Abstract
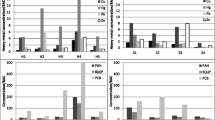
Increasing urbanization and changes in land use in Langat river basin lead to adverse impacts on the environment compartment. One of the major challenges is in identifying sources of organic contaminants. This study presented the application of selected chemometric techniques: cluster analysis (CA), discriminant analysis (DA), and principal component analysis (PCA) to classify the pollution sources in Langat river basin based on the analysis of water and sediment samples collected from 24 stations, monitored for 14 organic contaminants from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), sterols, and pesticides groups. The CA and DA enabled to group 24 monitoring sites into three groups of pollution source (industry and urban socioeconomic, agricultural activity, and urban/domestic sewage) with five major discriminating variables: naphthalene, pyrene, benzo[a]pyrene, coprostanol, and cholesterol. PCA analysis, applied to water data sets, resulted in four latent factors explaining 79.0% of the total variance while sediment samples gave five latent factors with 77.6% explained variance. The varifactors (VFs) obtained from PCA indicated that sterols (coprostanol, cholesterol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, and stigmastanol) are strongly correlated to domestic and urban sewage, PAHs (naphthalene, acenaphthene, pyrene, benzo[a]anthracene, and benzo[a]pyrene) from industrial and urban activities and chlorpyrifos correlated to samples nearby agricultural sites. The results demonstrated that chemometric techniques can be used for rapid assessment of water and sediment contaminations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Wahab, S. A., Bakheit, C. S., & Al-Alawi, S. M. (2005). Principal component and multiple regression analysis in modelling of ground-level ozone and factors affecting its concentrations. Environmental Modelling & Software, 20, 1263–1271.
Astel, A., Tsakovski, S., Barbieri, P., & Simeonov, V. (2007). Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Water Research, 41(19), 4566–4578.
Boruvka, L., Vecek, O., & Jenlika (2005). Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soil. Geoderma, 128, 289–300.
Brodnjak-Voncina, D., Dobcnik, D., Novic, M., & Zupan, J. (2002). Chemometrics characterisation of the quality of river water. Analytica Chimica Acta, 462, 87–100.
Brown, S. D., Skogerboe, R. K., & Kowalski, B. R. (1980). Pattern recognition assessment of water quality data: Coal strip mine drainage. Chemosphere, 9, 265–276.
Carreira, R. S., Wagener, A. L. R., & Readman, J. W. (2004). Sterols as markers of sewage contamination in a tropical urban estuary (Guanabara Bay, Brazil): Space–time variations. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 60, 587–598.
Chan, K.-H., Lam, M. H. W., Yeung, H.-Y., & Chiu, T. K. T. (1998). Application of sedimentary fecal stanol and sterols in tracing sewage pollution in costal waters. Water Research, 32(1), 225–235.
Department of Environmental Malaysia, DOE (2006). Malaysia environmental quality report 2006 in Impak, Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Science. Technology and Environment, 3, 1–16.
Gilli, G., Rovere, R., Traversi, D., Schiliro, T., & Pignata, C. (2006). Faecal sterols determination in wastewater and surface water. Journal of Chromatography B, 843, 120–124.
Goncalves, C., Carvalho, J. J., Azenha, M. A., & Alpendurada, M. F. (2006). Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of pesticide residues in soil by means of central composite design and analysis by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1110, 6–14.
Isobe, K. O., Tarao, M., Zakaria, M., Chiem, N. H., Minhle, Y., & Takada, H. (2002). Quantitative application of fecal sterols using gas-chromatography–mass spectrometry to investigate fecal pollution in tropical water: Western Malaysia and Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 4497–4507.
Isobe, K. O., Tarao, M., Chiem, N. H., & Minh, L. Y. (2004). Effect of environmental factors on the relationship between concentrations of coprostanol and fecal indicator bacteria in tropical (Mekong Delta) and temperate (Tokyo) freshwaters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(2), 814–821.
Juahir, H. (2008). Water Quality Data Analysis and Modeling at Langat River Basin. PhD dissertation, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Juahir, H., Zain, S. M., Khan, R. A., Yusoff, M. K., Mokhtar, M. B., & Toriman, M. E. (2009). Using chemometrics in assessing Langat River water quality and designing a cost-effective water sampling strategy. Maejo International Journal of Science and Technology, 3(01), 26–42.
Khalili, N. R., Scheff, P. A., & Holsen, T. M. (1995). PAHs source finger prints for coke ovens, diesel and gasoline engines, highway tunnels and wood combustion emm. Atmospheric Environment, 29, 533–542.
Kowalkowski, T., Zbytniewski, R., Szpejna, J., & Buszewski, B. (2006). Application of chemometrics in river water classification. Water Research, 40, 744–752.
