Abstract
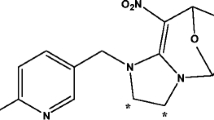
Tebufenozide is an insect growth regulator used to control pest caterpillar populations. As an ecdysone agonist, tebufenozide is equally toxic to several non-target arthropod species, binding the receptor sites of the molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone and causing premature and lethal molting. In this study, the toxic effects of tebufenozide were assessed, and biomarkers of tebufenozide exposure were identified, in the non-target soil collembolan species Yuukianura szeptyckii. Adult mortality and reproduction in Y. szeptyckii exposed to tebufenozide were evaluated after 28 days of exposure and were used to calculate LC50 and EC50, respectively. The LC50 could not be determined, because the mortality values observed were below 50%, even when exposed to the highest concentration tested (700 mg/kg), but the EC50 was 95.5 mg/kg. Effects on hatching and molting rates were evaluated using compressed soils, to prevent experimental individuals from burrowing; thus, all eggs and exuviae were detectable on the soil surface. Significant negative effects of tebufenozide exposure on the hatching rate and molting frequency were observed only at the highest concentration tested (700 mg/kg). Proteomic analyses were conducted to detect the cryptic effects of toxicity in adult collembolans exposed for 28 days to 43.8 mg/kg of tebufenozide, a concentration at which no toxicity effects were observed. The production rates of two ribosomal proteins, as well as proteins involved in apoptotic cell signaling, were higher in collembolans exposed to tebufenozide than in the control group. However, the production of proteins involved in glycolysis and energy production was downregulated. Therefore, the ecotoxicoproteomic approach is a promising tool for measuring the cryptic effects of tebufenozide exposure in Y. szeptyckii at low concentrations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison, J. A. (1996). Safety testing of tebufenozide, a new molt-inducing insecticide, for effects on nontarget forest soil invertebrates. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 33(1), 55–61.
Bauer, H., Gromer, S., Urbani, A., Schnölzer, M., Schirmer, R. H., & Müller, H. M. (2003). Thioredoxin reductase from the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. European Journal of Biochemistry, 270(21), 4272–4281.
Bell, C. H. (2014). Pest control of stored food products: Insects and mites. In H. L. M. Leileveld, J. T. Holah & D. Napper (Eds.), Hygiene in food processing (pp. 494–538). Oxford: Woodhead Publishing.
Beuzelin, J. M., Akbar, W., Mészáros, A., Reay-Jones, F. P. F., & Reagan, T. E. (2010). Field assessment of novaluron for sugarcane borer, Diatraea saccharalis (F.) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), management in Louisiana sugarcane. Crop Protection, 29(10), 1168–1176.
Bridgham, J. T., Eick, G. N., Larroux, C., Deshpande, K., Harms, M. J., Gauthier, M. E. A., et al. (2010). Protein evolution by molecular tinkering: Diversification of the nuclear receptor superfamily from a ligand-dependent ancestor. PLoS Biology, 8(10), e1000497.
Campiche, S., Becker-van Slooten, K., Ridreau, C., & Tarradellas, J. (2006). Effects of insect growth regulators on the nontarget soil arthropod Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 63(2), 216–225.
Cao, G., & Han, Z. (2006). Tebufenozide resistance selected in Plutella xylostella and its cross-resistance and fitness cost. Pest Management Science, 62(8), 746–751.
Connon, R. E., Geist, J., Pfeiff, J., Loguinov, A. V., D’Abronzo, L. S., Wintz, H., et al. (2009). Linking mechanistic and behavioral responses to sublethal esfenvalerate exposure in the endangered delta smelt; Hypomesus transpacificus (Fam. Osmeridae). BMC Genomics, 10(1), 608.
Darvas, B., & Polgar, L. A. (1998). Novel-type insecticides: Specificity and effects on non-target organisms. In I. Ishaaya & D. Degheele (Eds.), Insecticides with novel modes of action (pp. 188–259). Berlin: Springer.
