Abstract
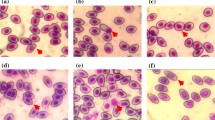
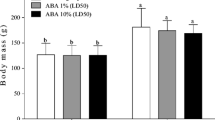
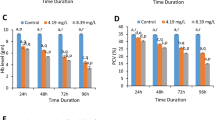
Bioinsecticides from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) are widely used around the world in biological control against larval stages of many insect species. Bt has been considered a biopesticide that is highly specific to different orders of insects, non-polluting and harmless to humans and other vertebrates, thus becoming a viable alternative for combating agricultural pests and insect vectors of diseases. The family of Bt δ-endotoxins are crystal-protein inclusions showing toxicity to insects’ midgut, causing cell lysis leading to starvation, septicemia and death. The aim of this study is to evaluate the genotoxic potential of recombinant Bt spore–crystals expressing Cry1Ia, Cry10Aa and Cry1Ba6 on peripheral erythrocyte cells of Oreochromis niloticus, through comet assay, micronucleus (MN) test and nuclear abnormalities (NA) analysis. Fish (n = 10/group) were exposed for 96 h at 107 spores 30 l−1, 108 spores 30 l−1 or 109 spores 30 l−1 of Bt spore–crystals. Cry1Ia showed a significant increase in comet cells at levels 1 and 2, but not at levels 3 and 4, so it was not mutagenic nor did it induce MN or NA. These three spore–crystals showed some fish toxicity at only the highest exposure level, which normally does not occur in the field.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar RWS et al (2012) Cry10Aa protein is highly toxic to Anthonomus grandis Boheman (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), an important insect pest in Brazilian cotton crop fields. Bt Res 3:20–28
Ali FK, El-Shehawi AM, Seehy MA (2008) Micronucleus test in the fish genome: a sensitive monitor for aquatic pollution. Afr J Biotechnol 7:606–612
Alves SB, Moraes SB (1998) Controle microbiano de insetos, 2nd edn. Piracicaba, São Paulo, p 329
Ayllon F, Garcia-Vazquez E (2000) Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutat Res 467:177–186
Betz FS, Hammond BG, Fuchs RL (2000) Safety and advantages of Bacillus thuringiensis protected plants to control insect pests. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 32:156–173
Bolognesi C, Hayashi M (2011) Micronucleus assay in aquatic animals. Mutagen 26:205–213
Cantón PE et al (2013) Membrane binding and oligomer membrane insertion are necessary but insufficient for Bacillus thuringiensis Cyt1Aa toxicity. Peptides. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2013.10.011
Cao S et al (2010) Safety assessment of Cry1C protein from genetically modified rice according to the standards of PR China for new food resource. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 58:474–481
Carlberg G, Tikkanen L, Abel-Hameed A (1995) Safety testing of Bacillus thuringiensis preparations, including thuringiensin, using the Salmonella Assay. J Invertebr Pathol 66:68–71
Carvalho JV et al (2011) Desempenho zootécnico e morfometria intestinal de alevinos de tilápia-do-nilo alimentados com Bacillus subtilis ou mananoligossacarídeo. Revista Brasileira Saúde e Produção Animal, p 121
Chen J et al (2013) A 104 kDa Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N is a putative receptor for the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43(12):1201–1208. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.09.007
Collins AR, Ai-Guo S, Duthie SJ (1995) The kinetics of repair of oxidative DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidised pyrimidines) in human cells. Mutat Res 336:69–77
Cuong DV et al (2006) Nitric oxide-cGMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway induces anoxic preconditioning through activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290(5):H1808–H1817
Douville M et al (2005) Tracking the source of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab endotoxin in the environment. Biochem Syst Ecol 33:219–232
Douville M, Gagné F, André C, Blaise C (2009) Occurrence of the transgenic corn Cry1Ab gene in freshwater mussels (Elliptio complanata) near corn fields: evidence of exposure by bacterial ingestion. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:17–25
EPA Microbial Pesticide Tests Guidelines. (1996) Freshwater Fish Testing number 885.4200/1996
Escudero IR et al (2006) Molecular and insecticidal characterization of a Cry1I protein toxic to insects of the families Noctuidae, Tortricidae, Plutellidae, and Chrysomelidae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4796–4804
Gallo D et al (2002) Entomologia agrícola. Piracicaba, São Paulo, p 586
Grisolia CK et al (2009a) Genotoxic evaluation of different delta-endotoxins from Bacillus thuringiensis on zebrafish adults and development in early life stages. Mutat Res 672:119–123
Grisolia CK et al (2009b) Acute toxicity and cytotoxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus sphaericus strains on fish and mouse bone marrow. Ecotoxicology 8:22–26. doi:10.1007/s10646-008-0252-7
Günther J, Jimenez-Montealegre R (2004) Efeito del probiótico Bacillus subtilis sobre el crescimento y alimentación de tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) e langostino (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) em laboratório. Revista de Biología Tropical 52:937–943
Heddle JA, Carrano AV (1977) The DNA content of micronuclei induced in mouse bone marrow by gamma-irradiation: evidence that micronuclei arise from acentric chromosomal fragments. Mutat Res 44:63–69
