Abstract
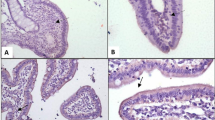
Small intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) play a major role in the absorption of nutrients and toxins. Due to the similarity of genome-wide single copy protein orthologues between cattle and human, establishment of ruminant’s primary small IEC culture could be a valuable tool for toxicity studies. Therefore, the current study focused on the development and characterization of buffalo IEC culture, as cattle slaughter is banned in India. The buffalo jejunum fragments were washed consecutively several times in saline, warm phosphate buffered saline (PBS), PBS with 5 mM dithiothreitol, digesting solution and 2% sorbitol in PBS. The cells were cultured on 17 µg/cm2 collagen coated plates and transwell plates with serum (2% Fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 10% FBS) and serum-free culture conditions. The cells were differentiated into typical epithelial cobblestone morphology from day 5 onwards in 50% successful cultures. The cultured IEC were characterized by gene expression of epithelial cell markers, cytokeratin and vimentin, and enterocyte markers like villin, zonula occluden (ZO1), fatty acid binding protein 2 (FABP2) and small intestinal peptidase (IP). Based on the morphology and gene expression profile, 10% FBS has been recommended for culturing primary buffalo IEC on collagen coated plates for 10 days. However, 50% of the successful cultures could not show epithelial phenotype on 10% FBS culture conditions even on collagen coated plates. Interestingly, undifferentiated IEC showed an increasing expression of FABP2, IP and ZO1 transcripts compared to differentiated intestinal cells with 10% FBS on collagen plates. Therefore, future studies are needed to understand the role of FABP2, IP and ZO1 in differentiation of buffalo IEC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IEC:
-
Intestinal epithelial cells
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- ZO1:
-
Zonula occludens
- FABP2:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 2
- IP:
-
Intestinal peptidase
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- ITS:
-
Insulin Transferrin Selenium
- cDNA:
-
complementary deoxyribonucleic acid
- dNTP:
-
Deoxynucleotide triphosphate
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction
- eTEM:
-
Experiments that showed typical epithelial morphology
- euTEM:
-
Experiments that did not show typical epithelial morphology
- RPLP:
-
Ribosomal Protein Lateral Stalk Subunit P1
References
Arpin M, Pringault E, Finidori J, Garcia A, Jeltsch JM, Vandekerckhove J, Louvard D (1988) Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J Cell Biol 107:1759–1766
Athman R, Fernandez MI, Gounon P, Sansonetti P, Louvard D, Philpott D, Robine S (2005) Shigella flexneri infection is dependent on villin in the mouse intestine and in primary cultures of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol 7:1109–1116
Autrup H, Stoner GD, Jackson F, Harris CC, Shamsuddin AKM, Barrett LA, Trump BF (1978) Explant culture of rat colon: a model system for studying metabolism of chemical carcinogens. In vitro 14:868–877
Benya RV, Schmidt LN, Sahi J, Layden TJ, Rao MC (1991) Isolation, characterization, and attachment of rabbit distal colon epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 101:692–702
Birkner S, Weber S, Dohle A, Schmahl G, Follmann W (2004) Growth and characterisation of primary bovine colon epithelial cells in vitro. Altern Lab Anim 32:555–571
Booth C, Patel S, Bennion GR, Potten CS (1994) The isolation and culture of adult mouse colonic epithelium. Epithel Cell Biol 4:76–86
Chandrakasan G, Hwang CB, Ryder M, Bhatnagar RS (1990) Keratin expression in cultures of adult human epidermal cells. Cell Mol Biol 37:847–852
Chen R, Zou Y, Mao D, Sun D, Gao G, Shi J, Liu X, Zhu C, Yang M, Ye W, Hao Q, Li R, Yu L (2014) The general amino acid control pathway regulates mTOR and autophagy during serum/glutamine starvation. J Cell Biol 206:173–182
