Abstract
Background
Nodular gastritis (NG) has been reported in adult dyspeptic patients, whereas information on NG in asymptomatic patients is limited.
Aims
To evaluate the prevalence, clinico-epidemiological characteristics, and expression profiles of inflammatory cytokines or cytokine regulatory factors of NG in asymptomatic adults.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted prospectively using 2,579 consecutive asymptomatic subjects who underwent screening esophagogastroduodenoscopy. The expression of inflammatory cytokines or cytokine regulatory factors in the gastric mucosa of NG patients was evaluated using immunofluorescence staining.
Results
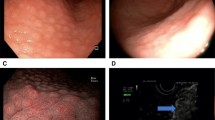
NG was diagnosed in 52 patients (2.0%) and showed a predilection for females (M:F = 1:1.89) and young adults (median age: 34 years; range: 25–51 years). All NG patients were positive for Helicobacter pylori infection. Based on multivariate analysis, the risk of NG was increased in patients younger than 40 years (OR, 7.57; 95% CI, 3.76–15.24) and of the female gender (OR, 2.12; 95% CI; 1.05–4.28). Immunofluorescent staining for interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-10, IL-18, IL-18 binding protein, IL-32, IL-33, and neutrophil proteinase 3 (PR3) was performed on cryosections of gastric mucosa. Interestingly, the expression of PR3 was highly increased in the gastric biopsies from asymptomatic NG patients but was expressed infrequently in the controls.
Conclusions
Asymptomatic NG is associated with H. pylori infection, and a predilection for this condition exists in young females. The PR3 expression of gastric mucosa might play an important role in the pathogenesis of NG.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takemoto M, Mizuno Y. Endoscopic diagnosis and gastric biopsy in chronic gastritis. Gastroenterol Endosc. 1962;4:310–319.
Czinn SJ, Dahms BB, Jacobs GH, Kaplan B, Rothstein FC. Campylobacter-like organisms in association with symptomatic gastritis in children. J Pediatr. 1986;109:80–83.
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Yoshihara M, et al. Nodular gastritis in adults is caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci. 2003;48:968–975.
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Yoshihara M, et al. Five cases of nodular gastritis and gastric cancer: a possible association between nodular gastritis and gastric cancer. Dig Liver Dis. 2002;34:819–820.
Chen MJ, Shih SC, Wang TE, et al. Endoscopic patterns and histopathological features after eradication therapy in Helicobacter pylori-associated nodular gastritis. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:1893–1897.
Dwivedi M, Misra SP, Misra V. Nodular gastritis in adults: clinical features, endoscopic appearance, histopathological features, and response to therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:943–947.
Shimatani T, Inoue M, Iwamoto K, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection, endoscopic gastric findings and dyspeptic symptoms among a young japanese population born in the 1970 s. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:1352–1357.
Sokmensuer C, Onal IK, Yeniova O, et al. What are the clinical implications of nodular gastritis? Clues from histopathology. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:2150–2154.
Shiotani A, Kamada T, Kumamoto M, et al. Nodular gastritis in japanese young adults: endoscopic and histological observations. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:610–615.
Chen MJ, Wang TE, Chang WH, et al. Nodular gastritis: an endoscopic indicator of Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:2662–2666.
Koh H, Noh TW, Baek SY, Chung KS. Nodular gastritis and pathologic findings in children and young adults with Helicobacter pylori infection. Yonsei Med J. 2007;48:240–246.
El-Omar EM, Rabkin CS, Gammon MD, et al. Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1193–1201.
Eaton KA, Mefford M, Thevenot T. The role of T cell subsets and cytokines in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in mice. J Immunol. 2001;166:7456–7461.
Gewirtz AT, Yu Y, Krishna US, Israel DA, Lyons SL, Peek RM Jr. Helicobacter pylori i flagellin evades toll-like receptor 5-mediated innate immunity. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:1914–1920.
Moran AP. Lipopolysaccharide in bacterial chronic infection: insights from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide and lipid A. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007;297:307–319.
Bulek K, Swaidani S, Aronica M, Li X. Epithelium. The interplay between innate and Th2 immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010;88:257–268.
Akcam M, Artan R, Gelen T, et al. Long-term aspects of nodular gastritis in children. Pediatr Int. 2007;49:220–225.
Bujanover Y, Konikoff F, Baratz M. Nodular gastritis and Helicobacter pylori. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990;11:41–44.
Kamada T, Tanaka A, Haruma K. Nodular gastritis and gastric cancer. Nippon Rinsho. 2005;63:557–559.
