Summary
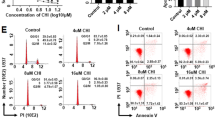
In recent years, a number of novel pharmaceutical agents have received approval for the management of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, there is still ample opportunity for enhancing efficacy. The Wee1 inhibitor adavosertib (ADA) shows promise for the treatment of AML. Based on the effect of drugs on DNA damage, we conducted a combination study involving ADA and fimepinostat (CUDC-907), a dual inhibitor of PI3K and histone deacetylase (HDAC). We observed that the combination of CUDC-907 and ADA exhibited a synergistic effect in enhancing the antileukemic activity in both AML cell lines and primary patient samples, demonstrating through flow cytometry analysis and MTT assay, respectively. Additionally, our study revealed that CUDC-907 has the ability to augment ADA-induced DNA damage, as determined by the measurement of γH2AX levels and the implementation of the alkaline comet assay. Through the utilization of western blotting analyses, targeted inhibitors, and ectopic overexpression, we propose that the downregulation of Wee1, CHK1, RNR, and c-Myc are the potential mechanisms. Our data support the development of ADA in combination with CUDC-907 for the treatment of AML.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bhansali RS, Pratz KW, Lai C (2023) Recent advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 16(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-023-01424-6
Matheson CJ, Backos DS, Reigan P (2016) Targeting WEE1 Kinase in Cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci 37(10):872–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2016.06.006
Qi W, Xie C, Li C, Caldwell JT, Edwards H, Taub JW, Wang Y, Lin H, Ge Y (2014) CHK1 plays a critical role in the anti-leukemic activity of the wee1 inhibitor MK-1775 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. J Hematol Oncol 7:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0053-9
Chen G, Zhang B, Xu H, Sun Y, Shi Y, Luo Y, Jia H, Wang F (2017) Suppression of Sirt1 sensitizes lung cancer cells to WEE1 inhibitor MK-1775-induced DNA damage and apoptosis. Oncogene 36(50):6863–6872. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.297
Hauge S, Macurek L (2019) p21 limits S phase DNA damage caused by the Wee1 inhibitor MK1775. 18(8):834–847. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1593649
Fu S, Wang Y, Keyomarsi K, Meric-Bernstam F, Meric-Bernstein F (2018) Strategic development of AZD1775, a Wee1 kinase inhibitor, for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27(9):741–751. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2018.1511700
Shafer D, Kagan AB, Rudek MA, Kmieciak M, Tombes MB, Shrader E, Bandyopadhyay D, Hudson D, Sankala H, Weir C, Lancet JE, Grant S (2023) Phase 1 study of belinostat and adavosertib in patients with relapsed or refractory myeloid malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 91(3):281–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-023-04511-0
Schutte T, Embaby A, Steeghs N, van der Mierden S, van Driel W, Rijlaarsdam M, Huitema A, Opdam F (2023) Clinical development of WEE1 inhibitors in gynecological cancers: A systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 115:102531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102531
Porter CC, Kim J, Fosmire S, Gearheart CM, van Linden A, Baturin D, Zaberezhnyy V, Patel PR, Gao D, Tan AC, DeGregori J (2012) Integrated genomic analyses identify WEE1 as a critical mediator of cell fate and a novel therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 26(6):1266–1276. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.392
Qi W, Xu X, Wang M, Li X, Wang C, Sun L, Zhao D, Sun L (2019) Inhibition of Wee1 sensitizes AML cells to ATR inhibitor VE-822-induced DNA damage and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 164:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.022
Garcia TB, Snedeker JC, Baturin D, Gardner L, Fosmire SP, Zhou C, Jordan CT, Venkataraman S, Vibhakar R, Porter CC (2017) A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of WEE1, AZD1775, Synergizes with Olaparib by Impairing Homologous Recombination and Enhancing DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Acute Leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 16(10):2058–2068. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-16-0660
Okabe S, Tanaka Y, Moriyama M, Gotoh A (2023) WEE1 and PARP-1 play critical roles in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia treatment. Cancer Cell Int 23(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02961-3
Qi W, Zhang W, Edwards H, Chu R, Madlambayan GJ, Taub JW, Wang Z, Wang Y, Li C, Lin H, Ge Y (2015) Synergistic anti-leukemic interactions between panobinostat and MK-1775 in acute myeloid leukemia ex vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 16(12):1784–1793. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2015.1095406
Zhou L, Zhang Y, Chen S, Kmieciak M, Leng Y, Lin H, Rizzo KA, Dumur CI, Ferreira-Gonzalez A, Dai Y, Grant S (2015) A regimen combining the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 with HDAC inhibitors targets human acute myeloid leukemia cells harboring various genetic mutations. Leukemia 29(4):807–818. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.296
Qian C, Lai CJ, Bao R, Wang DG, Wang J, Xu GX, Atoyan R, Qu H, Yin L, Samson M, Zifcak B, Ma AW, DellaRocca S, Borek M, Zhai HX, Cai X, Voi M (2012) Cancer network disruption by a single molecule inhibitor targeting both histone deacetylase activity and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 18(15):4104–4113. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-0055
Li X, Su Y, Madlambayan G, Edwards H, Polin L, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, Ma J, Knight T, Wang G, Wang Y, Yang J, Taub JW, Lin H, Ge Y (2019) Antileukemic activity and mechanism of action of the novel PI3K and histone deacetylase dual inhibitor CUDC-907 in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 104(11):2225–2240. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.201343
Li X, Su Y, Hege K, Madlambayan G, Edwards H, Knight T, Polin L, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, Yang J, Miller R, Wang G, Zhao L, Wang Y, Lin H, Taub JW, Ge Y (2021) The HDAC and PI3K dual inhibitor CUDC-907 synergistically enhances the antileukemic activity of venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 106(5):1262–1277. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.233445
