Abstract
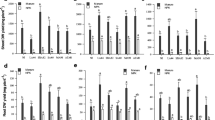
The objective of this study is to explore the response of an activated Rhizobium tibeticum inoculum with a mixture of hesperetin (H) and apigenin (A) to improve the growth, nodulation, and nitrogen fixation of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) grown under nickel (Ni) stress. Three different sets of fenugreek seed treatments were conducted, in order to investigate the activated R. tibeticum pre-incubation effects on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of fenugreek under Ni stress. Group (I): uninoculated seeds with R. tibeticum, group (II): inoculated seeds with uninduced R. tibeticum group (III): inoculated seeds with induced R. tibeticum. The present study revealed that Ni induced deleterious effects on rhizobial growth, nod gene expression, nodulation, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and glutamine synthetase activities, total flavonoids content and nitrogen fixation, while the inoculation with an activated R. tibeticum significantly improved these values compared with plants inoculated with uninduced R. tibeticum. PAL activity of roots plants inoculated with induced R. tibeticum and grown hydroponically at 75 and 100 mg L−1 Ni and was significantly increased compared with plants receiving uninduced R. tibeticum. The total number and fresh mass of nodules, nitrogenase activity of plants inoculated with induced cells grown in soil treated up to 200 mg kg−1 Ni were significantly increased compared with plants inoculated with uninduced cells. Plants inoculated with induced R. tibeticum dispalyed a significant increase in the dry mass compared with those treated with uninduced R. tibeticum. Activation of R. tibeticum inoculum with a mixture of hesperetin and apigenin has been proven to be practically important in enhancing nodule formation, nitrogen fixation and growth of fenugreek grown in Ni contaminated soils.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH (2011) Nodulation and nitrogen fixation in interspecies grafts of soybean and common bean is controlled by isoflavonoid signal molecules translocated from shoot. Plant Soil Environ 57:453–458
Abd-Alla HM, Yan F, Schubert S (1999) Effects of sewage sludge application on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and plant growth of faba bean, soybean and lupin. J Appl Botany 73:69–75
Abd-Alla MH, Omar SA, Karanzha S (2000) The impact of pesticides on arbuscular mycorrhizal and nitrogen-fixing symbioses in legumes. Appl Soil Ecol 14:191–200
Abd-Alla MH, Morsy FM, El-enany AE, Ohyama T (2012) Isolation and characterization of a heavy-metal-resistant isolate of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae potentially applicable for biosorption of Cd2+ and Co2+. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 67:48–55
Abd-Alla MH, Bagy MK, El-enany AE, Bashandy SR (2014a) Activation of Rhizobium tibeticum with flavonoid enhances nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of fenugreek (Trignoella foenum-graecum L.) grown in cobalted-polluted soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:303–315
Abd-Alla MH, El-enany AE, Bagy MK, Bashandy SR (2014b) Alleviating the inhibitory effect of salinity stress on nod gene expression in Rhizobium tibeticum fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) symbiosis by isoflavonoids treatment. J Plant Interact 9:275–284
Abd-Alla MH, Issa AA, Ohyama T (2014c). Impact of harsh environmental conditions on nodule formation and dinitrogen fixation of legumes. In: Ohyama T (ed) Advances in biology and ecology of nitrogen fixation. ISBN 978-953-51-1216-7. doi: 10.5772/56997, pp. 131–193
Abdelgani ME, Elsheikh EAE, Mukhtar NO (1999) The effect of Rhizobium inoculation and chemical fertilization on seed quality of fenugreek. Food Chem 64:289–293
Ahmad D, Mehmannavaz R, Damaj M (1997) Isolation and characterization of symbiotic N2-fixing Rhizobium meliloti from soils contaminated with aromatic and chloroaromatic hydrocarbons: PAHs and PCBs. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 39:33–43
Allen SE (1989) Chemical analysis of ecological materials, 2nd edn. Butter and Tanner, London
Alloway BJ (1995) Soil processes and the behavior of heavy metals. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metal in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, pp 25–34
