Abstract
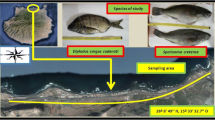
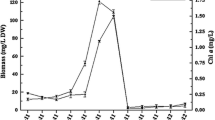
The aim of this study is to summarise the determination of concentrations of microcystins (MCs) in muscle and liver of freshwater fish species caught in stagnant waters of the Czech Republic. Within the years 2007–2009, 351 muscle samples and 291 liver samples of 16 freshwater fish species derived from four fishponds, and four water reservoirs were analysed. MCs were detected in 53 liver samples. The highest concentrations of microcystins were determined in liver samples of carnivorous fish species; 50.3 ng/g of fresh weight (FW) in perch (Perca fluviatilis) and 22.7 ng/g FW in pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). MCs in liver were detected in other five fish species; asp (Aspius aspius), pike (Esox lucius), common carp (Cyprinus carpio), grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) and European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Concentrations of MCs in liver of nine fish species (European bream, whitefish, tench, silver carp, European catfish, roach, chub, crucian carp and rudd) were below the detection limit of 1.2–5.4 ng/g FW for different MC congeners. However, the concentrations of MCs in all muscle samples were below the detection limit. The assessment of MCs concentrations might be influenced by the detection method used. Due to the concentrations of MCs being below the detection limit in muscle samples of all fish species analysed, it seems that there might be a low potential threat for human health in case of fish muscle consumption.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamovský, O., Kopp, R., Hilscherová, K., Babica, P., Palíková, M., Pašková, V., et al. (2007). Microcystin kinetics (bioaccumulation, elimination) and biochemical responses in common carp and silver carp exposed to toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Environ Toxicol Chem, 26(12), 2687–2693.
Amé, M. V., Galanti, L. N., Menone, M. L., Gerpe, M. S., Moreno, V. J., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2010). Microcystin-LR, -RR, -YR and -LA in water samples and fishes from a shallow lake in Argentina. Harmful Algae, 9(1), 66–73.
APHA (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association Inc., Washington D.C.
Babica, P., Kohoutek, J., Blaha, L., Adamovsky, O., & Marsalek, B. (2006). Evaluation of extraction approaches linked to ELISA and HPLC for analyses of microcystin-LR, -RR and -YR in freshwater sediments with different organic material contents. Anal Bioanal Chem, 385, 1545–1551.
Carbis, C. R., Rawlin, G. T., Grant, P., Mitchell, G. F., Anderson, J. W., & Mccauley, I. (1997). A study of feral carp, Cyprinus carpio L., exposed to Microcystis aeruginosa at Lake Mokoan, Australia and possible implications for fish health. J Fish Dis, 20(2), 81–91.
Chen, J., Xie, P., Guo, L., Zheng, L., & Ni, L. (2005). Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in a freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Environ Pollut, 134(3), 423–430.
Chen, J., Xie, P., Zhang, D., Ke, Z., & Yang, H. (2006). In situ studies on the bioaccumulation of microcystins in the phytoplanktivorous silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) stocked in Lake Taihu with dense toxic Microcystis blooms. Aquaculture, 261, 1026–1038.
Chen, J., Xie, P., Zhang, D., & Lei, H. (2007). In situ studies on the distribution patterns and dynamics of microcystins in a biomanipulation fish—bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis). Environ Pollut, 147, 150–157.
Chen, J., Xie, P., Li, L., & Xu, J. (2009). First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicol Sci, 108(1), 81–89.
Eriksson, J. E., Grönberg, L., Nyglrd, S., Slotte, J. P., & Meriluoto, J. (1990). Hepatocellular uptake of 3H-dihydromicrocystin-LR a cyclic peptide toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1025, 60–66.
Ernst, B., Hitzfeld, B., & Dietrich, B. (2001). Presence of Planktothrix sp. and cyanobacterial toxins in Lake Ammersse, Germany and their impact on white-fish (Coregonus lavaretus L.). Environ Toxicol, 16, 483–488.
Ernst, B., Dietz, L., Hoeger, S. J., & Dietrich, D. R. (2005). Recovery of MC-LR in fish liver tissues. Environ Toxicol, 20, 449–458.
Fischer, W. J., & Dietrich, D. R. (2000). Pathological and biochemical characterization of microcystin-induced hepatopancreas and kidney damage in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 164(1), 73–81.
Geis-Asteggiante, L., Lehotay, S. J., Fortis, L. L., Paoli, G., Wijey, C., & Heinzen, H. (2011). Development and validation of a rapid method for microcystins in fish and comparing LC-MS/MS results with ELISA. Anal Bioanal Chem, 401(8), 2617–2630.
Gkelis, S., Lanaras, T., & Sivonen, K. (2006). The presence of microcystins and other cyanobacterial bioactive peptides in aquatic fauna collected from Greek freshwaters. Aquat Toxicol, 78(1), 32–41.
Ibelings, B. W., Bruning, K., Jonge, J., Wolfstein, K., Dionisio Pires, L. M., Postma, J., et al. (2005). Distribution of microcystins in a Lake food web: no evidence for biomagnification. Microb Ecol, 49, 487–500.
Ibelings, B. W., & Chorus, I. (2007). Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater seafood and its consequences for public health: a review. Environ Pollut, 150(1), 177–192.