Leeming, R., & Nichols, P. (1996). Concentrations of coprostanol that correspond to existing bacterial indicator guideline limits. Water Research, 30(12), 2997–3006.
Li, J., Zhang, G., Li, X. D., Qi, S. H., Liu, G. Q., & Peng, X. Z. (2006). Source seasonality of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a subtropical city, Guangzhou, South China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 145–155.
Mohamed, A. F., Wan Yaacob, W. Z., Taha, M. R., & Shamsudin, A. R. (2009). Groundwater and soil vulnerability in the Langat Basin Malaysia. European Journal of Scientific Research, 27(4), 628–635.
Mokhtar, M., Mohamed, A. F., & Idrus, S. (2002). Preliminary survey of groundwater resources in the Langat basin: Towards a sustainable healthy ecosystem. In M. Mokhtar, S. Idrus, A. F. Mohamed, A. H. A. Shah, S. Aziz & A. G. Aziz (Eds.), Proceedings Langat basin research symposium 2001. Institute for Environmental and Development, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi.
Mudge, S. M., & Seguel, C. G. (1999). Organic contamination of San Vicente Bay, Chile. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38(11), 1011–1021.
Omar, N. Y. M. J., Abas, M. R. B., Ketuly, K. A., & Tahir, N. M. (2002). Concentrations of PAHs in atmospheric particles (PM-10) and roadside soil particles collected in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 247–254.
Osman, R., Saim, N., & Abdullah, M. P. (2008). Selective accelerated solvent extraction for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sterols from soil. The Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 12(2), 352–356.
Osman, R., Saim, N., & Abdullah, M. P. (2009). Simultaneous extraction of organic compounds with a wide polarity range in water using solid phase extraction technique. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 13(3), 7–18.
Preuss, R., Angerer, J., & Drexler, H. (2003). Naphthalene—An environmental and occupational toxicant. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 76, 556–576.
Reimann, C., & Filzmoser, P. (2000). Normal and lognormal data distribution in geochemistry: Death of a myth. Consequences for the statistical treatment of geochemical and environmental data. Environmental Geology, 39, 1001–1014.
Rogge, W. F., Hildemann, L. M., Mazurek, M. A., Cass, G. R., & Simoneit, B. R. T. (1998). Sources of fine organic aerosol. 9. Pine, oak, and synthetic log combustion in residential fireplaces. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 13–22.
Saim, N., Osman, R., Spian, D. R. S. A., Jaafar, M. Z., Juahir, H., Abdullah, M. P., et al. (2009). Chemometric approach to validating faecal sterols as source tracer for faecal contamination in water. Water Research, 43, 5023–5030.
Schwarzbauer, J., Littke, R., & Weigelt, V. (2000). Identification of specific organic contaminants for estimating the contribution of the Elbe river to the pollution of the German Bight. Organic Geochemistry, 31, 1713–1731.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji River basin Japan. Environmental Modelling and Software, 22(4), 464–475.
Simeonov, V., Einax, J. W., Stanimirova, I., & Kraft, J. (2002). Environmetric modeling and interpretation of river water monitoring data. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 374(5), 898–905.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)-a case study. Water Research, 38, 3980–3992.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Singh, V. K., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2005). Chemometric analysis of groundwater quality data of alluvial aquifer of Gangetic plain, North India. Analytica Chimica Acta, 550, 82–91.
Tahir, N. M., Seng, T. H., Ariffin, M., Suratman, S., & Hoe, L. S. (2006). Concentration and distribution of PAHs in soils affected by grassland fire. The Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 10(1), 41–46.
Takada, H., & Eganhouse, R. P. (1998). Molecular markers of anthropogenic waste. In R. A. Meyer (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Environmental Analysis and Remediation (pp. 2883–2940). New York: Wiley.
Tauler, R., Peré-Trepat, E., Lacorte, S., & Barceló, D. (2004). Chemometrics Modelling of Environmental Data. Department of Environmental Chemistry, Institute of Chemical and Environmental Research IIQAB-CSIC, Spain.
University Malaya Consultancy Unit (UPUM) (2002). Program Pencegahan Pencemaran dan Peningkatan Kualiti Air Sungai Lang at; Final Draft Report.
Vega, M., Pardom, R., Barrado, E., & Ddebaan, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32(12), 3581–3592.
Zhang, H. B., Wong, Y. M. L. H., Zhao, Q. G., & Zhang, G. L. (2006). Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils. Environmental Pollution, 141, 107–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osman, R., Saim, N., Juahir, H. et al. Chemometric application in identifying sources of organic contaminants in Langat river basin. Environ Monit Assess 184, 1001–1014 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2016-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2016-8