Chopra DP, Dombkowski AA, Stemmer PM, Parker GC (2010) Intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Stem cells Dev 19:131–142
Darimont C, Gradoux N, Persohn E, Cumin F, Pover AD (2000) Effects of intestinal fatty acid-binding protein overexpression on fatty acid metabolism in Caco-2 cells. J Lipid Res 41:84–92
Evans GS, Flint N, Somers AS, Eyden B, Potten CS (1992) The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures. J Cell Sci 101:219–231
Evans GS, Flint N, Potten CS (1994) Primary cultures for studies of cell regulation and physiology in intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol 56:399–417
Fairweather SJ, Broer A, O’Mara ML, Broer S (2012) Intestinal peptidases form functional complexes with the neutral amino acid transporter BoAT1. Biochem J 446:135–148
Follmann W, Weber S, Birkner S (2000) Primary cell cultures of bovine colon epithelium: isolation and cell culture of colonocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 14:435–445
Friederich E, Huet C, Arpin M, Louvard D (1989) Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell 59:461–475
Fukamachi HI (1992) Proliferation and differentiation of fetal rat intestinal epithelial cells in primary serum-free culture. J Cell Sci 103:511–519
Gibson PR, Van De Pol E, Maxwell LE, Gabriel A, Doe WF (1989) Isolation of colonic crypts that maintain structural and metabolic viability in vitro. Gastroenterology 96:283–291
Gomez LC, Real SM, Ojeda MS, Gimenez S, Mayorga LS, Roque M (2007) Polymorphism of the FABP2 gene: a population frequency analysis and an association study with cardiovascular risk markers in Argentina. BMC Med Genet 8:1
Goodyear AW, Kumar A, Dow S, Ryan EP (2014) Optimization of murine small intestine leukocyte isolation for global immune phenotype analysis. J Immunol Methods 405:97–108
Hague A, Paraskeva C (1996) The intestinal epithelial cell. In: Harris A (ed) Epithelial cell culture. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 25–41
Hata Y, Ota S, Nagata T, Uehara Y, Terano A, Sugimoto T (1993) Primary colonic epithelial cell culture of the rabbit producing prostaglandins. Prostaglandins 45:129–141
Hoey DE, Sharp L, Currie C, Lingwood CA, Gally DL, Smith DG (2003) Verotoxin 1 binding to intestinal crypt epithelial cells results in localization to lysomomes and abrogation of toxicity. Cell Microbiol 5:85–97
Hofmann RR (1989) Evolutionary steps of ecophysiological adaptation and diversification of ruminants: a comparative view of their digestive system. Oecologia 78:443–457
Holtkamp GM, Rossem MV, Devos AF, Willekens B, Peek R, Kijlstra A (1998) Polarized secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 112:34–43
Kaeffer B (2002) Mammalian intestinal epithelial cells in primary culture: a mini-review. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 38:123–134
Kaeffer B, Bottreau E, Velge P, Pardon P (1993) Epithelioid and fibroblastic cell lines derived from the ileum of an adult histocompatible miniature boar (d/d haplotype) and immortalized by SV40 plasmid. Eur J Cell Biol 62:152–162
Kaushik RS, Begg AA, Wilson HL, Aich P, Abrahamsen MS, Potter A, Babiuk LA, Griebel P (2008) Establishment of fetal bovine intestinal epithelial cell cultures susceptible to bovine rotavirus infection. J Virol Methods 148:182–196
Kedinger M, Simon-Assmann PM, Lacroix B, Marxer A, Hauri HP, Haffen K (1986) Fetal gut mesenchyme induces differentiation of cultured intestinal endodermal and crypt cells. Dev Biol 113:474–483
Kedinger M, Haffen K, Simon-Assmann P (1987) Intestinal tissue and cell cultures. Differentiation 36:71–85
Kersting S, Bruewer M, Schuermann G, Klotz A, Utech M, Hansmerten M, Krieglstein CF, Senninger N, Schulzke JD, Naim HY, Zimmer KP (2004) Antigen transport and cytoskeletal characteristics of a distinct enterocyte population in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Pathol 165:425–437
