Summary
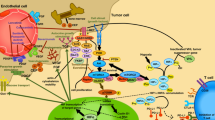
Several angiogenic mechanisms are involved in the pathology of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Increasing knowledge of angiogenesis and the associated signalling pathways has led to the development of targeted antiangiogenic agents for the treatment of metastatic RCC and the introduction of these agents has significantly improved outcomes for these patients. This article provides an overview of the angiogenic mechanisms implicated in RCC, focusing on the main vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathways. Targeted antiangiogenic agents for the treatment of mRCC include receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (such as sunitinib, sorafenib, pazopanib, axitinib, cediranib and tivozanib), monoclonal antibodies (such as bevacizumab) and mTOR inhibitors (such as temsirolimus and everolimus). In this article, we consider the modes of action of these targeted agents and their differing target receptor profiles and we also evaluate how these correlate with their clinical efficacy and tolerability profiles.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM (1996) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 335:865–875
Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Schwartz LH, Reuter V, Russo P, Marion S, Mazumdar M (2004) Prognostic factors for survival in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 22:454–463
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86:353–364
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Duensing A, Heinrich MC, Fletcher CD, Fletcher JA (2004) Biology of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: KIT mutations and beyond. Cancer Invest 22:106–116
Marmor MD, Skaria KB, Yarden Y (2004) Signal transduction and oncogenesis by ErbB/HER receptors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:903–913
Rini BI, Small EJ (2005) Biology and clinical development of vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 23:1028–1043
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 359:(abstr)
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8:579–591
Qian CN, Huang D, Wondergem B, Teh BT (2009) Complexity of tumor vasculature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 115:2282–2289
Guo P, Hu B, Gu W, Xu L, Wang D, Huang HJ, Cavenee WK, Cheng SY (2003) Platelet-derived growth factor-B enhances glioma angiogenesis by stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor expression in tumor endothelia and by promoting pericyte recruitment. Am J Pathol 162:1083–1093
Pietras K, Sjoblom T, Rubin K, Heldin CH, Ostman A (2003) PDGF receptors as cancer drug targets. Cancer Cell 3:439–443
Pietras K, Hanahan D (2005) A multitargeted, metronomic, and maximum-tolerated dose “chemo-switch” regimen is antiangiogenic, producing objective responses and survival benefit in a mouse model of cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:939–952
Xu L, Tong R, Cochran DM, Jain RK (2005) Blocking platelet-derived growth factor-D/platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta signaling inhibits human renal cell carcinoma progression in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res 65:5711–5719
Sulzbacher I, Birner P, Traxler M, Marberger M, Haitel A (2003) Expression of platelet-derived growth factor-alpha alpha receptor is associated with tumor progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 120:107–112
Bousquet G, Dreyer C, Faivre RE (2007) TOR (target of rapamycin) as an anti-cancer target. Drug Discov Today: Ther Strateg 4:211–217
Le Tourneau C, Faivre S, Serova M, Raymond E (2008) mTORC1 inhibitors: is temsirolimus in renal cancer telling us how they really work? Br J Cancer 99:1197–1203
Cho D, Signoretti S, Regan M, Meir JW, Atkins MB (2007) The role of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in the treatment of advanced renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13: (abstr)
Velickovic M, Delahunt B, McIver B, Grebe SK (2002) Intragenic PTEN/MMAC1 loss of heterozygosity in conventional (clear-cell) renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. Mod Pathol 15:479–485
Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM (2003) SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2:471–478
Beeram M, Patnaik A, Rowinsky EK (2005) Raf: a strategic target for therapeutic development against cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:6771–6790
