Abstract
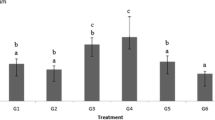
Combining genotoxicity/mutagenicity tests and physico-chemical methodologies can be useful for determining the potential genotoxic contaminants in soil samples. The aim of our study was to evaluate the genotoxicity of soil by applying an integrated physico-chemical-biological approach. Soil samples were collected at six sampling points in a Slovenian industrial and agricultural region where contamination by heavy metals and sulphur dioxide (SO2) are primarily caused by a nearby power plant. The in vitro alkaline version of the comet assay on water soil leachates was performed with Caco-2 and HepG2 cells. A parallel genotoxicity evaluation of the samples was performed by Ames test using Salmonella typhimurium and the Tradescantia micronucleus test. Pedological analyses, heavy metal content determination, and different physico-chemical analyses, were also performed utilizing standard methodology. Water leachates of soil samples were prepared according to standard methods. Since only a battery of biotests with prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms or cells can accurately estimate the effects of (geno)toxicants in soil samples and water soil leachates, a combination of three bioassays, with cells or organisms belonging to different trophic levels, was used. Genotoxicity of all six water soil leachates was proven by the comet assay on both human cell lines, however no positive results were detected by bacterial assay, Ames test. The Tradescantia micronucleus assay showed increase in micronuclei formation for three samples. According to these results we can assume that the comet assay was the most sensitive assay, followed by the micronucleus test. The Ames test does not appear to be sensitive enough for water soil leachates genotoxicity evaluations where heavy metal contamination is anticipated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu, A., Mahat, J., Gupta, S., & Giri, A. K. (2001). Genetic toxicology of a paradoxical human carcinogen arsenic: A review. Mutation Research, 488, 17–194.
Békaert, C., Ferrier, V., Marty, J., Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A., Bispo, A., Jourdain, M. J., et al. (2002). Evaluation of toxic and genotoxic potential of stabilized industrial waste and contaminated soils. Waste Management, 22, 241–247.
Békaert, C., Rast, C., Ferrier, V., Bispo, A., Jourdain, M. J., & Vasseur, P. (1999). Use of in vitro (Ames and Mutatox tests) assays to assess the genotoxicity of leachates from contaminated soil. Organic Geochemistry, 30, 953–962.
Bispo, A., Jourdain, M. J., & Jauzein, M. (1999). Toxicity and genotoxicity of industrial soils polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Organic Geochemistry, 30, 947–952.
Cavas, T., & Ergene-Gözükara, S. (2005). Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in Oreochromis niloticus following exposure to petroleum refinery and chromium processing plant effluents. Aquatic Toxicology, 74, 264–271.
Chenon, P., Gauthier, L., Loubieres, P., Severac, A., & Delpoux, M. (2003). Evaluation of the genotoxic and teratogenic potential of a municipal sludge and sludge-amended soil using the amphibian Xenopus laevis and the tobacco: Nicotina tabacum L. var xanthi Dulieu. Science of the Total Environment, 301, 139–150.
Cottele, S., Masfaraud, J.-F., & Ferard, J.-F. (1999). Assessment of the genotoxicity of contaminated soil with the Allium/Vicia-micronucleus and the Tradescantia-micronucleus assays. Mutation Research Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 426, 167–171.
Crebelli, R., Conti, L., Monarca, S., Feretti, D., Zerbini, I., Zani, C., et al. (2005). Genotoxicity of the disinfection by-products resulting from paracetic acid- or hypochlorite-disinfected sewage wastewater. Water Research, 39, 1105–1113.
Duthie, S. J., Johnson, W., & Dobson, V. L. (1997). The effect of dietary flavonoids on DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidised pyrimidines) and growth in human cells. Mutation Research, 340, 141–151.
Ehrlichmann, H., Dott, W., & Eisentraeger, A. (2000). Assessment of the water-extractable genotoxic potential of soil samples from contaminated sites. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 46, 73–80.
Ejchart, A., & Sadlej-Sosnowska, N. (2003). Statistical evaluation and comparison of comet assay results. Mutation Research. Genetic Toxicology, 534, 85–92.
Duthie, S. J., & Collins, A. (1997). The influence of cell growth detoxifying enzymes and DNA repair on hydrogen peroxide-mediated DNA damage (measured using the comet assay) in human cells. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 4, 717–724.
Fatur, T., Tusek, M., Falnoga, I., Scancar, J., Lah, T. T., & Filipic, M. (2002). DNA damage and metallothionein synthesis in human hepatoma cells (HepG2) exposed to cadmium. Food & Chemical Toxicology, 40, 1069–1076.
Fent, K. (2004). Ecotoxicological effects at contaminated sites. Toxicology, 20, 22–240.
Gatehouse, D. G., Wilcox, P., Forster, R., Rowland, I. R., & Callander, R. D. (1990). In D. J. Kirkland (Ed.), Bacterial mutation assays UKEM recommended procedures guidelines for mutagenicity testing (pp. 13–59). Massachusetts: Cambridge University Press.
