Abstract
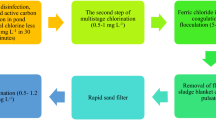
Coagulation is the most important stage in drinking water treatment processes for the maintenance of acceptable treated water quality and economic plant operation, which involves many complex physical and chemical phenomena. Moreover, coagulant dosing rate is non-linearly correlated to raw water characteristics such as turbidity, conductivity, pH, temperature, etc. As such, coagulation reaction is hard or even impossible to control satisfactorily by conventional methods. Traditionally, jar tests are used to determine the optimum coagulant dosage. However, this is expensive and time-consuming and does not enable responses to changes in raw water quality in real time. Modelling can be used to overcome these limitations. In this study, an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) was used for modelling of coagulant dosage in drinking water treatment plant of Boudouaou, Algeria. Six on-line variables of raw water quality including turbidity, conductivity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, ultraviolet absorbance, and the pH of water, and alum dosage were used to build the coagulant dosage model. Two ANFIS-based Neuro-fuzzy systems are presented. The two Neuro-fuzzy systems are: (1) grid partition-based fuzzy inference system (FIS), named ANFIS-GRID, and (2) subtractive clustering based (FIS), named ANFIS-SUB. The low root mean square error and high correlation coefficient values were obtained with ANFIS-SUB method of a first-order Sugeno type inference. This study demonstrates that ANFIS-SUB outperforms ANFIS-GRID due to its simplicity in parameter selection and its fitness in the target problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirtarajah, A., & Trusler, S. L. (1986). Destabilisation of particles by turbulent rapid mixing. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 112(6), 1085–108.
Amirtharajah, A., & Mills, K. M. (1982). Rapid-mix design for mechanisms of alum flocculation. Journal of American Water Works Association, 74(4), 210–216.
Amirtharajah, A., & O’Melia, C. R. (1990). Coagulation processes: destabilization, mixing, and flocculation. In F. W. Pontius (Ed.), Water quality and treatment (4th ed., pp. 269–365). Toronto: McGraw-Hill.
Baxter, C. W., Stanley, S. J., & Zhang, Q. (1999). Development of a fullscale artificial neural network model for the removal ofnatural organic matter by enhanced coagulation. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology. AQUA, 48(4), 129–136.
Baxter, C. W., Zhang, Q., Stanley, S. J., Shariff, R., Tupas, R.-R. T., & Stark, H. L. (2001). Drinking waer quality and treatment: the use of artificial neural networks. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 28(Suppl. S1), 26–35.
Bazer-Bachi, A., Puech-Coste, E., Ben Aim, R., & Probst, J. L. (1990). Mathematical modeling of optimum coagulant dose in water treatment plant. Revue Des Sciences De L’eau, 3, 377–397.
Buckley, J. J., & Hayashi, Y. (1994). Fuzzy neural networks. In L. A. Zadeh, R. R. Yager (Eds.), Fuzzy sets, neural networks and soft computing (p. 233–249). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Chiu, S. (1994). Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2, 267–278.
Daly, R., Van Leeuwen, J., & Holmes, M. (2007). Modelling coagulation to maximise removal of organic matter. A Pilot Plant and Laboratory Based Study, Chemical Dose Prediction. CRC for Water Quality and Treatment. Research Report 36 14-19. ISBN 18766 1661X.
Edzwald, J. K. (1993). Coagulation in drinking water treatment: particles, organics and coagulants. Water Science and Technology, 37, 21–35.
Edzwald, J. K., & Tobaison, J. E. (1999). Enhanced coagulation: us requirements and a broader view. Water Science and Technology, 40(9), 63–70.
Edzwald, J. K., & Van Benschoten J. E. (1990). Aluminum coagulation of natural organic material. In H. H. Hahn & R. Klute (Eds.), Chemical water and wastewater treatment. Berlin: Springer.
Gagnon, C., Grandjean, B. P. A., & Thibault, J. (1997). Modelling of coagulant dosage in a water treatment plant. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 11, 401–404.
Gregor, J. E., Nokes, C. J., & Fenton, E. (1997). Optimising natural organic matter removal from low turbidity waters by controlled pH adjustment of aluminium coagulation. Water Research, 31(12), 2949–2958.
Hanson, A. T., & Cleasby J. L. (1990). The effect of temperature on turbulent flocculation: fluid dynamics and chemistry. Journal of American Water Works Association, 82(11), 56–73.
Hogg, R. (2000). Flocculation and dewatering. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 58, 223–236.
