Abstract
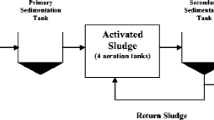
The quality of sewage-sludge samples obtained in Kolkata region was evaluated. Both sewage water and sludge components were analyzed for a number of physico-chemical, microbiological parameters using standard laboratory procedures, some heavy metals by AAS method and pesticide contents by GC method. Some of the physical and chemical constituents of the samples are within the allowable levels while the rest are not. The samples are rich in nutrients and have suitable pH for agricultural uses. In terms of Electrical Conductivity and Sodium Adsorption Ratio, sewage water is not suitable for irrigation. Fecal and coliform bacterial population is high in all samples. Pesticide and heavy metals in some places are alarming. So sewage-sludge produced in Kolkata cannot be used for agricultural purpose without any treatment. Thus proper care, maintenance, treatment and disposal of sewage water and sludge are most vital and should be the prime thrust for the nation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. (20th ed.). Washington, D.C.: APHA, AWWA.
Bhatia, A., Pathad, H., & Joshi, H. C. (2001). Use of sewage as a source of plant nutrient. Fertilizer News, 46(3), 55–58, 61–64.
Bindra, O. S. (1972). Pesticidal pollution of water. Pesticides, 6, 77–82.
Brown, A. W. A. (1979). Ecology of pesticides. New York: Wiley, 174 pp.
Disha (1996). A rapid assessment survey of the health and environmental impacts of solid waste recycling, final report (p. 42). Calcutta: Direct Initiative for Social and Health Action.
Eichelberger, J. W., & Lichtenberg, J. J. (1971). Persistence of pesticides in river water. Environmental Science and Technology, 5, 541–544. doi:10.1021/es60053a002.
EIP (1996). Sustaining Calcutta: Present status report of the urban people’s environment (p. 217). Calcutta: Environmental Improvement Program for Calcutta, CMDA.
EPA (1979). Methods for chemical analysis of waters, method 353.3. Washington, D.C.: US EPA.
Gupta, S. K., Mitra, A., & Adhikari, S. (1990). Post irrigation effect of Calcutta sewage effluents on soil and vegetation. In Proc. Natn. Symp. on Protection of Environment of City Water Fronts. New Delhi: Central Water Commission. (Vol. IV, pp. 7–13).
Jarvie, H. P., Whitton, B. A., & Neal, C. (1998). Nitrogen and phosphorus in east coast British Rivers; speciation, sources and biological significance. The Science of the Total Environment, 210–211, 79–109. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00109-0.
Joshi, H. C. (1992). Environmental mediated stress on flood plain lakes. II- Pesticides and agricultural run-off. In Y. S. Yadav & V. V. Suguman (Eds.), Compendium of FAO sponsored foodplain fish mgmt. Central Inland Capture Fisheries Institute Barrackpore.
Kole, R. K., & Bagchi, M. M. (1995). Pesticide residues in the aquatic environment and their possible ecological hazards. Journal of the Inland Fisheries Society of India, 27, 79–89.
Mcintosh, A. C., Yniguez, C. E. (Eds.) (1997). Second water utilities data book—Asian and Pacific region. Manila: ADB.
Mitra, A., Adhikari, S., & Gupta, S. K. (1998). Pollution metal content of vegetables irrigated with sewage water. J. Indian Soc. Sci, 46(1), 153–155.
Mitra, A., & Gupta, S. K. (2000). Assessment of the quality of the raw and treated sewage effluents from some selected treatment plants within the Calcutta Metropolitan area and potential health risk from their recycling. Pollution Research, 19(4), 677–683.
Mohapatra, S. P., Gajbhiye, V. T., Agnihotri, N. P., Manju, R., & Raina, M. (1995). Insecticide pollution in Indian rivers. The Environmentalist, 15, 41–44. doi:10.1007/BF01888888.
Rovedatti, M. G., Castane, P. M., Topalian, M. L., & Salibian, A. (2001). Monitoring of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides in water of the Reconquista River (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Water Research Oxford, 35, 3457–3461. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00058-6.
Simeonov, V., Simeonova, P., & Tisitouridou, R. (2004). Chemometric quality assessment of surface waters: Two case studies. Chemical and Engineering Ecology, 11(6), 449–469.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zahariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A. et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northen Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00398-1.
WWAP (2003). “Water for People, Water for Life” The 1st UN world water development report. Paris: WWAP.
Vasu, K. (1996). Pollution of ground water and methods to minimise from environmental angle. In N. K. Roy (Ed.), Agrochemicals and sustainable agriculture (p. 238). New Delhi: APC.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrado, E., & Deban, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32, 3581–3592. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00138-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Purkait, S., Ganguly, M., Aktar, M.W. et al. Impact assessment of various parameters polluting Ganga water in Kolkata Region: a study for quality evaluation and environmental implication. Environ Monit Assess 155, 443–454 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0447-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0447-7