Dhadialla, T. S., Carlison, G. R., & Le, D. P. (1998). New insecticides with ecdysteroidal and juvenile hormone activity. Annual Review of Entomology, 43(1), 545–569.
Durkin, P. R., & Klotzabach, J. (2004). Control/eradication agents for the gypsy moth: Human health and ecological risk assessment for tebufenozide (Mimic) (final report). New York.
EU. (1991). Council Directive 91/414/EEC of 15 July 1991 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market. Official Journal of the European Communities, L230, 1–32.
Fountain, M. T., & Hopkin, S. P. (2005). Folsomia candida (Collembola): A “standard” soil arthropod. Annual Review of Entomology, 50, 201–222.
Frampton, G. K., Jänsch, S., Scott-Fordsmand, J. J., Römbke, J., & Van den Brink, P. J. (2006). Effects of pesticides on soil invertebrates in laboratory studies: A review and analysis using species sensitivity distributions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(9), 2480–2489.
Haanstra, L., Doelman, P., & Voshaar, J. H. O. (1985). The use of sigmoidal dose response curves in soil ecotoxicological research. Plant and Soil, 84(2), 293–297.
Hahn, T., Liess, M., & Schulz, R. (2001). Effects of the hormone mimetic insecticide tebufenozide on Chironomus riparius larvae in two different exposure setups. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 49(2), 171–178.
Hook, S. E., Gallagher, E. P., & Batley, G. E. (2014). The role of biomarkers in the assessment of aquatic ecosystem health. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 10(3), 327–341.
Hsu, A. C. T., Fujimoto, T. T., & Dhadialla, T. S. (1991). Structure-activity study and conformational analysis of RH-5992, the first commercialized non-steroidal ecdysone agonist. In P. A. Hedin (Ed.), Phytochemicals for pest control, ACS Symposium Series 658 (pp. 206–219). Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
ISO. (1999). Soil quality—Inhibition of reproduction of Collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil pollutants. ISO 11267, International Standardization Organization, Geneva.
Jegede, O. O., Owojori, O. J., & Römbke, J. (2017). Temperature influences the toxicity of deltamethrin, chlorpyrifos and dimethoate to the predatory mite Hypoaspis aculeifer (Acari) and the springtail Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 140, 214–221.
Knight, A. L. (2000). Tebufenozide targeted against codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) adults, eggs, and larvae. Journal of Economic Entomology, 93(6), 1760–1767.
Lee, R. F., & Singer, S. C. (1981). Responses of cytochromeP-450 systems in marine crab and polychaetes to organic pollutants. Aquatic Toxicology, 1(5–6), 355–365.
Lee, Y. S., Yang, N. H., Son, J., Kim, Y., Park, K. H., & Cho, K. (2016). Effects of temperature on development, molting, and population growth of Yuukianura szeptyckii Deharveng & Weiner, 1984 (Collembola: Neanuridae). Applied Soil Ecology, 108, 325–333.
Mari Mutt, J. A., & Soto-Adames, F. N. (1987). Molting, fecundity, and longevity in Willowsia jacobsoni (Collembola: Entomobryidae). Caribbean Journal of Science, 23, 298–304.
Oberlander, H., Silhacek, D. L., & Porcheron, P. (1995). Non-steroidal ecdysteroid agonists: tools for the study of hormonal action. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 28, 209–223.
OECD. (1984). OECD guideline for testing of chemicals no. 207. Earthworm acute toxicity test, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris.
OECD. (2008). OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. Collembola reproduction test, OECD Guideline No. 232, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris.
Pollet, D. K. (2008). Insecticide applications for 2007 sugarcane research annual progress report 2007 (pp. 137). Baton Rouge, LA: LSU AgCenter.
Retnakaran, A., Hiruma, K., Palli, S. R., & Riddiford, L. M. (1995). Molecular analysis of the mode of action of RH-5992, a lepidopteran-specific, non-steroidal ecdysteroid agonist. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 25(1), 109–117.
Roesijadi, G. (1980). Influence of copper on the clam Protothaca staminea: Effects on gills and occurrence of copper-binding proteins. The Biological Bulletin, 158(2), 233–247.