Gomez-Rivera F, Santillan-Gomez AA, Younes MN, Kim S, Fooshee D, Zhao M, Jasser SA, Myers JN (2007) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor, AZD2171, inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling and growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer in an orthotopic nude mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 13:4519–4527
Kim DW, Jo YS, Jung HS, Chung HK, Song JH, Park KC, Park SH, Hwang JH, Rha SY, Kweon GR, Lee SJ, Jo KW, Shong M (2006) An orally administered multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, SU11248, is a novel potent inhibitor of thyroid oncogenic RET/papillary thyroid cancer kinases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4070–4076
Hurwitz HI, Dowlati A, Saini S, Savage S, Suttle AB, Gibson DM, Hodge JP, Merkle EM, Pandite L (2009) Phase I trial of pazopanib in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:4220–4227
Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G, Schreck RE, Abrams TJ, Ngai TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Carver J, Chan E, Moss KG, Haznedar JO, Sukbuntherng J, Blake RA, Sun L, Tang C, Miller T, Shirazian S, McMahon G, Cherrington JM (2003) In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res 9:327–337
Murray LJ, Abrams TJ, Long KR, Ngai TJ, Olson LM, Hong W, Keast PK, Brassard JA, O’Farrell AM, Cherrington JM, Pryer NK (2003) SU11248 inhibits tumor growth and CSF-1R-dependent osteolysis in an experimental breast cancer bone metastasis model. Clin Exp Metastasis 20:757–766
O’Farrell AM, Abrams TJ, Yuen HA, Ngai TJ, Louie SG, Yee KW, Wong LM, Hong W, Lee LB, Town A, Smolich BD, Manning WC, Murray LJ, Heinrich MC, Cherrington JM (2003) SU11248 is a novel FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Blood 101:3597–3605
Podar K, Tonon G, Sattler M, Tai YT, Legouill S, Yasui H, Ishitsuka K, Kumar S, Kumar R, Pandite LN, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2006) The small-molecule VEGF receptor inhibitor pazopanib (GW786034B) targets both tumor and endothelial cells in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19478–19483
Hu-Lowe DD, Zou HY, Grazzini ML, Hallin ME, Wickman GR, Amundson K, Chen JH, Rewolinski DA, Yamazaki S, Wu EY, McTigue MA, Murray BW, Kania RS, O’Connor P, Shalinsky DR, Bender SL (2008) Nonclinical antiangiogenesis and antitumor activities of axitinib (AG-013736), an oral, potent, and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases 1, 2, 3. Clin Cancer Res 14:7272–7283
Takeda M, Arao T, Yokote H, Komatsu T, Yanagihara K, Sasaki H, Yamada Y, Tamura T, Fukuoka K, Kimura H, Saijo N, Nishio K (2007) AZD2171 shows potent antitumor activity against gastric cancer over-expressing fibroblast growth factor receptor 2/keratinocyte growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 13:3051–3057
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA (2004) BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 64:7099–7109
Wedge SR, Kendrew J, Hennequin LF, Valentine PJ, Barry ST, Brave SR, Smith NR, James NH, Dukes M, Curwen JO, Chester R, Jackson JA, Boffey SJ, Kilburn LL, Barnett S, Richmond GH, Wadsworth PF, Walker M, Bigley AL, Taylor ST, Cooper L, Beck S, Jurgensmeier JM, Ogilvie DJ (2005) AZD2171: a highly potent, orally bioavailable, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 65:4389–4400
Harris PA, Boloor A, Cheung M, Kumar R, Crosby RM, vis-Ward RG, Epperly AH, Hinkle KW, Hunter RN III, Johnson JH, Knick VB, Laudeman CP, Luttrell DK, Mook RA, Nolte RT, Rudolph SK, Szewczyk JR, Truesdale AT, Veal JM, Wang L, Stafford JA (2008) Discovery of 5-[[4-[(2,3-dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)methylamino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2-m ethyl-benzenesulfonamide (Pazopanib), a novel and potent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor. J Med Chem 51:4632–4640
Schmidinger M, Bellmunt J (2010) Plethora of agents, plethora of targets, plethora of side effects in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev 36:416–424
Pfizer Inc; SUTENT, Summary of product characteristics; December 2010
Chang YS, Adnane J, Trail PA, Levy J, Henderson A, Xue D, Bortolon E, Ichetovkin M, Chen C, McNabola A, Wilkie D, Carter CA, Taylor IC, Lynch M, Wilhelm S (2007) Sorafenib (BAY 43–9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59:561–574
Bayer Heathcare AG (December 2010) Sorafenib, Summary of product characteristics
Kumar R, Knick VB, Rudolph SK, Johnson JH, Crosby RM, Crouthamel MC, Hopper TM, Miller CG, Harrington LE, Onori JA, Mullin RJ, Gilmer TM, Truesdale AT, Epperly AH, Boloor A, Stafford JA, Luttrell DK, Cheung M (2007) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlation from mouse to human with pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Mol Cancer Ther 6:2012–2021
