Abstract
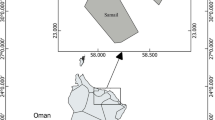
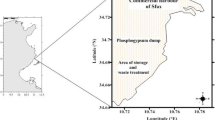
In the present study Cathorops spixii, was evaluated as a bioindicator fish for trace metal pollution. Concentrations of cobalt (Co), iron (Fe), selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) were determined by Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis in liver. Mercury (Hg) and methyl-mercury (MeHg) were analyzed by Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in muscles and livers. High concentrations of Co, Fe, Se and Zn were observed in C. spixii from Santos Bay in comparison to fish collected in a non-polluted site in the same Brazilian coast. These trace metal concentrations were out of the permissible levels for human consumption. Although, Hg and MeHg levels were low, the C. spixii could still be used as an effective bioindicator to observe trace metal behaviors in the environment in function of the bioaccumulation process observed mainly by other analyzed trace metals. Thus, the use of this species is strongly recommended to monitor the effects and behavior of trace metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems in Brazil due to its bioaccumulation function.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aguiar VMC, Braga ES (2007) Seasonal and tidal variability of phosphorus along a salinity gradient in the heavily polluted estuarine system of Santos/São Vicente—São Paulo, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 54:464–488. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.11.001
Agusa T, Kunito T, Yasunaga G, Iwata H, Subramanian A, Ismail A, Tanabe S (2005) Concentrations of trace elements in marine fish and its risk assessment in Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 51:896–911. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.06.007
Ansari TM, Marr IL, Tariq N (2004) Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective—a mini review. J Appl Sci 4(1):1–20
Anvisa (1998) Legislação Brasileira, Portaria 685. Available in http://www.anvisa.gov.br/legis/portarias/685_98.htm. Accessed 26 Jan 2008
Azevedo FA (2003) Toxicologia do Mercúrio. Rima, São Carlos
Boldrini CV, Navas-Pereira DN (1987) Metais pesados na baia de Santos e estuário de Santos e São Vicente. Ambiente 1(3):118–127
Boon JP, Lewis WE, Choy MR, Allchin CR, Law RJ, de Boer J (2002) Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants in animals representing different trophic levels of the North Sea food web. Environ Sci Technol 36:4025–4032. doi:10.1021/es0158298
Braga ES, Fonseca ALO, Bosquilha GE, Ducatti GMF, Aguiar VMC, Lima CAC, Arasaki E (2003) Eutrophication and bacterial pollution assessment risks on the Santos Bay sandy beaches (Brazil): influence of seasonal conditions. J Coast Res 35:516–524
Bryan GW (1979) Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 289:273–305
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00194-X
Cetesb (1979) Qualidade das praias paulistas 1976–1977. Cetesb, São Paulo, 181 p
Cetesb (2001) Sistema estuarino de Santos e São Vicente: Relatório Técnico, Agosto de 2001. CETESB, São Paulo, 178 p
Dural M, Göksu MZL, Özak AA (2007) Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically important fish species captured from the Tuzla lagoon. Food Chem 102:415–421. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.03.001
Eboh L, Mepba HD, Ekpo MB (2006) Heavy metal contaminants and processing effects on the composition, storage stability and fatty acid profiles of live common commercially available fish species in Oron Local Government, Nigeria. Food Chem 97:490–497. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.041
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (1999) Integrated risk information system (IRIS) on elemental mercury. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC. Available in http://www.epa.gov/reg3hscd/risk/human/index.htm. Accessed 03 Feb 2008
Farias LA, Azevedo J, Fávaro DIT, Saraiva ESBG (2005) Evaluation of mercury, selenium and methylmercury in fish consumed by Santos Bay Communities, São Paulo, Brasil. VII Encontro Nacional de Aplicações Nucleares—VII ENAN, vol 1. Anais do VII Encontro Nacional de Aplicações Nucleares, Santos, pp 1–9
