Abstract
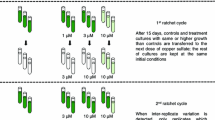
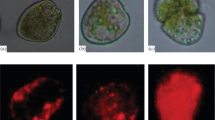
To understand the vulnerability of individual species to anthropogenic contamination, it is important to evaluate the different abilities of phytoplankton to respond to environmental changes induced by pollution. The ability of a species to adapt, rather than its initial tolerance, is the basis for survival under rapidly increasing levels of anthropogenic contamination. High doses of osmium (Os) cause massive destruction of diverse phytoplankton groups. In this study, we found that the coastal chlorophyte Tetraselmis suecica and the continental chlorophyte Dictyosphaerium chlorelloides were able to adapt to a lethal dose of Os. In these species, Os-resistant cells arose as a result of rare spontaneous mutations (at rates of approximately 10−6 mutants per cell division) that occurred before exposure to Os. The mutants remained in the microalgal populations by means of mutation–selection balance. The huge size of phytoplankton populations ensures that there are always enough Os-resistant mutants to guarantee the survival of the population under Os pollution. In contrast, we observed that neither a haptophyte species from open ocean regions nor a cyanobacterium from continental freshwater were able to adapt to the lethal Os dose. Adaptation of phytoplankton to Os contamination is relevant because industrial activities are leading to a rapid increase in Os pollution worldwide.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bañares-España E, López-Rodas V, Salgado C, Costas E, Flores-Moya A (2006) Interstrain variability in the photosynthetic use of inorganic carbon exemplified by the pH compensation point, in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquac Bot 85(2):159–162
Baos R, Garcia-Villada L, Agrelo M, López Rodas V, Hiraldo F, Costas E (2002) Short-Term adaptation of microalgae in highly stressful environments: an experimental model analysing the resistance of Scenedesmus intermedius (Chlorophyceae) to the heavy metals mixture from the Aznalcollar mine spill. Eur J Phycol 37:593–600
Barbante C, Veysseyre A, Ferrari C, Velde K, Morel C, Copodaglio G, Cescon P, Scarponi G, Boutron C (2001) Greenland snow evidence of large scale atmospheric contamination for platinum, palladium, and rhodium. Environ Sci Technol 35:835–839
Belfiore NM, Anderson SI (2001) Effects of contaminants on genetic patterns in aquatic organisms: a review. Mutat Res 489:97–122
Bhattacharya S (2004) Experts divided over poison bomb claim (Online article), New Scientist, Accessed 7 Apr 2004
Bickham J (2011) The four cornerstones of evolutionary toxicology. Ecotoxicology 20(3):497–502
Bradley K, Karl Esser, Turekian K (1993) Anthropogenic osmium in coastal deposits. Environ Sci Technol 27(13):2719–2724
Bradshaw AD, Hardwick K (1989) Evolution and stress—genotype and phenotype components. Biol J Linn Soc 37:137–155
Cairns J, Overbaugh J, Miller S (1988) The origin of mutants. Nature 335:142–145
Carrera-Martínez D, Mateos-Sanz A, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2010) Microalgae response to petroleum spill: an experimental model analysing physiological and genetic response of Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) to oil samples from the tanker Prestige. Aquat Toxicol 97:151–159
Chen C, Sedwick PN, Sharma M (2009) Anthropogenic osmium in rain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7724–7728
Costas E (1990) Genetic variability in growth rates in marine Dinoflagellates. Genetica 83:99–102
Costas E, Carrillo E, Ferrero LM, Agrelo M, García-Villada L, Juste J, López-Rodas V (2001) Mutation of algae from sensitivity to resistance against environmental selective agents: the ecological genetics of D. chlorelloides (Chlorophyceae) under lethal doses of 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea herbicide. Phycologia 40:391–398
Costas E, Flores-Moya A, Perdigones N, Maneiro E, Blanco JL, García ME, López-Rodas V (2007) How eukaryotic algae can adapt to the Spain’s Rio Tinto: a neo-Darwinian proposal for rapid adaptation to an extremely hostile ecosystem. New Phytol 175:334–339
Costas E, Flores-Moya A, López-Rodas V (2008) Rapid adaptation of algae to extreme environments (geothermal waters) by single mutation allows “Noah’s Arks” for photosynthesizers during the Neoproterozoic “Snowball Earth”. New Phytol 189:922–932
Costas E, Gonzalez R, López-Rodas V, Huertas IE (2013) Mutation of microalgae allows phytoplankton dispersion through ships biofouling. Biol Invasions. doi:10.1007/s10530-012-0405-8
Crow JF, Kimura M (1970) An introduction to population genetics theory. Harper and Row, New York
Flores-Moya A, Costas E, Bañares-España E, García-Villada L, Altamirano M, López-Rodas V (2005) Adaptation of Spirogyra insignis (Chlorophyta) to an extreme natural environment (sulphureous waters) through preselective mutations. New Phytol 165:655–661
Foster PL (2000) Adaptive mutation: implications for evolution. BioEssays 22(106):7–74
Gagnon ZE, Newkirk C, Hicks S (2006) Impact of platinum group metals on the environment: a toxicological, genotoxic and analytical chemistry study. J Environ Sci Health A 41:397–414
Garcia Villada L, Rico M, Altamirano M, Sanchez L, López Rodas V, Costas E (2004) Ocurrence of copper resistant mutants in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: characterization and future implications in the use of copper sulphate as algaecide. Water Res 38:2207–2213
Gonzalez A, Bell Graham (2011) Adaptation and evolutionary rescue in metapopulations experiencing environmental deterioration. Science 332:1327–1330
Gonzalez A, Ronce O, Ferriere R, Hochberg ME (2013) Evolutionary rescue: an emerging focus at the intersection between ecology and evolution. Philos Trans R Soc B 368:20120404