GlaxoSmithKline (2011) Votrient® (pazopanib), Prescribing information, June 2010
Inai T, Mancuso M, Hashizume H, Baffert F, Haskell A, Baluk P, Hu-Lowe DD, Shalinsky DR, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, McDonald DM (2004) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in cancer causes loss of endothelial fenestrations, regression of tumor vessels, and appearance of basement membrane ghosts. Am J Pathol 165:35–52
De LA, Normanno N (2010) Tivozanib, a pan-VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the potential treatment of solid tumors. IDrugs 13:636–645
Gerber HP, Ferrara N (2005) Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res 65:671–680
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, Ferrara N (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 362:841–844
Roche Products Ltd (January 2011) Avastin, Summary of product characteristics
Pfizer Inc (November 2010) Torisel, Summary of product characteristics
Boulay A, Zumstein-Mecker S, Stephan C, Beuvink I, Zilbermann F, Haller R, Tobler S, Heusser C, O’Reilly T, Stolz B, Marti A, Thomas G, Lane HA (2004) Antitumor efficacy of intermittent treatment schedules with the rapamycin derivative RAD001 correlates with prolonged inactivation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cancer Res 64:252–261
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grunwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A (2008) Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 372:449–456
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd.; Afinitor (everolimus), Summary of Product Characteristics, May 2010. -->
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O’Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ (2007) Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:2271–2281
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:115–124
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler WM, Vaena DA, Ou SS, Archer L, Atkins JN, Picus J, Czaykowski P, Dutcher J, Small EJ (2008) Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol 26:5422–5428
Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, Chevreau C, Filipek M, Melichar B, Bajetta E, Gorbunova V, Bay JO, Bodrogi I, Jagiello-Gruszfeld A, Moore N (2007) Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet 370:2103–2111
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Dror Michaelson M, Bukowski RM, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Pili R, Bjarnason GA, Garcia-del-Muro X, Sosman JA, Solska E, Wilding G, Thompson JA, Kim ST, Chen I, Huang X, Figlin RA (2009) Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib versus interferon alfa in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:3584–3590
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA, Kavina A, Zarba JJ, Chen M, McCann L, Pandite L, Roychowdhury DF, Hawkins RE (2010) Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 28:1061–1068
Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT, Chan KW, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Edeen PT, Faraoni R, Floyd M, Hunt JP, Lockhart DJ, Milanov ZV, Morrison MJ, Pallares G, Patel HK, Pritchard S, Wodicka LM, Zarrinkar PP (2008) A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 26:127–132
Patel PH, Chaganti RS, Motzer RJ (2006) Targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 94:614–619
Sridhar SS, Mackenzie MJ, Hotte SJ, Mukherjee SD, Kollmannsberger C, Haider MA, Chen EX, Wang R, Srinivasan R, Ivy SP, Moore MJ; Activity of cediranib (AZD2171) in patients (pts) with previously untreated metastatic renal cell cancer (RCC). A phase II trial of the PMH Consortium. 2008, pp (Abstract 5047)
Rini BI, Wilding G, Hudes G, Stadler WM, Kim S, Tarazi J, Rosbrook B, Trask PC, Wood L, Dutcher JP (2009) Phase II study of axitinib in sorafenib-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4462–4468
Rixe O, Bukowski RM, Michaelson MD, Wilding G, Hudes GR, Bolte O, Motzer RJ, Bycott P, Liau KF, Freddo J, Trask PC, Kim S, Rini BI (2007) Axitinib treatment in patients with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal-cell cancer: a phase II study. Lancet Oncol 8:975–984
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grunwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Kay A, Ravaud A (2010) Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer 116:4256–4265
