Summary
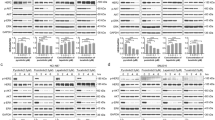
Pharmacologic options for patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer are limited. It has been suggested that targeting intracellular molecules, which have been altered during neoplastic development, may slow tumor growth. Therefore, the growth-blocking potential of the histone deacetylase-inhibitor LBH589 and the multiple tyrosine kinase-inhibitor TKI258, applied alone or in combination, was investigated in a panel of prostate cancer cell lines. PC-3, DU-145 or LNCaP cells were treated with various concentrations of LBH589 and/or TKI258. Tumor cell growth, cell cycle regulating proteins, HDAC3- and HDAC4-expression and histone H3 and H4 acetylation were then evaluated by MTT assay and Western blotting. LBH589 dose-dependently blocked prostate cancer cell growth. In contrast, TKI258 did not down-regulate tumor cell growth up to a 1,000 nM dosage. LBH589 elevated histone H3 and H4 acetylation. The cell cycle regulators cyclin B, cyclin D1, cdk1 and cdk4 were down-regulated in PC-3, whereas the suppressor proteins p21 and p27 were up-regulated in LNCaP by LBH589. TKI258 up-regulated p27 in PC-3 or p21 in LNCaP and additionally elevated cyclin B, cyclin D1, cdk1 and cdk4 in both cell lines. Presumably, the increase in cyclin and cdk caused by TKI258 counteracts the benefit of p21 or p27 up-regulation, resulting in TKI258 non-responsiveness. The LBH589/TKI258-combination was not superior to the LBH589 single-drug use in terms of growth reduction. Obviously, TKI258 did not enhance the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells towards an HDAC based regimen. Therefore, the LBH589/TKI258-combination probably does not provide an optimum strategy in fighting advanced prostate cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249. doi:10.3322/caac.20006
Petrylak D (2005) Therapeutic options in androgen-independent prostate cancer: building on docetaxel. BJU Int 96(Suppl 2):41–46
Rosenberg JE, Weinberg VK, Kelly WK, Michaelson D, Hussain MH, Wilding G, Gross M, Hutcheon D, Small EJ (2007) Activity of second-line chemotherapy in docetaxel-refractory hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients: randomized phase 2 study of ixabepilone or mitoxantrone and prednisone. Cancer 110:556–563. doi:10.1002/cncr.22811
Chou YW, Chaturvedi NK, Ouyang S, Lin FF, Kaushik D, Wang J, Kim I, Lin MF (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid suppresses the growth and increases the androgen responsiveness of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett 311:177–186. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.07.015
Hudak L, Tezeeh P, Wedel S, Makarević J, Juengel E, Tsaur I, Bartsch G, Wiesner C, Haferkamp A, Blaheta RA (2012) Low dosed interferon alpha augments the anti-tumor potential of histone deacetylase inhibition on prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. Prostate. doi:10.1002/pros.22525
Kim NH, Kim SN, Kim YK (2011) Involvement of HDAC1 in E-cadherin expression in prostate cancer cells; its implication for cell motility and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:915–921. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.081
Drake JM, Graham NA, Stoyanova T, Sedghi A, Goldstein AS, Cai H, Smith DA, Zhang H, Komisopoulou E, Huang J, Graeber TG, Witte ON (2012) Oncogene-specific activation of tyrosine kinase networks during prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1643–1648. doi:10.1073/pnas.1120985109
Dror Michaelson M, Regan MM, Oh WK, Kaufman DS, Olivier K, Michaelson SZ, Spicer B, Gurski C, Kantoff PW, Smith MR (2009) Phase II study of sunitinib in men with advanced prostate cancer. Ann Oncol 20:913–920. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp111
Whang YE, Armstrong AJ, Rathmell WK, Godley PA, Kim WY, Pruthi RS, Wallen EM, Crane JM, Moore DT, Grigson G, Morris K, Watkins CP, George DJ (2011) A phase II study of lapatinib, a dual EGFR and HER-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.09.018
Gnoni A, Marech I, Silvestris N, Vacca A, Lorusso V (2011) Dasatinib: an anti-tumour agent via Src inhibition. Curr Drug Targets 12:563–578
Nabhan C, Lestingi TM, Galvez A, Tolzien K, Kelby SK, Tsarwhas D, Newman S, Bitran JD (2009) Erlotinib has moderate single-agent activity in chemotherapy-naïve castration-resistant prostate cancer: final results of a phase II trial. Urology 74:665–671. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.05.016