Kagalou, I., Papadimitriou, T., Bacopoulos, V., & Leonardos, I. (2008). Assessment of microcystins in lake water and the omnivorous fish (Carassius gibelio, Bloch) in Lake Pamvotis (Greece) containing dense cyanobacterial bloom. Environ Monit Assess, 137(1–3), 185–195.
Kohoutek, J., Adamovský, O., Oravec, M., Šimek, Z., Palíková, M., Kopp, R., et al. (2010). LC-MS analyses of microcystins in fish tissues overestimate toxin levels-critical comparison with LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem, 398, 1231–1237.
Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B., Wilson, A. E., & Ferrao-Filho, A. S. (2012). Biomagnification or biodilution of microcystins in aquatic food webs? Meta-analyses of laboratory and field studies. Harmful Algae, 18, 47–55.
Landsberg, J. H. (2002). The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev Fish Sci, 10(2), 113–390.
Lawton, L. A., Edwards, C., & Codd, G. A. (1994). Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst, 119, 1525–1530.
Lorenzen, C. J. (1967). Determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr, 12, 343–346.
Mackintosch, R. W., Dalby, K. N., Campbell, D. G., Cohen, P. T. W., Cohen, P., & Mackinthosh, C. (1995). The cyanobacterial toxin microcystin binds covalently to cysteine-273 on protein phosphatase-1. FEBS Lett, 371(3), 236–240.
Magalhaes, V. F., Soares, R. M., & Azevedo, S. M. F. O. (2001). Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): ecological implication and human health risk. Toxicon, 39, 1077–1085.
Magalhaes, V. F., Marinho, M. M., Domingos, P., Oliveira, A. C., Costa, S. M., Azevedo, L. O., et al. (2003). Microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) bioaccumulation in fish and crustaceans from Sepetiba Bay (RJ, Brazil). Toxicon, 42, 289–295.
Malbrouck, C., & Kestemont, P. (2006). Effects of microcystin on fish. Environ Toxicol Chem, 25(1), 72–86.
Mohamed, Z. A., Carmichael, W. W., & Hussein, A. A. (2003). Estimation of microcystins in the freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus in an Egyptian fish farm containing a Microcystis bloom. Environ Toxicol, 18(2), 137–141.
Orr, P. T., Jones, J. G., Hunter, A. R., & Berger, K. (2003). Exposure of beef cattle to sub-clinical doses of Microcystis aeruginosa: toxin bioaccumulation, physiological effects and human health risk assessment. Toxicon, 41, 613–620.
Poste, E. A., Hecky, E. R., & Guildford, J. S. (2011). Evaluating microcystin exposure risk through fish consumption. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(13), 5806–5811.
Romo, S., Fernández, F., Ouahid, Y., & Báron-Sola, Á. (2012). Assessment of microcystins in lake water and fish (Mugilidae, Liza sp.) in the largest Spanish coastal lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessement, 184, 939–949.
Soares, R. M., Magalhaes, V. F., & Azevedo, S. M. F. O. (2004). Accumulation and depuration of microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) in Tilapia rendalli (Cichlidae) under laboratory conditions. Aquat Toxicol, 70, 1–10.
Wetzel, G. R. (1983). Limnology. Orlando USA: Saunders College Publishing. 766 p.
Wood, S. A., Briggs, L. R., Sprosen, J., Ruck, J. G., Wear, R. G., Holland, P. T., et al. (2006). Changes in concentrations of microcystins in rainbow trout, freshwater mussels and cyanobacteria in Lakes Rotoiti and Rotoehu. Environ Toxicol, 21(3), 205–222.
Xie, L., Xie, P., Ozawa, K., Honma, T., Yokoyama, A., & Park, H. (2004). Dynamics of microcystins-LR and -RR in the phytoplanktivorous silver carp in a sub-chronic toxicity experiment. Environ Pollut, 127, 431–439.
Xie, L., Xie, P., Guo, L., Li, L., Miyabara, Y., & Park, H. (2005). Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu China. Environ Toxicol, 20, 293–300.
Xie, L., Yokoyama, A., Nakamura, K., & Park, H. (2007). Accumulation of microcystins in various organs of the freshwater snail Sinotaia histrica and three fishes in a temperate lake, the eutrophic Lake Suwa, Japan. Toxicon, 49(5), 646–652.
Zhang, H. J., Zhang, J. Y., Hong, Y., & Chen, Y. X. (2007). Evaluation of organ distribution of microcystins in the freshwater phytoplanktivorous fish Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 8(2), 116–120.
Zhao, M., Xie, S., Zhu, X., Yang, Y., Gan, N., & Song, L. (2006). Effect of dietary cyanobacteria on growth and accumulation of microcystins in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture, 261, 960–966.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research project funded by the ministry of education, youth and sports of the Czech Republic “Veterinary Aspects of Food Safety and Quality” (MSM 62 15712402) and by the National Agency for Agricultural Research” (grant no. QH 71015). Infrastructure is supported by a project CETOCOEN (no. CZ.1.05/2.1.00/01.0001) from the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopp, R., Palíková, M., Adamovský, O. et al. Concentrations of microcystins in tissues of several fish species from freshwater reservoirs and ponds. Environ Monit Assess 185, 9717–9727 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3285-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3285-1