Mills EJ, Rachlis B, O’Regan C, Thabane L, Perri D (2009) Metastatic renal cell cancer treatments: An indirect comparison meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 9:34
Escudier B, Bellmunt J, Negrier S, Bajetta E, Melichar B, Bracarda S, Ravaud A, Golding S, Jethwa S, Sneller V (2010) Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus Interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): final analysis of overall survival. J Clin Oncol 28:2144–2150
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler WM, Vaena DA, Archer L, Atkins JN, Picus J, Czaykowski P, Dutcher J, Small EJ (2010) Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa versus interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results of CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol 28:2137–2143
Sternberg CN, Hawkins RE, Szczylik C, Davis ID, Wagstaff J, McCann L, Chen M, Rubin SD (2010) Randomized, double blind phase III study of pazopanib in patients with advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC): Final overall survival (OS) results. Oral presentation at the 35th European Society of Medical Oncology Congress, Milan, Italy
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Staehler M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Anderson S, Hofilena G, Shan M, Pena C, Lathia C, Bukowski RM (2009) Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Final efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol 27:3312–3318
Dutcher JP, de Souza P, McDermott D, Figlin RA, Berkenblit A, Thiele A, Krygowski M, Strahs A, Feingold J, Hudes G (2009) Effect of temsirolimus versus interferon-alpha on outcome of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma of different tumor histologies. Med Oncol 26:202–209
Atkins MB, Choueiri TK, Cho D, Regan M, Signoretti S (2009) Treatment selection for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 115:2327–2333
Jacobsen J, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T, Ljungberg B (2006) Different isoform patterns for vascular endothelial growth factor between clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 97:1102–1108
Ljungberg BJ, Jacobsen J, Rudolfsson SH, Lindh G, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T (2006) Different vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF-receptor 1 and -2 mRNA expression profiles between clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 98:661–667
Maulik G, Shrikhande A, Kijima T, Ma PC, Morrison PT, Salgia R (2002) Role of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:41–59
Bhargava P, Nosov DA, Esteves B, Al-Adhami M, Lipatov O, Lyulko A, Anishchenko AA, Chacko RT, Doval DC, Slichenmyer W (2010) Phase 2 randomized discontinuation trial (RDT) of tivozanib in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Results in patients randomized to tivozanib vs placebo. Oral presentation at the 35th European Society of Medical Oncology Congress, Milan, Italy
Kamba T, McDonald DM (2007) Mechanisms of adverse effects of anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Br J Cancer 96:1788–1795
Verheul HM, Pinedo HM (2007) Possible molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of angiogenesis inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer 7:475–485
Robert C, Faivre S, Raymond E, Armand JP, Escudier B (2005) Subungual splinter hemorrhages: a clinical window to inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors? Ann Intern Med 143:313–314
Iitaka M, Miura S, Yamanaka K, Kawasaki S, Kitahama S, Kawakami Y, Kakinuma S, Oosuga I, Wada S, Katayama S (1998) Increased serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels and intrathyroidal vascular area in patients with Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:3908–3912
Ramsden JD (2000) Angiogenesis in the thyroid gland. J Endocrinol 166:475–480
Viglietto G, Romano A, Manzo G, Chiappetta G, Paoletti I, Califano D, Galati MG, Mauriello V, Bruni P, Lago CT, Fusco A, Persico MG (1997) Upregulation of the angiogenic factors PlGF, VEGF and their receptors (Flt-1, Flk-1/KDR) by TSH in cultured thyrocytes and in the thyroid gland of thiouracil-fed rats suggest a TSH-dependent paracrine mechanism for goiter hypervascularization. Oncogene 15:2687–2698
Wang JF, Milosveski V, Schramek C, Fong GH, Becks GP, Hill DJ (1998) Presence and possible role of vascular endothelial growth factor in thyroid cell growth and function. J Endocrinol 157:5–12
Eskens FA, Verweij J (2006) The clinical toxicity profile of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) targeting angiogenesis inhibitors; a review. Eur J Cancer 42:3127–3139