Lee SH, Lopes de Menezes D, Vora J, Harris A, Ye H, Nordahl L, Garrett E, Samara E, Aukerman SL, Gelb AB, Heise C (2005) In vivo target modulation and biological activity of CHIR-258, a multitargeted growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, in colon cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 11:3633–3641. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2129
Giles F, Fischer T, Cortes J, Garcia-Manero G, Beck J, Ravandi F, Masson E, Rae P, Laird G, Sharma S, Kantarjian H, Dugan M, Albitar M, Bhalla K (2006) A phase I study of intravenous LBH589, a novel cinnamic hydroxamic acid analogue histone deacetylase inhibitor, in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 12:4628–4635. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0511
Gravina GL, Marampon F, Giusti I, Carosa E, Di Sante S, Ricevuto E, Dolo V, Tombolini V, Jannini EA, Festuccia C (2012) Differential effects of PXD101 (belinostat) on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer models. Int J Oncol 40:711–720. doi:10.3892/ijo.2011.1270
Zhou X, Yang XY, Popescu NC (2012) Preclinical evaluation of combined antineoplastic effect of DLC1 tumor suppressor protein and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420:325–330. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.158
Lai MT, Yang CC, Lin TY, Tsai FJ, Chen WC (2008) Depsipeptide (FK228) inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells. Urol Oncol 26:182–189. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2007.01.020
Björkman M, Iljin K, Halonen P, Sara H, Kaivanto E, Nees M, Kallioniemi OP (2008) Defining the molecular action of HDAC inhibitors and synergism with androgen deprivation in ERG-positive prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 123:2774–2781. doi:10.1002/ijc.23885
Khandelwal A, Gediya L, Njar V (2008) MS-275 synergistically enhances the growth inhibitory effects of RAMBA VN/66-1 in hormone-insensitive PC-3 prostate cancer cells and tumours. Br J Cancer 98:1234–1243. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604295
Gediya LK, Belosay A, Khandelwal A, Purushottamachar P, Njar VC (2008) Improved synthesis of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDIs) (MS-275 and CI-994) and inhibitory effects of HDIs alone or in combination with RAMBAs or retinoids on growth of human LNCaP prostate cancer cells and tumor xenografts. Bioorg Med Chem 16:3352–3360. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.12.007
Wedel S, Hudak L, Seibel JM, Makarević J, Juengel E, Tsaur I, Wiesner C, Haferkamp A, Blaheta RA (2011) Impact of combined HDAC and mTOR inhibition on adhesion, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:479–491. doi:10.1007/s10585-011-9386-8
Gravina GL, Marampon F, Giusti I, Carosa E, Di Sante S, Ricevuto E, Dolo V, Tombolini V, Jannini EA, Festuccia C (2012) Differential effects of PXD101 (belinostat) on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer models. Int J Oncol 40:711–720. doi:10.3892/ijo.2011
Pili R, Salumbides B, Zhao M, Altiok S, Qian D, Zwiebel J, Carducci MA, Rudek MA (2012) Phase I study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat in combination with 13-cis retinoic acid in patients with solid tumours. Br J Cancer 106:77–84. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.527
Munster PN, Thurn KT, Thomas S, Raha P, Lacevic M, Miller A, Melisko M, Ismail-Khan R, Rugo H, Moasser M, Minton SE (2011) A phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat combined with tamoxifen for the treatment of patients with hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer. Br J Cancer 104:1828–1835. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.156
Munster P, Marchion D, Bicaku E, Lacevic M, Kim J, Centeno B, Daud A, Neuger A, Minton S, Sullivan D (2009) Clinical and biological effects of valproic acid as a histone deacetylase inhibitor on tumor and surrogate tissues: phase I/II trial of valproic acid and epirubicin/FEC. Clin Cancer Res 15:2488–2496. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1930
Yong WP, Goh BC, Soo RA, Toh HC, Ethirajulu K, Wood J, Novotny-Diermayr V, Lee SC, Yeo WL, Chan D, Lim D, Seah E, Lim R, Zhu J (2011) Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of an orally administered novel inhibitor of histone deacetylases, SB939, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. Ann Oncol 22:2516–2522. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq784
Festuccia C, Muzi P, Millimaggi D, Biordi L, Gravina GL, Speca S, Angelucci A, Dolo V, Vicentini C, Bologna M (2005) Molecular aspects of gefitinib antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in PTEN-positive and PTEN-negative prostate cancer cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:983–998. doi:10.1677/erc.1.00986
