Abstract
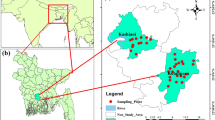
A study was conducted to evaluate the heavy metal contamination status of groundwater in Brahmaputra flood plain Barpeta District, Assam, India. The Brahmaputra River flows from the southern part of the district and its many tributaries flow from north to south. Cd, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn are estimated by using atomic absorption spectrometer, Perkin Elmer AA 200. The quantity of heavy metals in drinking water should be checked time to time; as heavy metal accumulation will cause numerous problems to living being. Forty groundwater samples were collected mainly from tube wells from the flood plain area. As there is very little information available about the heavy metal contamination status in the heavily populated study area, the present work will help to be acquainted with the suitability of groundwater for drinking applications as well as it will enhance the database. The concentration of iron exceeds the WHO recommended levels of 0.3 mg/L in about 80% of the samples, manganese values exceed 0.4 mg/L in about 22.5% of the samples, and lead values also exceed limit in 22.5% of the samples. Cd is reported in only four sampling locations and three of them exceed the WHO permissible limit (0.003 mg/L). Zinc concentrations were found to be within the prescribed WHO limits. Therefore, pressing awareness is needed for the betterment of water quality; for the sake of safe drinking water. Statistical analysis of the data was carried out using Special Package for Social Sciences (SPSS 16).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbulut, N. E., & Tuncer, A. M. (2011). Accumulation of heavy metals with water quality parameters in Kızılırmak River Basin (Delice River) in Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173, 387–395. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1394-7.
Aktar, Md. W., Paramasivam, M., Ganguly, M., Purkait, S., & Sengupta, D. (2010). Assessment and occurrence of various heavy metals in surface water of Ganga River around Kolkata: a study for toxicity and ecological impact. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 207–213. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0688-5.
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998). Standard method for examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: APHA.
Babiker, I. S., Mohamed, M. A. A., & Hiyama, T. (2007). Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resour Manage, 21, 699–715. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9059-6.
Bruins, M. R., Kapil, S., & Oehme, F. W. (2000). Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 45, 198–207. doi:10.1006/eesa.1999.1860.
Buragohain, M., Bhuyan, B., & Sarma, H. P. (2010). Seasonal variations of lead, arsenic, cadmium and aluminium contamination of groundwater in Dhemaji district, Assam, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170(1–4), 345–351. doi:10.1007/s10661-s10661-009-1237-6.
CGWB. (2008). Ground water information booklet Barpeta district, Assam, CGWB. North Eastern region, Ministry of Water Resource, Govt. of India. Guwahati: Central Ground Water Board
Chakrabarty, S., & Sarma, H. P. (2011). Heavy metal contamination of drinking water in Kamrup district, Assam, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 179, 479–486. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1750-7.
El Khalil, H., El Hamiani, O., Bitton, G., Ouazzani, N., & Boularbah. (2008). Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: monitoring metal content and toxicity of soil runoff and groundwater. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136, 147–160. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9671-9.
Elinder, C. G. (1986). Zinc. In L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg, & V. B. Vouk (Eds.), Handbook on the toxicology of metals (2nd ed., pp. 664–679). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants. London: Academic Press.
Nduka, J. K., & Orisakwe, O. E. (2010). Water-quality issues in the Niger Delta of Nigeria: a look at heavy metal levels and some physicochemical properties. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0366-3.
Nriagu, J. O. (Ed.). (1980). Zinc in the environment. Part I, ecological cycling. New York: Wiley.
Numberg, H. W. (1982). Yoltametric trace analysis in ecological chemistry of toxic metals. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 54(4), 853–878.
Ramesh, R., Shiv Kumar, K., Eswaramoorthi, S., & Purvaja, G. R. (1995). Migration and contamination of major and trace elements in ground water of Madras city, India. Environmental Geology, 25, 126–136.
Singh, A. K. (2004). Arsenic contamination in groundwater of North Eastern India. Roorkee: Proceedings of national seminar on hydrology held at National Institute of Hydrology.
Tiwari, T. N., & Ali, M. (1988). Water quality index for Indian rivers. In R. K. Trivedy (Ed.), Ecology and pollution of Indian rivers (1st ed., pp. 271–286). New Delhi: Ashish.
Venugopal, T., Giridharan, L., Jayaprakash, M., & Periakali, P. (2009). Environmental impact assessment and seasonal variation study of the groundwater in the vicinity of River Adyar, Chennai, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 149, 81–97. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0185-x.
Watson, S. B., & Lawrence, J. (2003). Drinking water quality and sustainability. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 38(1), 3–13.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality (3rd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yayıntas, O. T., Yılmaz, S., Turkogluv, M., & Dilgin, Y. (2007). Determination of heavy metal pollution with environmental physicochemical parameters in waste water of Kocabas Stream (Biga, Canakkale, Turkey) by ICP-AES. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 127, 389–397. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9288-4.
Acknowledgments
Nabanita Haloi is thankful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi for financial assistance in the form of Rajib Gandhi National Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haloi, N., Sarma, H.P. Heavy metal contaminations in the groundwater of Brahmaputra flood plain: an assessment of water quality in Barpeta District, Assam (India). Environ Monit Assess 184, 6229–6237 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2415-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2415-x