Assuncao AGL, Schat H, Aarts MGM (2003) Thlaspi caerulescens, an attractive model species to study heavy metal hyperaccumulation in plants. New Phytol 159:351–360
Astros M, Bjorklund A (1996) Hydrogeochemistry of a stream draining sulfide bearing postglacial sediments in Finland. Water Air Soil Pollut 89:233–246
Bednarek P, Kerhoas L, Einhorn J, Frański R, Wojtaszek P, Rybus- Zając M, Stobiecki M (2003) Profiling of flavonoid conjugates in Lupinus albus and Lupinus angusitfolius responding to biotic and abiotic stimuli. J Chem Ecol 29:1127–1142
Begum A, Leibovitch S, Migner P, Zhang F (2001) Specific flavonoid induced nod gene expression and pre-activated nod genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum increased pea (Pisum sativum L.) and lentil (Lens culinaris L.) nodulation in controlled growth chamber environments. 52: 1537-. J Exp Bot 52:1537–1543
Brito B, Palacios JM, Hidalgo E, Imperial J, Ruiz-Argüeso T (1994) Nickel availability to pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants limits hydrogenase activity of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae bacteroids by affecting the processing of the hydrogenase structural subunits. J Bacteriol 176:5297–5303
Broughton WJ, Dilworth MJ (1970) Plant nutrient solutions. In: Somasegaran P, Hoben HJ (eds) Handbook for rhizobia. Methods in Legume-Rhizobium technology Niftal Project. University of Hawaii, Hawaii, pp 245–249
Bukhari SB, Bhanger MI, Memon S (2008) Antioxidative activity of extracts from fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Pak J Anal Environ Chem 9:78–83
Cai S, Xiong Z, Li L, Li M, Zhang L, Liu C, Xu Z (2014) Differential responses of root growth, acid invertase activity and transcript level to copper stress in two contrasting populations of Elsholtzia haichowensis. Ecotoxicology 23:76–91
Chaparro JM, Badri DV, Bakker MG, Sugiyama A, Manter DK, Jorge M. Vivanco JM (2013) Root exudation of phytochemicals in Arabidopsis follows specific patterns that are developmentally programmed and correlate with soil microbial functions. PLoS One 8. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055731
Chaudri AM, McGrath SP, Giller KE, Angle JS, Chaney L (1993) Screening of isolates and strains of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv trifolii for heavy metal resistance using buffered media. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1643–1651
Chen C, Huang D, Liu J (2009) Functions and toxicity of Ni in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Clean Soil Air Water 37:304–313
Cooper JE (2007) Early interactions between legumes and rhizobia: disclosing complexity in a molecular dialogue. J Appl Microbiol 103:1355–1365
Cooper JE, Rao JR (1992) Localized changes in flavonoid biosynthesis in roots of Lotus pedunculatus after infection by Rhizobium loti. Plant Physiol 100:444–450
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Easton DF, Peto J, Morgan LG, Metcalfe LP, Usher V, Doll R (1992) Respiratory cancer mortality in Welsh nickel refiners: which nickel compounds are responsible? In: Nieboer E, Nriagu JO (eds) Ni and human health, current perspectives. Wiley, New York, pp 604–619
El-Enany AE, Atia MA, Abd-Alla MH, Rmadan T (2000) Response of bean seedlings to nickel toxicity: role of calcium. Pak J Biol Sci 3:1447–1452
Elsokkary IH (1978) Contamination of roadside soils and slants near highway traffic With Cd, Ni, Pb and Zn in Alexandria District, Egypt. Stud Environ Sci 8:433–438
Gagnon H, Ibrahim RK (1997) Effects of various elicitors on the accumulation and secretion of isoflavonoids in white lupin. Phytochemistry 44:1463–1467
Gajewska E, Sklodowska M, Slaba M, Mazur J (2006) Effect of Ni on antioxidative enzyme activities, proline and chlorophyll content in wheat shoots. Biol Plant 50:653–659
Gajewska E, Marzena W, Katarzyna B, Maria S (2009) Ni-induced depression of nitrogen assimilation in wheat roots. Acta Physiol Plant 31:1291–1300
Gawronski JD, Benson DR (2004) Microtiter assay for glutamine synthetase biosynthetic activity using inorganic phosphate detection. Anal Biochem 327:114–118
Grandmaison J, Ibrahim R (1995) Ultrastructural localization of diprenylated isoflavone in Rhizobium lupine-Lupinus albus symbiotic association. J Exp Bot 46:31–237