González R, García-Balboa C, Rouco M, Lopez-Rodas V, Costas E (2012) Adaptation of microalgae to lindane: a new approach for bioremediation. Aquat Toxicol 109:25–32
Heidenreich E (2007) Adaptive mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crit Rev Biochem Mol 42:285–311
Huertas IE, Rouco M, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2010) Estimating the capability of different phytoplankton groups to adapt to contamination: herbicides will affect phytoplankton species differently. New Phytol 188:478–487
Huertas IE, Rouco M, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2011) Warming will affect phytoplankton differently: evidence through a mechanistic approach. Proc R Soc B 278:3534–3543
Kimura M, Maruyama T (1966) The mutational load with epistatic gene interactions in fitness. Genetics 54:1337–1351
Lopez-Rodas V, Agrelo M, Carrillo E, Ferrero L, Larrauri A, Martín-Otero L, Costas E (2001) Resistance of microalgae to modern water contaminants as the result of rare spontaneous mutations. Eur J Phycol 36:179–190
Lopez-Rodas V, Marvá F, Costas E, Flores-Moya A (2008a) Microalgal adaptation in the stressful acidic, metal-rich mine waters from Mynydd Parys (N Wales, UK) could be due to selection of pre-selective mutants. Environ Exp Bot 61:43–48
Lopez-Rodas V, Marvá F, Rouco M, Costas E, Flores-Moya A (2008b) Adaptation of the chlorophycean Dictyosphaerium chlorelloides to the stressful acidic, mine metal-rich waters from Aguas Agrias Stream (SW Spain) as result of pre-selective mutations. Chemosphere 72:703–707
López-Rodas V, Flores-Moya A, Maneiro E, Perdigones N, Marvá F, García ME, Costas E (2007) Resistance to glyphosate in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa as result of pre-selective mutations. Evol Ecol 21:535–547
López-Rodas V, Costas E, Maneiro E, Marvá F, Rouco M, Delgado A, Flores-Moya A (2009) Living in vulcan’s forge: algae adaptation to stressful geothermal ponds on Vulcano Island (S Italy) as result of pre-selective mutations. Phycol Res 57:111–117
López-Rodas V, Rouco M, Sánchez-Fortún S, Flores-Moya A, Costas E (2011) Genetic adaptation and acclimation of phytoplankton along a stress gradient in the extreme waters of the Agrio river–Caviahue lake (Argentina). J Phycol 47(5):1036–1043
Luria SE, Delbrück M (1943) Mutations of bacteria from virus sensitivity to virus resistance. Genetics 28:491–511
Luttrell WE, Giles CB (2007) Toxic tips: osmium tetroxide. J Chem Health Saf 14(5):40
Marvá F, López-Rodas V, Rouco M, Navarro MC, Toro FJ, Costas E, Flores-Moya A (2010) Adaptation of green microalgae to the herbicides simazine and diquat as result of pre-selective mutations. Aquat Toxicol 96(2):130–134
Poirier A, Gariepy C (2005) Isotopic signature and impact of car catalysts on the anthropogenic osmium budget. Environ Sci Technol 39:4431–4434
Pomati F, Nizzetto L (2013) Assessing triclosan-induced ecological and trans-generational effects in natural phytoplankton communities: a trait-based field method. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1068-7
Rauch S, Hemond H, Barbante C, Owari M, Morrison GM, Peucker-Ehrenbrink B, Wass U (2005) Importance of automobile exhaust catalyst emissions for the deposition of platinum, palladium, and rhodium in the Northern Hemisphere. Environ Sci Technol 39:8156–8162
Romero J, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2012) Estimating the capability of microalgae to physiological acclimatization and genetic adaptation to petroleum and diesel oil contamination. Aquat Toxicol 124:227–237
Sager R (1954) Mendelian and non-Mendelian inheritance of streptomycin resistance in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 40(5):356–363
Sager R (1962) Streptomycin as a mutagen for nonchromosomal genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 48(12):2018–2026
Sager R, Burton WG, Roberts JR, Myers PA (1977) A site-specific single-strand endonuclease from the eukaryote Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74(7):2687–2691
Sharma M, Wasserburg GJ (1997) Osmium in the rivers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(24):5411–5416
Sivonen K, Jones G (1999) Cyanobacterial toxins. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in water. A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. Routledge, London, pp 41–111
Skulberg OM, Carmichael WW, Codd GA, Skulberg R (1993) Taxonomy of toxic cyanophyceae (Cyanobacteria). In: Falconer IR (ed) Algal toxins in seafood and drinking water. Academic Press, London, pp 145–164
Smith IC, Carson BL, Ferguson TL (1974) Osmium: an appraisal of environmental exposure. Environ Health Perspect 8:201–213
Sniegowski PD (2005) Linking mutation to adaptation: overcoming stress at the spa. New Phytol 166:360–362
Sniegowski PD, Lenski RE (1995) Mutation and adaptation: the directed mutation controversy in evolutionary perspective. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 26:553–578
Spiess EB (1989) Genes in populations, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Wedepohl KH (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59(7):1217–1232
Westbroek P, van Hinte JE, Brummer GJ, Veldhuis M, Brownlee C, Green J, Harris R, Heimdal BR (1994) Emiliania huxleyi as a key to biosphere–geosphere interactions. In: Green JC, Leadbeater BSC (eds) The haptophyte algae. Systematics association special, vol 5. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 321–334
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Secretaría de Estado de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación (Grant CTM 2012-34757). We thank Eva Salgado for technical support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marvá, F., García-Balboa, C., Baselga-Cervera, B. et al. Rapid adaptation of some phytoplankton species to osmium as a result of spontaneous mutations. Ecotoxicology 23, 213–220 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1164-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1164-8