Qiao X, Ma J, Knight T, Su Y, Edwards H, Polin L, Li J, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, Wang J, Lin H, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang G, Taub JW, Ge Y (2021) The combination of CUDC-907 and gilteritinib shows promising in vitro and in vivo antileukemic activity against FLT3-ITD AML. Blood Cancer J 11(6):111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00502-7
Hege Hurrish K, Qiao X, Li X, Su Y, Carter J, Ma J, Kalpage HA, Hüttemann M, Edwards H, Wang G, Kim S, Dombkowski A, Bao X, Li J, Taub JW, Ge Y (2022) Co-targeting of HDAC, PI3K, and Bcl-2 results in metabolic and transcriptional reprogramming and decreased mitochondrial function in acute myeloid leukemia. Biochem Pharmacol 205:115283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115283
Oki Y, Kelly KR, Flinn I, Patel MR, Gharavi R, Ma A, Parker J, Hafeez A, Tuck D, Younes A (2017) CUDC-907 in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, including patients with MYC-alterations: results from an expanded phase I trial. Haematologica 102(11):1923–1930. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2017.172882
Landsburg DJ, Barta SK, Ramchandren R, Batlevi C, Iyer S, Kelly K, Micallef IN, Smith SM, Stevens DA, Alvarez M, Califano A, Shen Y, Bosker G, Parker J, Soikes R, Martinez E, von Roemeling R, Martell RE, Oki Y (2021) Fimepinostat (CUDC-907) in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell and high-grade B-cell lymphoma: report of a phase 2 trial and exploratory biomarker analyses. Br J Haematol 195(2):201–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17730
O’Connor MJ (2015) Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Mol Cell 60(4):547–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.040
Uphoff CC, Drexler HG (2005) Detection of mycoplasma contaminations. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 290:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-838-2:013
Taub JW, Matherly LH, Stout ML, Buck SA, Gurney JG, Ravindranath Y (1996) Enhanced metabolism of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine in Down syndrome cells: a contributing factor to the superior event free survival of Down syndrome children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 87(8):3395–3403
Li X, Su Y, Hege K, Madlambayan G, Edwards H, Knight T, Polin L, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, Yang J, Miller R, Wang G, Zhao L, Wang Y, Lin H, Taub JW, Ge Y (2020) The HDAC and PI3K dual inhibitor CUDC-907 synergistically enhances the antileukemic activity of venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica: haematol 2019. 233445. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.233445
Dai Y, Grant S (2010) New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 16(2):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-09-1029
Sun K, Atoyan R, Borek MA, Dellarocca S, Samson ME, Ma AW, Xu GX, Patterson T, Tuck DP, Viner JL, Fattaey A, Wang J (2017) Dual HDAC and PI3K Inhibitor CUDC-907 Downregulates MYC and Suppresses Growth of MYC-dependent Cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 16(2):285–299. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-16-0390
Fu XH, Zhang X, Yang H, Xu XW, Hu ZL, Yan J, Zheng XL, Wei RR, Zhang ZQ, Tang SR, Geng MY, Huang X (2019) CUDC-907 displays potent antitumor activity against human pancreatic adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of HDAC6 to downregulate c-Myc expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40(5):677–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0108-5
Li X, Su Y, Madlambayan G, Edwards H, Polin L, Kushner J, Dzinic SH, White K, Ma J, Knight T, Wang G, Wang Y, Yang J, Taub JW, Lin H, Ge Y (2019) Antileukemic activity and mechanism of action of the novel PI3K and histone deacetylase dual inhibitor CUDC-907 in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.201343
Bose P, Dai Y, Grant S (2014) Histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) mechanisms of action: emerging insights. Pharmacol Ther 143(3):323–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.04.004
Wang Z, Huang Y, Zhang J (2014) Molecularly targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway can sensitize cancer cells to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 19(2):233–242. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11658-014-0191-7
Krajewska M, Heijink AM, Bisselink YJ, Seinstra RI, Sillje HH, de Vries EG, van Vugt MA (2013) Forced activation of Cdk1 via wee1 inhibition impairs homologous recombination. Oncogene 32(24):3001–3008. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.296
Brown JS, O’Carrigan B, Jackson SP, Yap TA (2017) Targeting DNA Repair in Cancer: Beyond PARP Inhibitors. Cancer Discov 7(1):20–37. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-16-0860
Rohban S (1849) Campaner S (2015) Myc induced replicative stress response: How to cope with it and exploit it. Biochem Biophys Acta 5:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.008
Solvie D, Baluapuri A, Uhl L, Fleischhauer D, Endres T, Papadopoulos D, Aziba A, Gaballa A, Mikicic I, Isaakova E, Giansanti C, Jansen J, Jungblut M, Klein T, Schülein-Völk C, Maric H, Doose S, Sauer M, Beli P, Rosenwald A, Dobbelstein M, Wolf E, Eilers M (2022) MYC multimers shield stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase. Nature 612(7938):148–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05469-4
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,NSFC82100076,Projects of Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan,20220101284JC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception and design were from Guan Wang and Yue Wang (the First Hospital of Jilin University). Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Yue Wang (School of Life Sciences) and Xingyu Lin. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Guan Wang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Human Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Jilin University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lin, X., Wang, Y. et al. Synergistic effect of adavosertib and fimepinostat on acute myeloid leukemia cells by enhancing the induction of DNA damage. Invest New Drugs 42, 70–79 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01415-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01415-x