Abstract
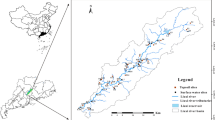
31 topsoil samples were collected by grid method in Xiaodian sewage irrigation area, Taiyuan City, North of China. The concentrations of 16 kinds of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) were determined by gas chromatograph coupled with mass spectrum. Generally speaking, the distribution order of PAHs in the area is: those with five and six rings > those with four rings > those with two and three rings. Source apportionment shows a significant zonation of the source of PAHs: the civil coal pollution occurred in the north part, the local and far factory pollution happened in the middle area and the mixed pollution sources from coal and wood combustion, automotive emission, presented in the south area. The distribution of PAHs has a definite relationship with the sewage water flow and soil adsorption. The related coefficient between PAHs and physicochemical property showed there was a negative correlation between pH, silt, clay and PAHs while there was a positive correlation between total organic carbon, sand and PAHs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brnner BA, Wise SA, Currie LA, Klouda GA, Klinedinst DB, Zweidinger RB, Stevens RK, Lewis CW (1995) Distinguishing the contributions of residential wood combustion and mobile source emis-sions using relative concentrations of dimethy phenanthrene isomers. Environ Sci Technol 29(9):2382–2389
Budzinski H, Jones I, Bellocq J, Pierard C, Garrigues P (1997) Evaluation of sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde es-tuary. Mar Chem 58(1–2):85–97
Chen Y, Wang CX, Wang ZJ, Huang SB (2004) Assessment of the contamination and genotoxicity of soil irrigated with wastewater. Plant Soil 261(1–2):189–196
Chen Y, Wang CX, Wang ZJ (2005) Residues and source identification of persistent organic pollutants in farmland soils irrigated by effluents from biological treatment plants. Environ Int 31(6):778–783
Clark BW, Di Giulio RT (2012) Fundulus heteroclitus adapted to PAHs are cross-resistant to multiple insecticides. Ecotoxicology 21(2):465–474
Glaser B, Dreyer A, Bock M, Fiedler S, Mehring M, Heitmann T (2005) Source apportionment of organic pollutants of a highway-traffic-influenced urban area in Bayreuth (Germany) using biomarker and stable carbon isotope signatures. Environ Sci Technol 39(11):3911–3917
Guillon A, Le Menach K, Flaud PM, Marchand N, Budzinski H, Villenave E (2013) Chemical characterization and stable carbon isotopic composition of particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons issued from combustion of 10 Mediterranean woods. Atmos Chem Phys 13(5):2703–2719
Harrison RM, Smith DJT, Luhana L (1996) Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from an urban location in Birmingham. UK Environ Sci Technol 30(3):825–832
Ilani T, Schulz E, Chefetz B (2005) Interactions of organic compounds with wastewater dissolved organic matter: role of hydrophohic fractions. J Environ Qual 34(2):552–562
Johnsen AR, Wick LY, Harms H (2005) Principles of microbial PAH-degradation in soil. Environ Pollut 133(1):71–84
Kavouras IG, Koutrakis P, Tsapakis M, Lagoudaki E, Stephanou EG, Von Baer D, Oyola P (2001) Source apportionment of urban particulate aliphatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using multivariate methods. Environ Sci Technol 35(11):2288–2294
Khalili NR, Scheff PA, Holsen TM (1995) PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmos Environ 29(4):533–542
Lee ML, Novotny M, Bartle KD (1981) Analytical chemistry of polycyclic aromatic compounds. Academic Press, New York
Li K, Christensen ER, Van Camp RP, Imamoglu I (2001) PAHs in dated sediments of Ashtabula River, Ohio. USA Environ Sci Technol 35(14):2896–2902
Li WH, Tian YZ, Shi GL, Guo CS, Li X, Feng YC (2012) Concentrations and sources of PAHs in surface sediments of the Fenhe reservoir and watershed, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 75:198–206
Lin C, Liu JL, Wang RM, Wang Y, Huang B, Pan XJ (2013) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils of Kunming, China: concentrations, distribution, sources, and potential risk. Soil Sediment Contam 22(7):753–766
Liu Y, Chen L, Zhao JF, Huang QH, Zhu ZL, Gao HW (2008) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of rivers and an estuary in Shanghai. China Environ Pollut 154(2):298–305
Liu Y, Chen L, Huang QH, Li WY, Tang YJ, Zhao JF (2009) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of the Huangpu River, Shanghai. China Sci Total Environ 407(8):2931–2938