Festuccia C, Gravina GL, Biordi L, D’Ascenzo S, Dolo V, Ficorella C, Ricevuto E, Tombolini V (2009) Effects of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in prostate cancer cells in vitro. Prostate 69:1529–1537. doi:10.1002/pros.20995
Oh SJ, Erb HH, Hobisch A, Santer FR, Culig Z (2012) Sorafenib decreases proliferation and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inhibition of the androgen receptor and Akt signaling pathways. Endocr Relat Cancer 19:305–319. doi:10.1530/ERC-11-0298
Makhov P, Golovine K, Kutikov A, Teper E, Canter DJ, Simhan J, Uzzo RG, Kolenko VM (2012) Modulation of Akt/mTOR signaling overcomes sunitinib resistance in renal and prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0907
Wedel S, Hudak L, Seibel JM, Juengel E, Oppermann E, Haferkamp A, Blaheta RA (2011) Critical analysis of simultaneous blockage of histone deacetylase and multiple receptor tyrosine kinase in the treatment of prostate cancer. Prostate 71:722–735. doi:10.1002/pros.21288
Dey JH, Bianchi F, Voshol J, Bonenfant D, Oakeley EJ, Hynes NE (2010) Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors blocks PI3K/AKT signaling, induces apoptosis, and impairs mammary tumor outgrowth and metastasis. Cancer Res 70:4151–4162. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4479
Lamont FR, Tomlinson DC, Cooper PA, Shnyder SD, Chester JD, Knowles MA (2011) Small molecule FGF receptor inhibitors block FGFR-dependent urothelial carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 104:75–82. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6606016
Wesche J, Haglund K, Haugsten EM (2011) Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem J 437:199–213
Ortholan C, Durivault J, Hannoun-Levi JM, Guyot M, Bourcier C, Ambrosetti D, Safe S, Pagès G (2010) Bevacizumab/docetaxel association is more efficient than docetaxel alone in reducing breast and prostate cancer cell growth: a new paradigm for understanding the therapeutic effect of combined treatment. Eur J Cancer 46:3022–3036. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.021
Cai X, Zhai HX, Wang J, Forrester J, Qu H, Yin L, Lai CJ, Bao R, Qian C (2010) Discovery of 7-(4-(3-ethynylphenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yloxy)-N-hydroxyheptanamide (CUDc-101) as a potent multi-acting HDAC, EGFR, and HER2 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 53:2000–2009. doi:10.1021/jm901453q
Bruzzese F, Leone A, Rocco M, Carbone C, Piro G, Caraglia M, Di Gennaro E, Budillon A (2011) HDAC inhibitor vorinostat enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck by modulating ErbB receptor expression and reverting EMT. J Cell Physiol 226:2378–2390. doi:10.1002/jcp.22574
Lachenmayer A, Toffanin S, Cabellos L, Alsinet C, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Minguez B, Tsai HW, Ward SC, Thung S, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2012) Combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: additive preclinical efficacy of the HDAC inhibitor panobinostat with sorafenib. J Hepatol. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.009
Baradari V, Höpfner M, Huether A, Schuppan D, Scherübl H (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 alone or combined with bortezomib or sorafenib exhibits strong antiproliferative action in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 13:4458–4466
Juengel E, Engler J, Mickuckyte A, Jones J, Hudak L, Jonas D, Blaheta RA (2010) Effects of combined valproic acid and the epidermal growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor AEE788 on renal cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro. BJU Int 105:549–557. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08759.x
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Karen Nelson for critically reading the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stefan Vallo and Jens Mani contributed equally to this work.
Axel Haferkamp and Roman A. Blaheta contributed equally as senior authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallo, S., Mani, J., Stastny, M. et al. The prostate cancer blocking potential of the histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 is not enhanced by the multi receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor TKI258. Invest New Drugs 31, 265–272 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9851-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9851-5