Abstract
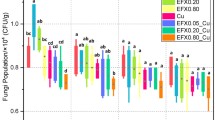
The production of commercial livestock and poultry often involves using with antibiotics and feed additives, such as oxytetracycline (OTC) and copper (Cu). These are often excreted into the soil by animal feces; hence, combined pollutants may contaminate the soil. To evaluate single and combined toxic effects of OTC and Cu on the soil ecology, changes in quantities of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes in the soil were studied over a 28-d incubation period by a plate count method, microbes numbers counted on days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Abundances of ammonia monooxygenase (amoA) gene expression by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) in soil samples also were tested by real-time polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCRs) on day 21. The results revealed that the numbers of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes and amoA genes copies of AOA and AOB were reduced seriously by exposure to Cu (1.60 mmol/kg). Similarly, the combined pollution treatments (mole ratios of OTC: Cu was 1:2, 1:8, and 1:32) also had inhibitory effect on bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes numbers and amoA gene copies of AOA and AOB; the inhibitory rate was on obvious growth trend with the increasing mole ratios. Effects from single OTC pollution were found on bacteria (days 7 and 14), fungi (days 7, 14, 21, and 28), and AOA-amoA gene copies (day 21), with promotion at a low concentration (0.05 mmol/kg) and suppression at higher concentrations (0.2 and 0.8 mmol/kg). Also, numbers of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes decreased with longer culture times. Combining OTC and Cu led to a higher inhibition of soil microbes than when either chemical was used alone. However, there was no significant relationship between single and combined toxic chemicals because of their complicated interactions, either antagonistic or synergistic. The results also indicated the sensitivity of bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes on toxic chemicals existed difference and that the AOA were more tolerant than the AOB to these chemicals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagot, N., Nybroe, O., Nielsen, P., & Johnsen, K. (2001). An altered pseudomonas diversity is recovered from soil by using nutrient-poorpseudomonas-selective soil extract media. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(11), 5233–5239.
Brandt, K. K., Amézquita, A., Backhaus, T., Boxall, A., Coors, A., Heberer, T., et al. (2015). Ecotoxicological assessment of antibiotics: A call for improved consideration of microorganisms. Environment International, 85, 189–205.
Brandt, K. K., Sjøholm, O. R., Krogh, K. A., Halling-Sørensen, B., & Nybroe, O. (2009). Increased pollution-induced bacterial community tolerance to sulfadiazine in soil hotspots amended with artificial root exudates. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(8), 2963–2968.
Chen, W. R., & Huang, C. H. (2008). Transformation of tetracyclines mediated by Mn(II) and Cu (II) ions in the presence of oxygen. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(2), 401–407.
Chen, X., Zhang, L. M., Shen, J. P., Wei, W. X., & He, J. Z. (2011). Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in an acid paddy soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 47(3), 323–331.
Cheng, J., Song, J., Ding, C., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2014). Ecotoxicity of benzo [a] pyrene assessed by soil microbial indicators. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 33(9), 1930–1936.
Colinas, C., Ingham, E., & Molina, R. (1994). Population responses of target and non-target forest soil organisms to selected biocides. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 26(1), 41–47.
Davis, K. E., Joseph, S. J., & Janssen, P. H. (2005). Effects of growth medium, inoculum size, and incubation time on culturability and isolation of soil bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(2), 826–834.
Demoling, L. A., Bååth, E., Greve, G., Wouterse, M., & Schmitt, H. (2009). Effects of sulfamethoxazole on soil microbial communities after adding substrate. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41(4), 840–848.
Fang, H., Wang, H., Cai, L., & Yu, Y. (2014). Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial pathogens in long-term manured greenhouse soils as revealed by metagenomic survey. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(2), 1095–1104.
Francis, C. A., Roberts, K. J., Beman, J. M., Santoro, A. E., & Oakley, B. B. (2005). Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(41), 14683–14688.
Gao, M., Song, W., Zhou, Q., Ma, X., & Chen, X. (2013). Interactive effect of oxytetracycline and lead on soil enzymatic activity and microbial biomass. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 36(2), 667–674.