Matson CW, Gillespie AM, McCarthy C, McDonald TJ, Bickham JW, Sullivan R, Donnelly KC (2009) Wildlife toxicology: biomarkers of genotoxic exposures at a hazardous waste site. Ecotoxicology 18(7):886–898
Motelay-Massei A, Ollivon D, Garban B, Tiphagne-Larcher K, Zimmerlin I, Chevreuil M (2007) PAHs in the bulk atmospheric deposition of the Seine river basin: source identification and apportionment by ratios, multivariate statistical techniques and scanning electron microscopy. Chemosphere 67(2):312–321
Park SU, In HJ, Kim SW, Lee YH (2000) Estimation of sulfur deposition in South Korea. Atmos Environ 34:3259–3269
Patnaik P (1997) In: Patnaik P (ed) Handbook of environmental analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 165
Simoneit BRT (1985) Application of molecular marker analysis to vehicle exhaust for source reconciliations. Int J Environ Anal Chem 22:203–233
Song YF, Wilke BM, Song XY, Gong P, Zhou QX, Yang GF (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and heavy metals (HMs) as well as their genotoxicity in soil after long-term wastewater irrigation. Chemosphere 65(10):1859–1868
Sun L, Zang SY (2013) Relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and particle size in dated core sediments in Lake Lianhuan, Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 461:180–187
Sun L, Zang SY, Xiao HF (2011) Historical record and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Lianhuan Lake sediments. Ecotoxicology 20(5):951–958
Theodore OI, Qi SH, Kong XS, Liu HF, Li J, Li J, Wang XQ, Wang YH (2008) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Datuo karst Tiankeng of South China. Environ Geochem Health 30(5):423–429
Tremolada P, Burnett V, Calamari D, Jones KC (1996) Spatial distribution of PAHs in the UK atmosphere using pine needles. Environ Sci Technol 30:3570–3577
Tsibart AS, Gennadiev AN (2013) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils: sources, behavior, and indication significance (a review). Eurasian Soil Sci 46(7):728–741
Wang XC, Zhang YX, Chen RF (2001) Distribution and partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in different size fractions in sediments from Boston Harbor. US Mar Pollut Bull 42(11):1139–1149
Wang YL, Xia ZH, Liu D, Qiu WX, Duan XL, Wang R, Liu WJ, Zhang YH, Wang D, Tao S, Liu WX (2013) Multimedia fate and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a coking industry city in Northern China. Environ Pollut 181:115–121
Wilcke W, Krauss M, Amelung W (2002) Carbon isotope signature of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): evidence for different sources in tropical and temperate environments? Environ Sci Technol 36(16):3530–3535
Williams PT (1990) Sampling and analysis of polycyclic aromatic compounds from combustion systems—a review. J Energy Inst 63:22–30
Xiao R, Du XM, He XZ, Zhang YJ, Yi ZH, Li FS (2008) Vertical distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Hunpu wastewater-irrigated area in northeast China under different land use patterns. Environ Monit Assess 142:23–34
Xing XL, Qi SH, Zhang JQ, Wu CX, Zhang Y, Yang D, Odhiambo JO (2011) Spatial distribution and source diagnosis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Chengdu Economic Region, Sichuan Province, western China. J Geochem Explor 110(2):146–154
Yunker MB, Acdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser river basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33(4):489–515
Zencak Z, Klanova J, Holoubek I, Gustafsson O (2007) Source apportionment of atmospheric PAHs in the Western Balkans by natural abundance radiocarbon analysis. Environ Sci Technol 41(11):3850–3855
Zhang CX, Liao XP, Li JL, Xu L, Liu M, Du B, Wang YX (2013) Influence of long-term sewage irrigation on the distribution of organochlorine pesticides in soil-groundwater systems. Chemosphere 92(4):337–343
Zhao ZY, Chu YL, Gu JD (2012) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Mai po inner deep bay ramsar site in Hong Kong. Ecotoxicology 24(6):1743–1752
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40830748 and No. 41372255). The authors thank Zhao Xu, Xiang Qingqing, Li Feng, Liu Yuan, Liu Lian, Tao Zhihao for their help in sampling and sample treatment, thank Chen Wei, Song Qi for their assistance in GC-MS analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JL., Wang, YX., Zhang, CX. et al. The source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the topsoil in Xiaodian sewage irrigation area, North of China. Ecotoxicology 23, 1943–1950 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1328-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1328-1