Farkas A, Salánki J, Specziár A (2003) Age- and size-specific patterns of heavy metals in the organs of freshwater fish Abramis brama L. populating a low-contaminated site. Water Res 37:959–964. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00447-5
Fávaro DIT, Afonso C, Vasconcellos MBA, Cozzolino SMF (2000) Determinação de Elementos MInerais e Traços por Ativação Neutrônica, em refeições servidas no restaurante da Faculdade de Saúde Pública/USP. Cienc Tecnologia Alimentos 20(2):176–182
Figueiredo JL, Menezes NA (1978) Manual de peixes marinhos do sudeste do Brasil. II Teleostei (1). Universidade de São Paulo, Museu de Zoologia, São Paulo, Brazil, 110 p
Fisk AT, Hobson KA, Norstrom RJ (2001) Influence of chemical and biological factors on trophic transfer of persistent organic pollutants in the Northwater Polynya marine food web. Environ Sci Technol 35:732–738. doi:10.1021/es001459w
Fúlfaro VJ, Requejo CS, Landim PMB, Fúlfaro R (1983) Distribuição de elementos metálicos nos sedimentos da baía de Santos, SP. Atas do Simpósio regional de Geologia, vol 4. Atas da Sociedade Brasileira de Geologia, São Paulo, pp 275–289
Furness RW, Raibow PS (1990) Heavy metals in the marine environment, 1st edn. CRC, Boca Raton
Grigg RW (1994) Effects of sewage discharge, fishing pressure and habitat complexity on coral ecossystem and reef fishes in Hawaii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 103:25–34. doi:10.3354/meps103025
Heath AG (1990) Water pollution and fish physiology, 2nd edn. CRC, Boca Raton, Boston
Hellou J, Warren WG, Payne JF, Belkhode S, Lobel P (1992) Heavy metals and other dements in three tissues of cod, Gadus morhua, from the Northwest Atlantic. Mar Pollut Bull 24:452–458. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(92)90345-7
Hellou J, Zitkob V, Friel J, Alkanani T (1996) Distribution of elements in tissues of yellowtail flounder Pleuronectes ferruginea. Sci Total Environ 181:137–146. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04963-0
Homem JCM (1983) Balneabilidade das praias de Santos e São Vicente. In: Seminário sobre uma síntese do conhecimento sobre a Baixada Santista. CETESB, p 61–64
Horvat M (1996) Mercury analysis and speciation in environmental samples. In: Baeyens W et al (eds) Global and regional mercury cycles: sources, fluxes and mass balances. NATO ASI Series, Partnership Sub-Series, 2. Environment, vol 21. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp 1–31
Islam MS, Tanaka M (2004) Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: a review and synthesis. Mar Pollut Bull 48:624–649. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.12.004
Jones WG, Walker KF (1979) Accumulation of iron, manganese, zinc and cadmium by the Australian freshwater mussel Velesunio ambiguus (Phillipi) and its potential as a biological monitor. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 30:741–751. doi:10.1071/MF9790741
Kakulu SE, Osibanjo O, Ajayi SO (1987) Trace metal content of fish and shellfishes of the niger delta area of Nigeria. Environ Int 13:247–251. doi:10.1016/0160-4120(87)90136-X
Karadede H, Unlϋ E (2000) Concentrations of some heavy metals in water, sediment and fish species from the Atatϋrk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Chemosphere 41:1371–1376. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00563-9
Karadede H, Oymak SA, Unlϋ E (2004) Heavy metals in mullet, Liza abu, and catfish, Silurus triostegus, from the Atatürk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Environ Int 30:183–188. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00169-7
Kojadinovic J, Potier M, Le Corre M, Cosson RP, Bustamante P (2007) Bioaccumulation of trace elements in pelagic fish from the Western Indian Ocean. Environ Pollut 146:548–566. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.07.015
Lacerda LD (1998) Biogeochemistry of trace metals and diffuse pollution in mangrove ecosystems. Mangrove ecosystems occasional papers no. 2. International Society for Mangrove Ecosystems, Okinawa, p 65
Marcovecchio JE (2004) The use of Micropogonias furnieri and Mugil liza as bioindicators of heavy metals pollution in La Plata river estuary, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 323:219–226. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.09.029
Markert B (1996) Instrumental element and multielement analysis of plant samples—methods and applications. Wiley, Chichester, p 263