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Hiyama T, et al. High incidence of B-cell monoclonality in follicular gastritis: a possible association between follicular gastritis and malt lymphoma. Virchows Arch. 2002;440:376–380.
Al-Enezi SA, Alsurayei SA, Aly NY, et al. Endoscopic nodular gastritis in dyspeptic adults: prevalence and association with Helicobacter pylori infection. Med Princ Pract. 2010;19:40–45.
Nakamura S, Mitsunaga A, Imai R, et al. Clinical evaluation of nodular gastritis in adults. Dig Endosc. 2007;19:74–79.
Jung KW, Park S, Won YJ, et al. Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2011. Cancer Res Treat. 2011;43:12–18.
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Imanishi J. Helicobacter pylori CAGA gene and expression of cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:1744–1752.
Mattsson A, Quiding-Jarbrink M, Lonroth H, et al. Antibody-secreting cells in the stomachs of symptomatic and asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori-infected subjects. Infect Immun. 1998;66:2705–2712.
D’Elios MM, Manghetti M, Almerigogna F, et al. Different cytokine profile and antigen-specificity repertoire in Helicobacter pylori-specific T cell clones from the antrum of chronic gastritis patients with or without peptic ulcer. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:1751–1755.
Crabtree JE. Immune and inflammatory responses to Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996;215:3–10.
Blaser MJ. Hypotheses on the pathogenesis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:720–727.
Shimatani T, Inoue M, Iwamoto K, et al. Gastric acidity in patients with follicular gastritis is significantly reduced, but can be normalized after eradication for Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter. 2005;10:256–265.
Israel DM, Hassall E. Treatment and long-term follow-up of Helicobacter pylori-associated duodenal ulcer disease in children. J Pediatr. 1993;123:53–58.
Kamada T, Tanaka A, Yamanaka Y, et al. Nodular gastritis with Helicobacter pylori is strongly associated with diffuse-type gastric cancer in young patients. Dig Endosc. 2007;19:180–184.
Fukase K, Kato M, Kikuchi S, et al. Effect of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on incidence of metachronous gastric carcinoma after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer: AN open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:392–397.
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:784–789.
Kato S, Sugiyama T, Kudo M, et al. Caga antibodies in japanese children with nodular gastritis or peptic ulcer disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:68–70.
Chung J, Lim SJ, Han TH. Expression of lewis antigen in gastric mucosa of children with Helicobacter pylori infection. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2007;14:97–103.
Shirota K, LeDuy L, Yuan SY, Jothy S. Interleukin-6 and its receptor are expressed in human intestinal epithelial cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58:303–308.
Naef M, Ishiwata T, Friess H, et al. Differential localization of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in human gastric mucosa and overexpression in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1997;71:131–137.
Lindholm C, Quiding-Jarbrink M, Lonroth H, Hamlet A, Svennerholm AM. Local cytokine response in Helicobacter pylori-infected subjects. Infect Immun. 1998;66:5964–5971.
Ohara H, Isomoto H, Wen CY, et al. Expression of mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 on vascular endothelium of gastric mucosa in patients with nodular gastritis. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2701–2705.
Padrines M, Wolf M, Walz A, Baggiolini M. Interleukin-8 processing by neutrophil elastase, cathepsin g and proteinase-3. FEBS Lett. 1994;352:231–235.
Csernok E, Szymkowiak CH, Mistry N, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) expression and interaction with proteinase 3 (PR3) in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (AN CA)-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996;105:104–111.
Robache-Gallea S, Morand V, Bruneau JM, et al. In vitro processing of human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23688–23692.
Coeshott C, Ohnemus C, Pilyavskaya A, et al. Converting enzyme-independent release of tumor necrosis factor alpha and il-1beta from a stimulated human monocytic cell line in the presence of activated neutrophils or purified proteinase 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1999;96:6261–6266.
Sugawara S, Uehara A, Nochi T, et al. Neutrophil proteinase 3-mediated induction of bioactive il-18 secretion by human oral epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:6568–6575.
Novick D, Rubinstein M, Azam T, et al. Proteinase 3 is an IL-32 binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3316–3321.
Acknowledgment
This paper was supported by Konkuk University in 2009.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Sung Noh Hong and Seunghyun Jo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S.N., Jo, S., Jang, J.H. et al. Clinical Characteristics and the Expression Profiles of Inflammatory Cytokines/Cytokine Regulatory Factors in Asymptomatic Patients with Nodular Gastritis. Dig Dis Sci 57, 1486–1495 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2053-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2053-3