Römbke, J., Jänsch, S., Junker, T., Pohl, B., Scheffczyk, A., & Schallnaß, H. J. (2006). Improvement of the applicability of ecotoxicological tests with earthworms, springtails, and plants for the assessment of metals in natural soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(3), 776–787.
SAS Institute. (2011). SAS/IML 9.3 user’s guide. SAS Institute.
Schmidt, A., Endo, N., Rutledge, S. J., Vogel, R., Shinar, D., & Rodan, G. A. (1992). Identification of a new member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily that is activated by a peroxisome proliferator and fatty acids. Molecular Endocrinology, 6(10), 1634–1641.
Smagghe, G., Carton, B., Decombel, L., & Tirry, L. (2001). Significance of absorption, oxidation, and binding to toxicity of four ecdysone agonists in multi-resistant cotton leafworm. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 46(3), 127–139.
Smagghe, G., Gelman, D., & Tirry, L. (1999). In vivo and in vitro effects of tebufenozide and 20-hydroxyecdysone on chitin synthesis. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 41(1), 33–41.
Smit, C. E., & Van Gestel, C. A. (1998). Effects of soil type, prepercolation, and ageing on bioaccumulation and toxicity of zinc for the springtail Folsomia candida. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17(6), 1132–1141.
Son, J., Lee, S. E., Park, B. S., Jung, J., Park, H. S., Bang, J. Y., et al. (2011). Biomarker discovery and proteomic evaluation of cadmium toxicity on a collembolan species, Paronychiurus kimi (Lee). Proteomics, 11(11), 2294–2307.
Son, J., Lee, Y. S., Lee, S. E., Shin, K. I., & Cho, K. (2017). Bioavailability and toxicity of copper, manganese, and nickel in Paronychiurus kimi (Collembola), and biomarker discovery for their exposure. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72(1), 142–152.
Son, J., Mo, H. H., Yang, N. H., Shin, K. I., & Cho, K. (2009). Determination of Paronychiurus kimi (Collembola: Onychiuridae) age structures by head width measurements with reference to cadmium toxicity. Applied Soil Ecology, 43(1), 47–52.
Stegeman, J. J. (1978). Influence of environmental contamination on cytochrome P-450 mixed-function oxygenases in fish: Implications for recovery in the Wild Harbor Marsh. Journal of the Fisheries Board of Canada, 35(5), 668–674.
Sun, X. X., DeVine, T., Challagundla, K. B., & Dai, M. S. (2011). Interplay between ribosomal protein S27a and MDM2 protein in p53 activation in response to ribosomal stress. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 22730–22741.
Tomlin, C. D. S. (2006). A world compendium: The e-Pesticide manual (14th ed.). Alton: British Crop Protection Council.
Van Straalen, N. M., & Van Gestel, C. A. M. (1993). Soil invertebrates and microorganisms. In P. Calow (Ed.), Handbook of exotoxicology (Vol. 1, pp. 251–277). Oxford: Blackwell.
Wattenberg, L. W., Patterson, S., & Antonides, J. D. (2010). Chitin or chitin-like glycans as targets for late-term cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Prevention Research, 3(12), 1519–1522.
Zortéa, T., Segat, J. C., Maccari, A. P., Sousa, J. P., Da Silva, A. S., & Baretta, D. (2017). Toxicity of four veterinary pharmaceuticals on the survival and reproduction of Folsomia candida in tropical soils. Chemosphere, 173, 460–465.
Acknowledgements
This subject is supported by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as “Chemical Accident Prevention and Response Technology Development Project” (2016001970003) and National Research Foundation of Korea as “Prediction of soil invertebrate habitat fitness under climate change using fuzzy rule based model” (NRF-2016R1A2B4015651).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YS., Lee, SE., Son, J. et al. Toxicity effects and biomarkers of tebufenozide exposure in Yuukianura szeptyckii (Collembola: Neanuridae). Environ Geochem Health 40, 2773–2784 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0143-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0143-7