Markert B, Wappelhorst O, Weckert V, Herpin U, Siewers U, Friese K, Breulmann G (1999) The use of bioindicators for monitoring the heavy-metal status of the environment. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 240(2):425–429. doi:10.1007/BF02349387
Maršálek P, Svobodová Z, Randák T (2007) The content of total mercury and methylmercury in common carp from selected Czech ponds. Aquacult Int 15:299–304. doi:10.1007/s10499-007-9076-3
Montone RC (1987) Hidrocarbonetos clorados no litoral do estado de São Paulo. MSc Dissertation, Instituto Oceanográfico, Universidade de São Paulo, 102 p
Olsson M, Jensen S (1975) Pike as the test organism for mercury, DDT and PCB pollution: a study of the contamination in the Stockholm Archipelago. Inst Fresh Res 54:20
Otaway NM, Gray CA, Craig JR, McVea TA, Ling JE (1995) Assessing the impacts of deepwater sewage disposal: a case study fro South Wales, Austrália. Mar Pollut Bull 33(4–12):347–354
Palheta D, Taylor A (1995) Mercury in environmental and biological samples from a gold mining area in the Amazon region of Brazil. Sci Total Environ 168:63–69. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04533-7
Parsons ECM (1999) Short communication: trace element concentrations in whole fish from North Lantau waters, Hong Kong. J Mar Sci 56:791–794
Phillips DJH (1977) The use of biological indicator organisms to monitor trace metals in marine and estuarine environments—a review. Environ Pollut 13:282–317
Phillips DJH, Segar DA (1986) Use of bio-monitors in monitoring conservative contaminants, programme design imperatives. Mar Pollut Bull 17:10–17. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(86)90797-6
Porvari P (1995) Mercury levels of fish in Tucuruí hydroelectric reservoir and in River Mojú in Amazonia, in the state of Pará, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 175:109–117. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04907-X
Puffer HW, Azen SP, Duda MJ (1982) Sportfishing activity and catches in polluted coastal regions of metropolitan Los Angeles. N Am J Fish Manage 1:74–79. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(1982)2<74:PHHFCO>2.0.CO;2
Reddy ML, Reif JS, Bachand A, Ridgway SH (2001) Opportunities for using Navy marine mammals to explore associations between organochlorine contaminants and unfavorable effects on reproduction. Sci Total Environ 274:171–182. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00741-0
Reuther R (1994) Mercury accumulation in sediments and fish from rivers affectedby alluvial gold mining in the Madeira river basin, Brazil. Ambio 19:11–15
Rios EP (2001) Papel do estuário no ciclo de vida das espécies dominantes da ictiofauna do Complexo Estuarino-lagunar de Cananéia-Iguape. M.Sc. Dissertation, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, p 128
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer, Heidelberg, p 337
Sinderman CJ (1996) Ocean pollution: effects on living resources and humans. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 275
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Nieman N (2002) Princípios de Análise Instrumental, 5th edn. Bookman, São Paulo
Turkmen M, Ciminli C (2007) Determination of metals in fish and mussel species by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Food Chem 103:670–675
Voigt HR (1999) Concentrations of heavy metals in fish from coastal waters around the Baltic Sea (extended abstract). ICES J Mar Sci 56:140–141. doi:10.1006/jmsc.1999.0623
Zagatto PA, Bertoletti E (2006) Ecotoxicologia Aquática: Princípios e Aplicações. Rima Editora, São Carlos, p 464
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the R/v Albacora crew from Oceanographic Institute of University of São Paulo, for their help in the fieldwork and appreciate the financial support of the São Paulo Foundation for Research Support—FAPESP (Process 2005/50769-2) and Brazilian Agencies for Science and Technology—CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo, J.S., Fernandez, W.S., Farias, L.A. et al. Use of Cathorops spixii as bioindicator of pollution of trace metals in the Santos Bay, Brazil. Ecotoxicology 18, 577–586 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0315-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0315-4