Abstract
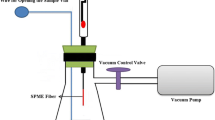
A method based on headspace (HS) sampling coupling with portable gas chromatography (GC) with photo ionization detector (PID) was developed for rapid determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (BTEX) in soils. Optimal conditions for HS gas sampling procedure were determined, and the influence of soil organic matter on the recovery of BTEX from soil was investigated using five representative Chinese soils. The results showed that the HS-portable-GC-PID method could be effectively operated at ambient temperature, and the addition of 15 ml of saturated NaCl solution in a 40-ml sampling vial and 60 s of shaking time for sample solution were optimum for the HS gas sampling procedure. The recoveries of each BTEX in soils ranged from 87.2 to 105.1 %, with relative standard deviations varying from 5.3 to 7.8 %. Good linearity was obtained for all BTEX compounds, and the detection limits were in the 0.1 to 0.8 μg kg−1 range. Soil organic matter was identified as one of the principal elements that affect the HS gas sampling of BTEX in soils. The HS-portable-GC-PID method was successfully applied for field determination of benzene and toluene in soils of a former chemical plant in Jilin City, northeast China. Considering its satisfactory repeatability and reproducibility and particular suitability to be operated in ambient environment, HS sampling coupling with portable GC-PID is, therefore, recommended to be a suitable screening tool for rapid on-site determination of BTEX in soils.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat, B. F. A., Al-Rub, F. A., & Simandl, J. (1999). Experimental study of the salt effect in vapor/liquid equilibria using headspace gas chromatography. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 22, 761–765.
Basheer, C., Alnedhary, A. A., Rao, B. S. M., Valliyaveettil, S., & Lee, H. K. (2006). Development and application of porous membrane-protected carbon nanotube micro-solid-phase extraction combined with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2853–2858.
Bossert, I., & Bartha, R. (1984). The fate of petroleum in soil ecosystems. In R. M. Atlas (Ed.), Petroleum microbiology. New York: Macmillan.
Buddhadasa, S. C., Barone, S., Gibson, E., Bigger, S. W., & Orbell, J. D. (2002). Method dependency in the measurement of BTEX levels in contaminated soil. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2, 137–142.
Ezquerro, Ó., Pons, B., & Tena, M. T. (2003). Evaluation of multiple solid-phase microextraction as a technique to remove the matrix effect in packaging analysis for determination of volatile organic compounds. Journal of Chromatography A, 1020, 189–197.
Ezquerro, Ó., Ortiz, G., Pons, B., & Tena, M. T. (2004). Determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes in soils by multiple headspace solid-phase microextraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1035, 17–22.
Flórze Menéndez, J. C., Fernández Sánchez, M. L., Sánche Uría, J. E., Fernández Martínez, E., & Sanz-Medel, A. (2000). Static headspace, solid-phase microextraction and headspace solid-phase microextraction for BTEX determination in aqueous samples by gas chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta, 415, 9–20.
Henry, C. (1997). Taking the show on the road—Portable GC and GC/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 69, 195A–200A.
Isetun, S., Nilsson, U., Colmsjö, A., & Johansson, R. (2004). Air sampling of organophosphate triesters using SPME under non-equilibrium conditions. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 378, 1847–1853.
Ji, J., Deng, C., Shen, W., & Zhang, X. (2006). Field analysis of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene in water by portable gas chromatography-microflame ionization detector combined with headspace solid-phase microextraction. Talanta, 69, 894–899.
Kolb, B., & Ettre, L. S. (2006). Static headspace-gas chromatography: Theory and practice (2nd ed.). New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Kotowska, U., Żalikowski, M., & Isidorov, V. A. (2012). HS-SPME/GC–MS analysis of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds emitted from municipal sewage sludge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 2893–2907.
Lee, M. R., Chang, C. M., & Dou, J. P. (2007). Determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes in water at sub-ng l-1 levels by solid-phase microextraction coupled to cryo-trap gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere, 69, 1381–1387.
Lin, H. Q., Ye, Q., Deng, C. H., & Zhang, X. M. (2008). Field analysis of acetaldehyde in mainstream tobacco smoke using solid-phase microextraction and a portable gas chromatograph. Journal of Chromatography A, 1198–1199, 34–37.
Llompart, M., Li, K., & Fingas, M. (1999). Headspace solid phase microextraction (HSSPME) for the determination of volatile and semivolatile pollutants in soils. Talanta, 48, 451–459.
Mena, M. L., Martı´nez-Ruiz, P., Reviejo, A. J., & Pingarro´n, J. M. (2002). Molecularly imprinted polymers for on-line preconcentration by solid phase extraction of pirimicarb in water samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 451, 297–304.
Meney, K. M., Davidson, C. M., & Littlejohn, D. (1998). Use of solid-phase extraction in the determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene and cumene in spiked soil and investigation of soil spiking methods. Analyst, 123, 195–200.
Nollet, L. M. L. (2006). Chromatographic analysis of the environment (3rd ed.). Florida: CRC Press.
Pinto, C. G., Martín, S. H., Pavón, J. L. P., & Cordero, B. M. (2011). A simplified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe approach for the determination of trihalomethanes and benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes in soil matrices by fast gas chromatography with mass spectrometry detection. Analytica Chimica Acta, 689, 129–136.
Sarafraz-Yazdi, A., Amiri, A. H., & Es′haghi, Z. (2008). BTEX determination in water matrices using HF-LPME with gas chromatography-flame ionization detector. Chemosphere, 71, 671–676.
Shinohara, A., Sato, A., Ishii, H., & Onda, N. (1991). Capillary headspace-gas chromatography for the characterization of the flavour of fresh vegetables. Chromatographia, 32, 357–364.
USEPA. (1991). Manual for coordination of VOC emissions: Testing using EPA methods 18, 21, 25, and 25A, EPA 340/1-91-008. Washington.
Voice, T. C., & Kolb, B. (1993). Static and dynamic headspace analysis of volatile organic compounds in soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 27, 709–713.
Zhang, Z., & Pawliszyn, J. (1993). Analysis of organic compounds in environmental samples by headspace solid phase microextraction. Journal of High Resolution Chromatography, 16, 689–692.
Zygmunt, B., & Namiesnik, J. (2001). Solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic determination of volatile monoaromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 370, 1096–1099.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the constructive comments of the two anonymous reviewers on an earlier version of this manuscript. Thanks are also given to Angel Perez Sainz for his helpful comments and assistance in the technical review of this manuscript. This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21075114) and the Special Environmental Protection Fund for Public Welfare project of China (no. 201009015, no. 200809095, and no. 201009032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, YY., Yu, JF., Yan, ZG. et al. Application of portable gas chromatography-photo ionization detector combined with headspace sampling for field analysis of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene in soils. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3037–3048 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2771-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2771-1