Jaloszynski P et al (1997) Bleomycin-induced DNA damage and its removal in lymphocytes of breast cancer patients studied by comet assay. Mutat Res 385:223–233
Johnson DE, McGaughey WH (1996) Contribution of Bacillus thuringiensis spore to toxicity of purified cry protein towards indianmeal moth larvae. Curr Microbiol 33:54–59
Jonsson CM, Maia AHN, Capalbo D, Carballo-Hondal O (2009) Avaliação de Risco do Biopesticida Bacillus thuringiensis (Cepa 344) em Organismos Bioindicadores Presentes em Sistemas de Reprodução Aquicola. In: Anais Zootec, Águas de Lindóia, São Paulo, p 988
Leite EMA, Amorim LCA (2001) Toxicologia Geral. Departamento de Análises Clínicas e Toxicologia Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, p 695
Marec F, Matha V, Weiser J (1989) Analysis of genotoxic activity of Bacillus thuringiensis β-exotoxin by means of the Drosophila wing test. J Invertebr Pathol 53:347–353
Martins ES et al (2008) Recombinant Cry1Ia protein is highly toxic to cotton boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis Boheman) and fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). J Appl Microbiol 104:1363–1371
Martins ES et al (2010) Midgut GPI-anchored proteins with alkaline phosphatase activity from the cotton boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis) are putatite receptors for the Cry1B protein of Bacillus thurigiensis. Insect Biochem Mol Bio 40:138–145
Meher SM et al (2002) Toxicity studies of microbial insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis var. kenyae in rats, rabbits, and fish. Int J Toxicol 21:99–105
Mezzomo BP et al (2013) Hematotoxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis as spore–crystal strains Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac or Cry2Aa in Swiss Albino Mice. J Hematol Thromb Dis 1:1–9
Miranda-Vilela AL et al (2010) Gene polymorphisms against DNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in leukocytes of healthy humans through comet assay: a quasi-experimental study. Environ Health. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-9-21
Monnerat RG, Praça LBB (2006) Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus sphaericus. In: Oliveira-Filho EC, Monnerat RG (eds) Fundamento para a Regulação de Semioquímicos. Inimigos Naturais e Agentes Microbiológicos de Controle de Pragas. E-Publising Inc., Planaltina, pp 121–155
Monnerat RG et al (2007) Characterization of Brazilian Bacillus thuringiensis strains active against Spodoptera frugiperda, Plutella xylostella and Anticarsia gemmatalis. Biol Control 41:291–295
OECD Guideline for testing of chemicals (1992) Fish, Acute Toxicity Test number 203/1992
Oliveira-Filho EC et al (2011) Susceptibility of non target invertebrates to brazilian microbial pest control agents. Ecotoxicology 20:1354–1360
Patetsini E, Dimitriadis VK, Kaloyianni M (2013) Biomarkers in marine mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to environmentally relevant levels of the pesticides, chlorpyrifos and penoxsulam. Aquat Toxicol 126:338–345
Reardon R, Dubois N, McLane W (1994) Bacillus thuringiensis for manaing gypsy moth: a review. National Center of Forest Health Management, Morgantown, p 854
Ren Z, Ma E, Guo Y (2002) Chromosome aberration assays for the study of cyclophosphamide and Bacillus thuringiensis in Oxya chinensis (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Mutat Res 520:141–150
Rivero CL et al (2008) Evaluation of genotoxicity and effects on reproduction of nonylphenol in Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces: Cichlidae). Ecotoxicology 17:732–737
Rivero-Wendt CL et al (2013) Cytogenetic toxicity and gonadal effects of 17 α-methyltestosterone in Astyanax bimaculatus (Characidae) and Oreochromis niloticus (Cichlidae). Genet Mol Res 12:3862–3870
Sanches V et al (1999) Development and field performance of a broad-sprctrum nonviable asporogenic recombinant strain of Bacillus thuringiensis with greater potency and UV resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4032–4039
Schnepf E et al (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:774–806
Silva-Filho MC, Falco MC (2000) Interação planta-inseto: adaptação dos insetos aos inibidores de proteinase produzidos pelas plantas. Biotecnologia Ciência Desenvolvimento 2:38–42
Silva-Werneck JO, Ellar DJ (2008) Characterization of a novel Cry9Bb δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. J Invertebr Pathol 98:320–328
Singh NP et al (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Souza TS, Fontanetti CS (2006) Micronucleus test and observation of nuclear alterations in erythrocytes of Nile tilapia exposed to waters affected by refinery effluent. Mutat Res 605:87–93
Yang W et al (2012) pH-controlled Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac protoxin loading and release from polyelectrolyte microcapsules. PLoS One 9:1–7
Zhou G et al (2008) The residual occurrences of Bacillus thuringiensis biopesticides in food and beverages. Int J Food Microbiol 127:68–72
Acknowledgments
Research project supported by the Brazilian National Council for Research and Biotechnology (CNPq), Grant 552113/2011-5. Ingrid S. Freire had a fellowship from the Brazilian Ministry of Education.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freire, I.S., Miranda-Vilela, A.L., Fascineli, M.L. et al. Genotoxic evaluation in Oreochromis niloticus (Fish: Characidae) of recombinant spore–crystal complexes Cry1Ia, Cry10Aa and Cry1Ba6 from Bacillus thuringiensis . Ecotoxicology 23, 267–272 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1170-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1170-x