Abstract
Background
Hepatic steatosis in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients has been shown to enhance the progression of liver fibrosis and decrease the response to antiviral therapy.
Aims
We aimed to determine the role of HCV genotype 4 (HCV-G4) in the prevalence of hepatic steatosis, its impact on antiviral therapy, and its associations and predictive factors in comparison to HCV-G1-infected patients.
Methods
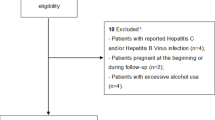
Treatment-naïve HCV patients who were started on pegylated interferon a-2b plus ribavirin therapy in two centers in Saudi Arabia were included. The severity of steatosis was assessed using the METAVIR and NAS (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD] activity score) scoring systems. Sustained virological response (SVR) was studied in relation to the degree of steatosis. Associations between steatosis and multiple demographic, laboratory, and virological factors were examined. HCV-G1 and HCV-G4 patients were compared.
Results
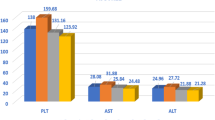
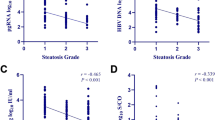
A total of 116 patients (HCV-G4 85 [73.3%]; HCV-G1 31 [26.7%]) were included. The mean age was 50.4 ± 10.7 years and 56.9% were males. In terms of steatosis grading using the NAS scoring system, 50% had steatosis grade 0, 26.7% grade 1, 14.7% grade 2, and 8.6% grade 3, while the overall staging of steatosis revealed that 43.1% had mild steatosis, 42.2% moderate, and 14.7% severe. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), platelet count, body mass index (BMI), cholesterol level, presence of hyperlipidemia, liver histology stage, and grade were significantly correlated with hepatic steatosis in one or more of the statistical analyses. Twenty-two out of 55 patients (40.0%) had an SVR in the mild steatosis group, compared to 52.7% in the moderate group and 7.3% in the severe group (P = 0.03). The HCV genotype did not correlate with steatosis or SVR.
Conclusion
Our study confirms the high prevalence of steatosis in HCV-G4 and HCV-G1 patients, but with no difference in the grade or score of steatosis between the two genotypes. The grade of steatosis correlates with GGT, platelet count, and BMI, while the NAS score of steatosis correlates with response to antiviral therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alter MJ. Epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;7:2436–2441.
Soresi M, Tripi S, Franco V, et al. Impact of liver steatosis on the antiviral response in the hepatitis C virus-associated chronic hepatitis. Liver Int. 2006;26:1119–1125.
Osoba AO. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2002;23:7–12.
Negro F. Mechanisms and significance of liver steatosis in hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;14:6756–6765.
Alaei M, Negro F. Hepatitis C virus and glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34:692–700.
Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996;24:289–293.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321.
Khattab MA, Abdel-Fattah ME, Eslam M, et al. Hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C patients: implication for therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; (Epub ahead of print).
Leandro G, Mangia A, Hui J, et al. Relationship between steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1636–1642.
Tsochatzis E, Papatheodoridis GV, Manesis EK, et al. Hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C is mainly because of metabolic factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:634–641.
Reddy KR, Govindarajan S, Marcellin P, et al. Hepatic steatosis in chronic hepatitis C: baseline host and viral characteristics and influence on response to therapy with peginterferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin. J Viral Hepat. 2008;15(2):129–136.
Khattab M, Eslam M, Sharwae MA, et al. Insulin resistance predicts rapid virologic response to peginterferon/ribavirin combination therapy in hepatitis C genotype 4 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; (Epub ahead of print).
Esmat G, El Akel W, Metwally M, et al. Improvement of steatosis after interferon therapy in HCV genotype 4 is related to weight loss. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2009;28:45–48.
Patton HM, Patel K, Behling C, et al. The impact of steatosis on disease progression and early and sustained treatment response in chronic hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol. 2004;40:484–490.
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, et al. Efficacy of interferon monotherapy to 394 consecutive naïve cases infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 2a in Japan: therapy efficacy as consequence of tripartite interaction of viral, host and interferon treatment-related factors. J Hepatol. 2002;37:831–836.
Lo Iacono O, Venezia G, Petta S, et al. The impact of insulin resistance, serum adipocytokines and visceral obesity on steatosis and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25(10):1181–1191.
Bressler BL, Guindi M, Tomlinson G, et al. High body mass index is an independent risk factor for nonresponse to antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:639–644.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the efforts of Mabel Kwei, Esther Robles, Grace Angeles, Abeer Salota, Alhassan Khalafahllah Hassan, and Waleed Saud Al-Zwidan in retrieving the patient records and biopsy slides, collecting the data, and other logistical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AlQaraawi, A.M., Sanai, F.M., Al-Husseini, H. et al. Prevalence and Impact of Hepatic Steatosis on the Response to Antiviral Therapy in Saudi Patients with Genotypes 1 and 4 Chronic Hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 56, 1222–1228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1417-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1417-9