Gauthier, L., Van der Gaag, M. A., Haridon, J. L., Ferrier, V., & Fernandez, M. (1993). In vivo detection of waste water and industrial effluent genotoxicity: Use of the Newt Micronucleus test (Jaylet test). Science of the Total Environment, 138, 249–269.
Gelman, A., Carlin, J. C., Stern, H., & Rubin, D. B. (2004). Bayesian data analysis (2nd ed., pp. 58488–388). New York: Chapman & Hall.
Giller, K. E., Witter, E., & McGrath, S. P. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 30, 1389–1414.
Gichner, T., & Velemínský, J. (1999). Monitoring the genotoxicity of soil extracts from two heavily polluted sites in Prague using the Tradescantia stamen hair and micronucleus (MNC) assays. Mutation Research Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 426, 163–166.
Glasenčnik, E., Ribarič Lasnik, C., Müller, M., Grill. D., & Batič, F. (2002). Impact of air pollution on genetic material of the shallot (Allium cepa L var ascalanicum) exposed in the vicinity of major Slovene local emission sources in 1999. Phyton, 42, 237–250.
Glatt, H., Gemperlein, I., Setiabudi, F., Platt, K. L., & Oesch, F. (1990). Expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes in propagatable cell cultures and induction of micronuclei by 13 compounds. Mutagenesis, 5, 241–249.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (1997). Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Bacteria reverse mutation test guideline 471. Paris, France: OECD
Hartmann, A., & Speit, G. (1994). Comparative investigations of the genotoxic effects of metals in the single cells gel (SCGE) assay and their sister chromatide (SCE) test. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 23, 299–305.
Ivask, A., François, M., Kahru, A., Dubourguier, H.-C., Virta, M., & Douay, F. (2004). Recombinant luminiscent bacterial sensors for the measurement of bioavailability of cadmium and lead in soils polluted by metal smelter. Chemosphere, 55, 147–156.
Kim, I.-Y., & Hyun, C.-K. (2006). Comparative evaluation of the alkaline comet assay with the micronucleus test for genotoxicity monitoring using aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 288–297.
Knasmüller, S., Gottmann, E., Steinkellner, H., Fomin, A., Pickl, C., Paschke, A., et al. (1998). Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassays. Mutation Research, 420, 37–48.
Knasmüller, S., Mersch-Sundermann, V., Kevekordes, S., Darroudi, F., Huber, W. W., Hoelzl, C., Bichler, J., & Majer, B. J. (2004). Use of human-derived liver cell lines for the detection of environmental and dietary genotoxicants: Current state of knowledge. Toxicology, 198, 315–328.
Knasmüller, S., Uhl, M., Gottmann, E., Hölzl, C., & Majer, B. J. (2003). The Tradescantia micronucleus bioassay. In J. Maluszynska & M. Plewa (Eds.), Bioassays in Plant cells for improvement of Ecosystem and Human Health (pp. 95–106). Katowice: Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Śląskiego
Kugonič, N., Pokorny, B., & Šešerko, M. (2004). Pollution of garden soils and vegetables in the Šalek Valley. Acta Biologica Slovenica, 1, 21–25.
Kugonič N., & Stropnik M. (2004). Heavy metal contents in agricultural soil and plants in Šaleška valley (p. 165). Final Research Report, Erico Velenje, Slovenija.
Lah, B., Zinko, B., Narat, M., & Marinsek-Logar, R. (2005a). Monitoring of genotoxicity in drinking water using in vitro comet assay and Ames test. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 432, 139–146.
Lah, B., Zinko, B., Tisler, T., & Marinsek-Logar, R. (2005b). Genotoxicity detection in drinking water by Ames test Zimmermann test and Comet assay. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 523, 341–348.
Levina, A., & Lay, P. A. (2005). Mechanistic studies of relevance to the biological activities of chromium. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 249, 281–298.
Liu, W., Zhou, Q.-X., Li, P.-J., Sun, T.-H., Yang, Y.-S., & Xiong, X.-Z. (2003). 124-trichlorobenzene induction of chromosomal aberrations and cell division of root-tip cells in Vicia faba seedlings. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 71, 689–697.
Loska, K., Weichula, D., & Korus, I. (2004). Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environment International, 30, 59–165.
Lovell, D. P., Thomas, G., & Dubow, R. (1999). Issues related to the experimental design and subsequent statistical analysis of in vivo and in vitro comet studies. Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis, and Mutagenesis, 19, 109–119.
Majer, B. J., Tscherko, D., Paschke, A., Wennrich, R., Kundi, M., Kandeler, E., et al. (2002). Effects of heavy metal contamination of soils on micronucleus induction in Tradescantia and on microbial enzyme activities: A comparative investigation. Mutation Research, 515, 111–124.
Ma, T. H., Cabrera, G. L., Cebulska-Wasilewska, A., Chen, R., Loarca, F., Vandenberg, A. L., et al. (1994). Tradescantia stamen hair mutation bioassay. Mutation Research, 310, 211–220.
Monarca, S., Donatella, F., Zerbini, I., Alberti, A., Zani, C., Sergio, R., et al. (2002). Soil contamination detected using bacterial and plant mutagenicity tests and chemical analyses. Environmental Research Agenda, 88, 64–69.