Gougoulias, C., Clark, J. M., & Shaw, L. J. (2014). The role of soil microbes in the global carbon cycle: Tracking the below-ground microbial processing of plant-derived carbon for manipulating carbon dynamics in agricultural systems. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 94(12), 2362–2371.
Hao, Y. J., Wu, S. W., Wu, W. X., & Chen, Y. X. (2007). Research progress on the microbial ecology of aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(4), 1573–1582.
He, J. Z., Hu, H. W., & Zhang, L. M. (2012). Current insights into the autotrophic thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidation in acidic soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 55, 146–154.
Herrmann, M., Saunders, A. M., & Schramm, A. (2008). Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(10), 3279–3283.
Hobel, C. F., Marteinsson, V. T., Hauksdóttir, S., Fridjónsson, Ó. H., Skírnisdóttir, S., Hreggvidsson, G. Ó., et al. (2004). Use of low nutrient enrichments to access novel amylase genes in silent diversity of thermophiles. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 20(8), 801–809.
Jechalke, S., Heuer, H., Siemens, J., Amelung, W., & Smalla, K. (2014). Fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics in soil. Trends in Microbiology, 22(9), 536–545.
Kong, W. D., & Zhu, Y. G. (2007). A review on ecotoxicology of veterinary pharmaceuticals to plants and soil microbes. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2(1), 1–9.
Kong, W. D., Zhu, Y. G., Fu, B. J., Marschner, P., & He, J. Z. (2006). The veterinary antibiotic oxytetracycline and Cu influence functional diversity of the soil microbial community. Environmental Pollution, 143(1), 129–137.
Kuligowski, K., Poulsen, T. G., Stoholm, P., Pind, N., & Laursen, J. (2008). Nutrients and heavy metals distribution in thermally treated pig manure. Waste Management and Research, 26(4), 347–354.
Kumar, R. R., Park, B. J., & Cho, J. Y. (2013). Application and environmental risks of livestock manure. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 56(5), 497–503.
Leininger, S., Urich, T., Schloter, M., Schwark, L., Qi, J., Nicol, G. W., et al. (2006). Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature, 442(7104), 806–809.
Leston, S., Nunes, M., Viegas, I., Nebot, C., Cepeda, A., Pardal, M. Â., et al. (2014). The influence of sulfathiazole on the macroalgae Ulva lactuca. Chemosphere, 100, 105–110.
Li, C., Chen, J., Wang, J., Ma, Z., Han, P., Luan, Y., et al. (2015). Occurrence of antibiotics in soils and manures from greenhouse vegetable production bases of Beijing, China and an associated risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 521, 101–107.
Liao, M., & Huang, C. Y. (2005). Effect of heavy metals on soil microbial activity and diversity in a reclaimed mining wasteland of red soil area. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 17(5), 832–837.
Liu, A. J., Liu, M., Li, M. H., Ma, X. X., Sun, X. J., & Wang, H. H. (2013). Collaborative effects of Cu and antibiotic on soil microbial activities. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(11), 1825–1829.
Lu, L., Han, W., Zhang, J., Wu, Y., Wang, B., Lin, X., et al. (2012). Nitrification of archaeal ammonia oxidizers in acid soils is supported by hydrolysis of urea. The ISME Journal, 6(10), 1978–1984.
Lu, M., Xu, K., & Chen, J. (2013). Effect of pyrene and cadmium on microbial activity and community structure in soil. Chemosphere, 91(4), 491–497.
Martins, V. V., Zanetti, M. O. B., Pitondo-Silva, A., & Stehling, E. G. (2014). Aquatic environments polluted with antibiotics and heavy metals: A human health hazard. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(9), 5873–5878.
Nicol, G. W., Leininger, S., Schleper, C., & Prosser, J. I. (2008). The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environmental Microbiology, 10(11), 2966–2978.
Olawoyin, R., Oyewole, S. A., & Grayson, R. L. (2012). Potential risk effect from elevated levels of soil heavy metals on human health in the Niger delta. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 85, 120–130.