Gupta DK, Huang HG, Nicoloso FT, Schetinger MR, Farias JG, Li TQ, Razafindrabe BHN, Aryal N, Inouhe M (2013) Effect of Hg, As and Pb on biomass production, photosynthetic rate, nutrients uptake and phytochelatin induction in Pfaffia glomerata. Ecotoxicology 22:1403–1412
Gyorgypal Z, Iyer N, Kondorosi A (1988) Three regulatory nodD alleles of diverged flavonoid speci¢city are involved in host- dependent nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet 212:85–92
Hahlbrock K, Ragg H (1975) Light-induced changes of enzyme activities in parsley cell suspension cultures. Arch Biochim Biophys 166:41–46
Hardy RWF, Holsten RD, Jackson EK, Burns RC (1968) The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol 43:1185–1207
Jayakumar K, Vijayarengan P, Zhao CX, Jaleel CA (2008) Soil applied cobalt alters the nodulation, leghaemoglobin content and antioxidant status of Glycine max (L.) Merr. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 67:272–275
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, p 413
Klucas RV, Hanus FJ, Russell SA, Evans HJ (1983) Ni a micronutrient element for hydrogen-dependent growth of Rhizobium japonicum and for expression of urease activity in soybean leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2253–2257
Kosslak RM, Bookland R, Barkei J, Paaren HE, Appelbaum ER (1987) Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7428–7432
Kovácik J, Backor M (2007) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and phenolic compounds in chamomile tolerance to cadmium and copper excess. Water Air Soil Pollut 185:185–193
Kovácik J, Grúz J, Backor M, Tomko J, Strnad M, Repcák M (2008) Phenolic compounds composition and physiological attributes of Matricaria chamomilla grown in copper excess. Environ Exp Bot 62:145–152
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Hedbavny J, Bačkor M (2009) Ni uptake and its effect on some nutrient levels, amino acid contents and oxidative status in Matricaria chamomilla. Water Air Soil Pollut 202:199–209
Krupa Z, Siedlecka A, Maksymiec W, Baszynski T (1993) In vitro responses of photosynthetic apparatus of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to Ni toxicity. Plant Physiol 142:664–668
Lou Y, Luo H, Hu T, Li H, Fu J (2013) Toxic effects, uptake, and translocation of Cd and Pb in perennial ryegrass. Ecotoxicology 22:207–214
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mahmoud A-LE, Abd-Alla MH (1993) Natural occurrence of mycotoxins in bean (Vicia faba L.) seeds and their effect on Rhizobium- legume symbiosis. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1081–1085
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London, p 889
McGrath SP (1995) Chromium and nickel. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, pp 152–174
Mehrafarin A, Rezazadeh S, Naghdi BH, Noormohammadi G, Zand E, Qaderi A (2011) A review on biology, cultivation and biotechnology of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) as a valuable medicinal plant and multipurpose. J Med Plants 10:1–24
Michalak A (2006) Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Pol J Environ Stud 15:523–530
Mihailovic N, Drazic G (2011) Incomplete alleviation of Ni toxicity in bean by nitric oxide supplementation. Plant Soil Environ 57:396–401
Miličić B, Delić D, Stajković O, Rasulić N, Kuzmanović Đ, Jošić D (2006) Effects of heavy metals on rhizobial growth. Rom Biotech Lett 11:2995–3003
Miller J (1992) A short course in bacterial genetics and handbook of E. coli and related bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 72–74
Mithöfer A, Schulze B, Boland W (2004) Biotic and heavy metal stress response in plants: evidence for common signals. FEBS Lett 566:1–5
Molas J (2002) Changes of chloroplast ultrastructure and total chlorophyll concentration in cabbage leaves caused by excess of organic Ni II complexes. Environ Exp Bot 47:115–126
Muth D, Kachlicki P, Krajewski P, Przystalski M, Stobiecki M (2009) Differential metabolic response of narrow leafed lupine (Lupinus angustifolius) leaves to infection with Colletotrichum lupine. Metabolomics 5:354–362
Novak K, Chovanec P, Skrdleta V, Kropacova M, Lisa L, Nemcova M (2002) Effect of exogenous flavonoids on nodulation of pea (Pisum sativum L.). J Exp Bot 53:1735–1745
