May-2004. Accessed 07 May 2015.
IAEA. (2009). Handbook of parameter values for the prediction of radionuclide transfer in terrestrial and freshwater environment (No. TRS 364). Vienna: IAEA.
ICRP. (2007). Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP Publication 103. Canada: ICRP.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2000). Trace elements in soils and plants, third edition (Vol. 8). CRC Press. http://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Nowwb0xl9fYC&pgis=1. Accessed 20 September 2014.
Kinyua, R., Atambo, V. O., & Ongeri, R. M. (2011). Activity concentrations of 40K, 232Th, 226Ra and radiation exposure levels in the Tabaka soapstone quarries of the Kisii Region, Kenya. Africa Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 5(9), 682–688.
Madruga, M. J. Ã. (2008). Environmental radioactivity monitoring in Portugal. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 66, 1639–1643. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.04.008.
Manigandan, P. K., & Chandar, S. B. (2014). Evaluation of radionuclides in the terrestrial environment of Western Ghats. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 7(3), 310–316. doi:10.1016/j.jrras.2014.04.001.
Milési, J. P., Ledru, P., Ankrah, P., Johan, V., Marcoux, E., & Vinchon, C. (1991). The metallogenic relationship between Birimian and Tarkwaian gold deposits in Ghana. Mineralium Deposita, 26(3), 228–238. doi:10.1007/BF00209263.
Ndontchueng, M. M., Mekongtso Nguelem, E. J., Simo, A., Njinga, R. L., & Joël, G. S. C. (2014). Gamma emitting radionuclides in soils from selected areas in Douala-Bassa zone, littoral region of Cameroon. ISRN Spectroscopy, 2014, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/245125.
Ng, Y.C., Thompson, S.E., & Colsher, C.S. (1982). Soil-to-plant concentration factors for radiological assessments (No. NUREG/CR-2975; UCID-19463 ON: DE83002251). http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/6728957. Accessed 24 April 2015.
Nguelem, E. J., Schandorf, C., Akiti, T., Bam, E. K. P., Darko, E., Muhulo, A., & Ndontchueng, M. (2013). The natural radioactivity in groundwater from selected areas in Greater Accra region of Ghana by gross alpha and gross beta measurements. Radiation Protection and Environment, 36(1), 14. doi:10.4103/0972-0464.121814.
Oresengun, M. O., Decker, K. M., & Sanderson, C. G. (2010). Determination of self absorption correction by computation in routine gamma-ray spectrometry for typical environmental samples. Journal of Radioactivity and Radiochemistry, 4, 38–45.
Pakade, V. E., Cukrowska, E. M., Darkwa, J., Darko, G., Torto, N., & Chimuka, L. (2012). Simple and efficient ion imprinted polymer for recovery of uranium from environmental samples. Water Science and Technology, 65(4), 728–736. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.911.
Palomo, M., Pen, A., Borrull, F., & Aguilar, C. Ã. (2007). Measurement of radioactivity in bottled drinking water in Spain. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 65, 1165–1172. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2007.04.022.
Pujol, L., & Sanchez-Cabeza, J. A. A. (2000). Natural and artificial radioactivity in surface waters of the Ebro river basin (Northeast Spain). Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 51(2), 181–210. doi:10.1016/S0265-931X(00)00076-X.
Shashikumar, T. S., Chandrashekara, M. S., & Paramesh, L. (2011). Studies on radon in soil gas and natural radionuclides in soil, rock and ground water samples around Mysore city. International Journal of Environmental Science, 1(5), 786–797.
Taskin, H., Karavus, M., Ay, P., Topuzoglu, A., Hidiroglu, S., & Karahan, G. (2009). Radionuclide concentrations in soil and lifetime cancer risk due to gamma radioactivity in Kirklareli, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 100(1), 49–53. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.10.012.
UNSCEAR. (2000). Dose assessment methodologies. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Report to the General Assembly, Annex A, Vienna. http://www.unscear.org/docs/reports/annexa.pdf. Accessed 07 May 15.
UNSCEAR. (2010). Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Report to the General Assembly, Annex A, New York. www.irpa.net/irpa9/cdrom/VOL.1/V1_3.PDF. Accessed 07 May 15.
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking, vol 1, 3rd edn, pp 1–515.
WHO. (2006). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd edn. Geneva: WHO.
Wrenn, M. E., Durbin, P. W., Howard, B., Lipsztein, J., & Still, E. T. (1985). Metabolism or ingested U and Ra. Health Physics, 8(5), 601–633.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darko, G., Faanu, A., Akoto, O. et al. Distribution of natural and artificial radioactivity in soils, water and tuber crops. Environ Monit Assess 187, 339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4580-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4580-9