Ollivier, J., Kleineidam, K., Reichel, R., Thiele-Bruhn, S., Kotzerke, A., Kindler, R., et al. (2010). Effect of sulfadiazine-contaminated pig manure on the abundances of genes and transcripts involved in nitrogen transformation in the root-rhizosphere complexes of maize and clover. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(24), 7903–7909.
Ollivier, J., Schacht, D., Kindler, R., Groeneweg, J., Engel, M., Wilke, B. M., et al. (2013). Effects of repeated application of sulfadiazine-contaminated pig manure on the abundance and diversity of ammonia and nitrite oxidizers in the root-rhizosphere complex of pasture plants under field conditions. Frontiers in Microbiology, 4, 22.
Park, K., Bang, H. W., Park, J., & Kwak, I. S. (2009). Ecotoxicological multilevel-evaluation of the effects of fenbendazole exposure to Chironomus riparius larvae. Chemosphere, 77(3), 359–367.
Qi, Y. S., Zhang, W., Liu, M. D., Yang, D., Yan, Y., & He, N. (2014). Effect of ciprofloxacin and copper combined pollution on the early growth of wheat. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 9, 014.
Rotthauwe, J. H., Witzel, K. P., & Liesack, W. (1997). The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: Molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63(12), 4704–4712.
Schloter, M., Dilly, O., & Munch, J. C. (2003). Indicators for evaluating soil quality. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 98(1), 255–262.
Su, Y. H., Zhu, Y. G., Lin, A. J., & Zhang, X. H. (2005). Interaction between cadmium and atrazine during uptake by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). Chemosphere, 60(6), 802–809.
Thiele-Bruhn, S. (2005). Microbial inhibition by pharmaceutical antibiotics in different soils—dose-response relations determined with the iron (III) reduction test. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24(4), 869–876.
Thiele-Bruhn, S., & Beck, I. C. (2005). Effects of sulfonamide and tetracycline antibiotics on soil microbial activity and microbial biomass. Chemosphere, 59(4), 457–465.
Wagg, C., Bender, S. F., Widmer, F., & van der Heijden, M. G. (2014). Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(14), 5266–5270.
Wang, C., Luo, Y., & Mao, D. Q. (2014). Sources, fate, ecological risks and mitigation strategies of antibiotics in the soil environment. Environmental Chemistry, 33(1), 19–29.
Wang, X., Wang, C., Bao, L., & Xie, S. (2015). Impact of carbon source amendment on ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in reservoir riparian soil. Annals of Microbiology, 65(3), 1411–1418.
Wang, R., & Wei, Y. S. (2013). Pollution and control of tetracyclines and heavy metals residues in animal manure. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 32(9), 1705–1719.
Wang, L. P., Zhang, M. K., & Zheng, S. A. (2008). Adsorption–desorption characteristics and biological effects of enrofloxacin in agricultural soils. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2, 036.
Yang, Z., Jia, S., Zhang, T., Zhuo, N., Dong, Y., Yang, W., et al. (2015). How heavy metals impact on flocculation of combined pollution of heavy metals–antibiotics: A comparative study. Separation and Purification Technology, 149, 398–406.
Zhang, L. M., Hu, H. W., Shen, J. P., & He, J. Z. (2012). Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. The ISME journal, 6(5), 1032–1045.
Zhang, C., Nie, S., Liang, J., Zeng, G., Wu, H., Hua, S., et al. (2016). Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 557, 785–790.
Zhang, Q., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Xie, H., Wang, J., Wang, F., et al. (2014). Effects of fomesafen on soil enzyme activity, microbial population, and bacterial community composition. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(5), 2801–2812.
Zhao, Y., Tan, Y., Guo, Y., Gu, X., Wang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Interactions of tetracycline with Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb(II) and their cosorption behavior in soils. Environmental Pollution, 180, 206–213.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Nos. 41671320 and 21377075]; the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China [Nos. 2016YFD0201203, 2016YFD0800202, 2016YFD0800304]; the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China [No. ZR2016JL02]; and the Special Funds of Taishan Scholar of Shandong Province, China. We also thank Cliff G. Martin for review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Wang, J., Zhu, L. et al. Toxic effects of oxytetracycline and copper, separately or combined, on soil microbial biomasses. Environ Geochem Health 40, 763–776 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0022-7