Oldroyd GE, Murray JD, Poole PS, Downie JA (2011) The rules of engagement in the legume-rhizobial symbiosis. Annu Rev Genet 45:119–144
Olson JW, Maier RJ (2000) Dual roles of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Niin protein in Ni storage and GTP-dependent Ni mobilisation. J Bacteriol 182:1702–1705
Pal SC, Bhattacharya DN (1989) Characterization of the effects of heavy metal ions (Ni) on growth and some biochemical parameters of rhizobial strains of Cicer arietinum L. In: Proceedings of the 6th National Botanical Society, Chittagong (Bangladesh), Bangladesh Botanical Society, Dhaka (Bangladesh); Chittagong Univ. (Bangladesh).- Chittagong (Bangladesh): BBS, p 19
Pawlak-Sprada S, Stobiecki M, Deckert J (2011a) Activation of phenylpropanoid pathway in legume plants exposed to heavy metals. Part ii. Profiling of isoflavonoids and their glycoconjugates induced in roots of lupine (Lupinus luteus) seedlings treated with cadmium and lead. Acta Biochim Pol 58:217–223
Pawlak-Sprada S, Arasimowicz-Jelonek M, Podgórska M, Deckert J (2011b) Activation of phenylpropanoid pathway in legume plants expose to heavy metals: Part I. Effects of cadmium and lead on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene expression, enzyme activity and lignin content. Acta Biochim Pol 58:211–216
Peters NK, Verma DS (1990) Phenolic compounds as regulators of gene expression in plant–microbe interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 3:4–8
Peters NK, Frost JW, Long SR (1986) A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science 233:977–980
Rana A, Ahmad M (2002) Heavy metal toxicity in legume microsymbiont system. J Plant Nutr 25:369–386
Rao KVM, Sresty TVS (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.) Millspauga in response to Zn and Ni stress. Plant Sci 157:113–128
Rao M, Blane U, Zonnenberg M (1985) PC-state version I A. The University of Georgia, Athens
Reddy PM, Rendón-Anaya M, de los Dolores Soto del Rio M, Khandual S (2007) Flavonoids as signalling molecules and regulators of root nodule development. Dyn Soil Dyn Plant 1:83–94
Redmond JW, Batley M, Djordjevic MA, Innes RW, Kuempel PL, Rolfe BG (1986) Flavones induce expression of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. : Nature 323:632
Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants. In: Raskin I, Ensley BD (eds) Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 193–228
Rice-Evans C (2001) Flavonoid antioxidants. Curr Med Chem 8:797–807
Salt DE, Kato N, Kramer U, Smith RD, Raskin I (2000) The role of root exudates in Ni hyperaccumulation and tolerance in accumulator and nonaccumulator species of Thlaspi. In: Terry N, Banuelos G (eds) Phytoremediation of contaminated soil and water. CRS Press LLC, London, pp 189–200
Schlaman HRM, Phillips DA, Kondorosi E (1998) Genetic organisation and transcriptional regulation of rhizobial nodulation genes. In: Spaink HP, Kondorosi A, Hooy-kaas PJJ (eds) The Rhizobiaceae. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 361–386
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Tsadilas C (2013) Fractionation of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in floodplain soils from Egypt. In: Pirrone N (ed) Proceedings of the 16th international conference on heavy metals in the environment. E3S web of conferences, vol 1, Rome, Italy, 23–27 September, 2012. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/20130133003
Singh RK, Rao PJM (1997) Biological significance of Ni on the nitrogen fixing ability of cowpea Bradyrhizobium. J Plant Nutr 20:1449–1455
Skorzynska-Polit E, Drazkiewicz M, Wianowska D, Maksymiec W, Dawidowicz AL, Tukiendorf A (2004) The influence of heavy metal stress on the level of some flavonols in the primary leaves of Phaseolus coccineus. Acta Physiol Plant 26:247–254
Smith SR, Giller KE (1992) Effective Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii present in five soils contaminated with heavy metals from long-term applications of sewage sludge or metal mine spoil. Soil Biol Biochem 24:781–788
Stan V, Gament E, Cornea CP, Voaideş C, Duşa M, Plopeanu G (2011) Effects of heavy metal from polluted soils on the Rhizobium diversity. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj Napoca 39:88–95
Stewart AJ, Chapman W, Jenkins GI, Graham I, Martin T, Crozier A (2001) The effect of nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency on flavonol accumulation in plant tissue. Plant Cell Environ 24:1189–1197