Ferraresi V, Catricala C, Ciccarese M, Ferrari A, Zeuli M, Cognetti F (2006) Severe skin reaction in a patient with gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with imatinib mesylate. Anticancer Res 26:4771–4774
O’Donnell A, Faivre S, Burris HA III, Rea D, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Shand N, Lane HA, Hazell K, Zoellner U, Kovarik JM, Brock C, Jones S, Raymond E, Judson I (2008) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 26:1588–1595
Raymond E, Alexandre J, Faivre S, Vera K, Materman E, Boni J, Leister C, Korth-Bradley J, Hanauske A, Armand JP (2004) Safety and pharmacokinetics of escalated doses of weekly intravenous infusion of CCI-779, a novel mTOR inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:2336–2347
Drevs J, Siegert P, Medinger M, Mross K, Strecker R, Zirrgiebel U, Harder J, Blum H, Robertson J, Jurgensmeier JM, Puchalski TA, Young H, Saunders O, Unger C (2007) Phase I clinical study of AZD2171, an oral vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:3045–3054
Siemann DW, Brazelle WD, Jurgensmeier JM (2009) The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor cediranib (Recentin; AZD2171) inhibits endothelial cell function and growth of human renal tumor xenografts. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:897–903
Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, Mino M, Cohen KS, Scadden DT, Hartford AC, Fischman AJ, Clark JW, Ryan DP, Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Chen HX, Shellito PC, Lauwers GY, Jain RK (2004) Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 10:145–147
Rini BI, Schiller JH, Fruehauf JP, Cohen EE, Tarazi JC, Rosbrook B, Ricart AD, Olszanski AJ, Kim S, Spano J-P (2008) Association of diastolic blood pressure (dBP) ≥90 mmHg with overall survival (OS) in patients treated with axitinib (AG- 013736). J Clin Oncol 26:(abstr)
Rini BI, Cohen DP, Lu D, Chen I, Hariharan S, Gore ME, Figlin RA, Baum MS, Motzer RJ (2010) Hypertension (HTN) as a biomarker of efficacy in patients (pts) with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) treated with sunitinib. American Socierty for Clinical Oncology 2010 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium Abstract 312
Carlomagno F, Anaganti S, Guida T, Salvatore G, Troncone G, Wilhelm SM, Santoro M (2006) BAY 43–9006 inhibition of oncogenic RET mutants. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:326–334
Schmidinger M, Vogl UM, Bojic M, Lamm W, Heinzl H, Haitel A, Clodi M, Kramer G, Zielinski CC (2010) Hypothyroidism in patients with renal cell carcinoma: blessing or curse? Cancer Epub ahead of print
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd. (2009) Afinitor (everolimus), Summary of Product Characteristics, March 2009
Schmidinger M, Zielinski CC, Vogl UM, Bojic A, Bojic M, Schukro C, Ruhsam M, Hejna M, Schmidinger H (2008) Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib and sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:5204–5212
Kido M, Du L, Sullivan CC, Li X, Deutsch R, Jamieson SW, Thistlethwaite PA (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha reduces infarction and attenuates progression of cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in the mouse. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:2116–2124
Parisi Q, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Abbate A, Santini D, Vasaturo F, Scarpa S, Bussani R, Leone AM, Petrolini A, Silvestri F, Biasucci LM, Baldi A (2005) Hypoxia inducible factor-1 expression mediates myocardial response to ischemia late after acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 99:337–339
Waltenberger J (1997) Modulation of growth factor action: implications for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Circulation 96:4083–4094
Merseburger AS, Simon A, Waalkes S, Kuczyk MA (2009) Sorafenib reveals efficacy in sequential treatment of metastatic renal cell cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 9:1429–1434
www.clinicaltrials.gov (2010)
Sosman J, Puzanov I (2009) Combination targeted therapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 115:2368–2375
Acknowledgements
Editorial support for this manuscript was provided by Cherry Bwalya and Caroline Masterman at ACUMED (Tytherington, UK) and was funded by Pfizer, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Négrier, S., Raymond, E. Antiangiogenic treatments and mechanisms of action in renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 30, 1791–1801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9677-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9677-6