Maron, D. M., & Ames, B. N. (1983). Revised methods for the salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutation Research, 113, 173–215.
Martin, F. L., Piearce, T. G., Hewer, A., Phillips, D. H., & Semple, K. T. (2005). A biomarker model of sublethal genotoxicity (DNA single-strand breaks and adducts) using the sentinel organism Aporrectodea longa in spiked soil. Environmental Pollution, 138, 307–315.
Mouchet, F., Gauthier, L., Mailhes, C., Jourdain, M. J., Ferrier, V., Triffault, G., et al. (2006). Biomonitoring of the genotoxic potential of aqueous extracts of soils and bottom ash resulting from municipal solid waste incineration using the comet and micronucleus tests on amphibian (Xenopus laevis) larave and bacterial assays (Mutatox® and Ames tests). Science of the Total Environment, 355, 232–246.
Official Gazette (1996). Uredba o vnosu nevarnih snovi in rastlinskih hranil v tla. Uradni list Republike Slovenije, 68, 5769.
Olive, P. L., Banath, P. J., & Durand, R. E. (1996). Heterogeneity in radiation-induced DNA damage and repair in tumor and normal cells measured using the »comet« assay. Radiation Research, 112, 86–94.
Patra, M., Bhowmik, N., Bandopadhyay, B., & Sharma, A. (2004). Comparison of mercury lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 52, 199–223.
R Development Core Team (2005). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org.
Radetski, C. M., Ferrari, B., Cotelle, S., Masfaraud, J.-F., & Ferard, J. F. (2004). Evaluation of the genotoxic mutagenic and oxidant stress potentials of municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash leachates. Science of the Total Environment, 333, 209–216.
Rudolf, E., Cervinka, M., Cerman, J., & Schroterova, L. (2005). Hexavalent chromium disrupts the actin cytoskeleton and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human fibroblasts. Toxicology In Vitro, 19, 713–723.
Sauvant, M. P., Pepin, D., Bohatier, J., & Grolierere, C. A. (1995). Comparison of six bioassays for the assessing in vitro acute toxicity and structure-activity relationships for vinyl chloride monomer its main metabolites and derivatives. Science of the Total Environment, 172, 79–92.
Sargeant, A., & Goswami, T. (2006). Hip implants-Paper VI-Ion concentrations. Materials & Design, 27, 287–307.
Singh, J., Carlisle, D. L., Pritchard, D. E., & Patierno, S. R. (1998). Chromium-induced genotoxicity and apoptosis: Relationship to chromium carcinogenesis (review). Oncology Reports, 5, 1307–1318.
SIST ISO 11464 (1994). Soil quality pre-treatment of samples for physico-chemical analyses. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST ISO 5666 (1996a). Water quality – Determination of mercury. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST ISO 10523 (1996). Water quality – Determination of pH. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST ISO 11083 (1996). Water quality – Determination of chromium (VI)-spectrometric method using 15-diphenylcarbazide. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST ISO 10381 (1996). Soil quality-sampling Part 6. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST EN ISO 10304-2 (1998). Water quality – Determination of dissolved anions by liquid chromatography of ions Part 2: Determination of bromide chloride nitrate nitrite orthophosphate and sulphate in waste water. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST DIN 38406-29 (2000). German standard methods for the examination of water wastewater and sludge-Cations (group E) – Part 29: Determination of highly volatile halogenated hydrocarbons – Gas-chromatographic methods. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization.
SIST ISO 8245 (2000). Water quality Guidelines for the determination of total organic carbon TOC and dissolved organic carbon DOC. Geneve, Switzerland: International organization for standardization.
Spiegelhalter, D. J., Thomas, A., Best, N. G., Gilks, W. R., & Lunn, D. (2003). BUGS: Bayesian inference using Gibbs sampling. Cambridge, England: MRC Biostatistics Unit. http://www.mrc-bsu.cam.ac.uk/bugs/.
Sturtz, S., Ligges, U., & Gelman, A. (2005). R2WinBUGS: A package for running WinBUGS from R. Journal of Statistical Software, 12, 3, 1–16. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v12/i03.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Foxx, D. N., Ishaque, A. B., & Shen, E. (2004). Lead-induced cytotoxicity and transcriptional activation of stress genes in human liver carcinoma Hep-G2) cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 255, 161–170.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1996). Health effects tests guidelines: OPPTS 8705265. The Salmonella typhimurium reverse mutation assay. EPA712-C-96–219. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Watanabe, T., & Hirayama, T. (2001). Genotoxicity of soil. Journal of Health Science, 47, 433–438.
White, P. (2002). The genotoxicity of priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in complex mixtures. Mutation Research, 515, 85–98.
White, P. A., & Claxton, L. D. (2004). Mutagens in contaminated soil: A review. Mutation Research, 567, 227–345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lah, B., Vidic, T., Glasencnik, E. et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of water soil leachates by Ames test, comet assay, and preliminary Tradescantia micronucleus assay. Environ Monit Assess 139, 107–118 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9819-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9819-7