Suominen L, Luukkainen R, Roos C, Lindstrom K (2003) Activation of the nodA promoter by the nodD genes of Rhizobium galegae induced by synthetic flavonoids or Galega orientalis root exudates. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:225–232
Sytar O, Kumar A, Latowski D, Kuczynska P, Strzałka K, Prasad MNV (2013) Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35:985–999
Tan Z, Liu R, Hu Y, Lin Z (2012) Production of isoflavone genistein in transgenic IFS tobacco roots and its role in stimulating the development of arbuscular mycorrhiza. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1863–1871
Vijayarengan P (2004) Growth, nodulation and dry matter yield of blackgram cultivars under Ni stress. J Environ Sci Eng 46:151–158
Wang J, Li W, Zhang C, Ke S (2010) Physiological responses and detoxific mechanisms to Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in young seedlings of Paulownia fortune. J Environ Sci (China) 22:1916–1922
Wani PA, Khan MS (2013) Ni detoxification and plant growth promotion by multi metal resistant plant growth promoting Rhizobium species RL9. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:117–124
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effect of metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting Rhizobium on the performance of pea grown in metal-amended soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:33–42
Wheeler CT, Hughes LT, Oldroyd J, Pulford ID (2001) Effects of Ni on Frankia and its symbiosis with Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Plant Soil 231:81–90
Woolfolk CA, Shapiro B, Stadtman ER (1966) Regulation of glutamine synthetase I. PuriWcation and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 116:177–192
Yan R, Gao S, Yang W, Cao M, Wang S, Chen F (2008) Ni toxicity induced antioxidant enzyme and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activities in Jatropha curcas L. cotyledons. Plant Soil Environ 54:294–300
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) Ni: an overview of uptake, essentiality and toxicity in plants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:1–17
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Ahmad A (2012) 24-Epibrassinolide modulates growth, nodulation, antioxidant system, and osmolyte in tolerant and sensitive varieties of Vigna radiata under different levels of Ni: a shotgun approach. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:143–153
Zhishen J, Tang M, Wu J (1999) The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem 64:555–559
Zon J, Amrhein N, Gancarz R (2002) Inhibitors of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: 1-aminobenzylphosphonic acids substituted in the benzene ring. Phytochem 59:9–21
Zuanazzi JAS, Clergeot PH, Quirion J-C, Husson HP, Kondorosi P, Ratet P (1998) Production of Sinorhizobium meliloti nod gene activation and repressor flavonoids from Medicago sativa roots. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:784–794
Zwolsman JJG, Van Bokhoven AJ (2007) Impact of summer droughts on water quality of the Rhine River-a preview of climate change. Water Sci Technol 56:45–55
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Anna Skorupska and Dominika Maj for kindly providing Escherichia coli α which contain expression vector pMP221. This research was financially supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF), Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Egypt, project Grant No. 12 awarded to Professor Dr. Mohamed Hemida Abd-Alla. The authors grateful to A. A. Farghaly, Virginia Commonwealth University, USA, for critical reading of the manuscript. The authors are very grateful for the insightful and helpful comments, constructive suggestions and careful corrections made by the Editor and the anonymous Referees for further improvements of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-Alla, M.H., Bashandy, S.R., Bagy, M.K. et al. Rhizobium tibeticum activated with a mixture of flavonoids alleviates nickel toxicity in symbiosis with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.). Ecotoxicology 23, 946–959 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1239-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1239-1