Hundt, T. R., & O’Melia, C. R. (1988). Aluminum–fulvic acid interactions: mechanisms and applications. Journal of American Water Works Association, 80(4), 176–186.
Jang, J. S. R. (1993). ANFIS Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685.
Jang, J. S. R., & Gulley, N. (1996). Fuzzy logic toolbox: Reference manual. Natick: The Mathworks Inc.
Johnson, P. N., & Amirtharajah, A. (1983). Ferric chloride and alum as single and dual coagulants. Journal of American Water Works Association, 75, 232–239.
Joo, D. S., Choi, D. J., & Park, H. (2000). The effects of data preprocessing in the determination of coagulant dosing rate. Water Research, 34(13), 3295–3302
Kang, L. S., & Cleasby, J. L. (1995). Temperature effects on flocculation kinetics using Fe(III) coagulant. Journal of Environmental Engineering, ASCE, 121(12), 893–910.
Letterman, R. D., Amirtharajah, A., & O’Melia, C. R. (1999). Coagulation and flocculation. In R. D. Letterman (Ed.), Water quality and treatment (pp. 6.1–6.66). New York: McGraw-Hill (Chapter 6)
Maier, H. R., Morgan, N., & Chow, C. W. K. (2004). Use of artificial neural networks for predicting optimal alum doses and treated water quality parameters. Environmental Modeling and Software, 19, 485–494.
Mamdani, E. H. (1976). Advances in the linguistic synthesis of fuzzy controllers. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 8, 669–678.
MathWorks, Inc. (2005). Matlab Programming, available at http://www.mathworks.com.
O’Melia, C. R. (1972). Coagulation and flocculation. In W. J. Weber Jr. (Ed.), Physicochemical processes for water quality control. New York: Wiley.
Pernitsky, D. J., & Edzwald, J. K. (2003). Solubility of polyaluminium coagulants. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology. AQUA, 52(6), 395–406.
Pernitsky, D. J., & Edzwald, J. K. (2006). Selection of alum and polyaluminium coagulants. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology. AQUA, 55(2), 121–141.
Prathumratana, L., Sthiannopkao, S., & Kim, K. W. (2008). The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the lower Mekong River. Environment International, 34, 860–866.
Randtke, S. J. (1988). Organic contaminant removal by coagulation and related process combinations. Journal of American Water Works Association, 80(5), 40–56.
Stumm, W., & O’Melia, C. R. (1968). Stoichiometry of coagulation. Journal of American Water Works Association, 60, 514.
Sugeno, M., & Kang, G. T. (1988). Structure identification of fuzzy model. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 28, 15–33.
Takagi, T., & Sugeno, M. (1985). Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to Modeling and control. IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 15, 116–132.11.
Tessem, B., & Davidsen, P. I. (1994). Fuzzy system dynamics: an approach to vague and qualitative variables in simulation. System Dynamics Review, 10, 49–62
Van Benschoten, J. E., & Edzwald, J. K. (1990). Chemical aspects of coagulation using aluminium salts-II. Coagulation of fulvic acid using alum and polyalurninum chloride. Water Research, 24(12), 1527–1535.
Van Leeuwen, J., Schell, H., Berger, M., Drikas, M., Bursill, D., Chow, C., & Clasen, J. (1997). Comparison of coagulant doses determined using a charge titration unit with a jar test procedure for eight German surface waters. Journal of Water Science Research and Technology. AQUA, 46(5), 261–273.
Van Leeuwen, J., Chow, C. W. K., Bursill, D., & Drikas, M. (1999). Empirical mathematical models and artificial neural networks for the determination of alum doses for treatment of southern Australian surface waters. Journal of Water Science Research and Technology. AQUA, 48(3), 115–127.
Weishaar, J. L., Aiken, G. R., Bergamaschi, B. A., Fram, M. S., Fujii, R., & Mopper, K. (2003). Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 4702–4708.
Wu, G. D., & Lo, S. L. (2008). Predicting real-time coagulant dosage in water treatment by artificial neural networks and adaptive network based fuzzy inference system. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 21(8), 1189–1195.
Yager, R. R., & Filev, D. P. (1994). Approximate clustering via the mountain method. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 24(8), 1279–1284.
Yu, R. F., Kang, S. F., Liaw, S. L., & Chen, M. C. (2000). Application of artificial neural network to control the coagulant dosing in water treatment plant. Water Science and Technology, 42(3–4), 403–408.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8, 338–353
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heddam, S., Bermad, A. & Dechemi, N. ANFIS-based modelling for coagulant dosage in drinking water treatment plant: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 184, 1953–1971 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2091-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2091-x