Kishida K, Aoyama M, Masaki M, Shidoji Y (2009) The Ala54Thr polymorphism in the fatty acid-binding protein 2 gene leads to higher food intake in Japanese women. Mol Psychiatry 14:466–467
Kondo Y, Rose I, Young GP, Whitehead RH (1984) Growth and differentiation of fetal rat small intestinal epithelium in tissue culture: relationship to fetal age. Exp Cell Res 153:121–134
Lechanteur A, Almeida A, Sarmento B (2017) Elucidation of the impact of cell culture conditions of Caco-2 cell monolayer on barrier integrity and intestinal permeability. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 119:137–141. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.06.013
Macartney KK, Baumgart DC, Carding SR, Brubaker JO, Offit PA (2000) Primary murine small intestinal epithelial cells, maintained in long-term culture, are susceptible to rotavirus infection. J Virol 74:5597–5603
Moon C, VanDussen KL, Miyoshi H, Stappenbeck TS (2014) Development of a primary mouse intestinal epithelial cell monolayer culture system to evaluate factors that modulate IgA transcytosis. Mucosal Immunol 7:818–828
Panja A (2000) A novel method for the establishment of a pure population of nontransformed human intestinal primary epithelial cell (HIPEC) lines in long term culture. Lab Investig 80:1473–1475
Perreault N, Beaulieu JF (1996) Use of the dissociating enzyme thermolysin to generate viable human normal intestinal epithelial cell cultures. Exp Cell Res 224:354–364
Perreault N, Beaulieu JF (1998) Primary cultures of fully differentiated and pure human intestinal epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 245:34–42
Pretlow TP, Stinson AJ, Pretlow TG (1978) Cytologic appearance of cells dissociated from rat colon and their separation by isokinetic and isopyknic sedimentation in gradients of Ficoll. J Natl Cancer Inst 61:1431–1438
Pringault E, Robine S, Louvard D (1991) Structure of the human villin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10811–10815
Quaroni A, May RJ (1980) Establishment and characterization of intestinal epithelial cell cultures. Methods Cell Biol 21:403–427
Rani P, Vashisht M, Golla N, Shandilya S, Onteru SK, Singh D (2017) Milk miRNAs encapsulated in exosomes are stable to human digestion and permeable to intestinal barrier in vitro. J Funct Foods 34:431–439
Reddy PM, Sahi J, Desai G, Vidyasagar D, Rao MC (1996) Altered growth and attachment of rabbit crypt colonocytes isolated from different developmental stages. Pediatr Res 39:287–294
Rusu D, Loret S, Peulen O, Mainil J, Dandrifosse G (2005) Immunochemical, biomolecular and biochemical characterization of bovine epithelial intestinal primocultures. BMC Cell Biol 6:1
Ryeom SW, Paul D, Goodenough DA (2000) Truncation of mutants of the tight junction protein ZO-1 disrupt corneal epithelial cell morphology. Mol Biol Cell 11:1687–1696
Sacchettini JC, Hauft SM, Van Camp SL, Cistola DP, Gordon JI (1990) Developmental and structural studies of an intracellular lipid binding protein expressed in the ileal epithelium. J Biol Chem 265:19199–19207
Sanderson IR, Ezzell RM, Kedinger M, Erlanger M, Xu ZX, Pringault E, Leon-Robine S, Louvard D, Walker WA (1996) Human fetal enterocytes in vitro: modulation of the phenotype by extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7717–7722
Schlage WK, Bulles H, Friedrichs D, Kuhn M, Teredesai A (1998) Cytokeratin expression patterns in the rat respiratory tract as markers of epithelial differentiation in inhalation toxicology I. Determination of normal cytokeratin expression patterns in nose, larynx, trachea, and lung. Toxicol Pathol 26:324–343
Sun TT, Shih C, Green H (1979) Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:2813–2817
Tomar A, Wang Y, Kumar N, George S, Ceacareanu B, Hassid A, Chapman KE, Aryal AM, Waters CM, Khurana S (2004) Regulation of cell motility by tyrosine phosphorylated villin. Mol Biol Cell 15:4807–4817
Tomar A, George S, Kansal P, Wang Y, Khurana S (2006) Interaction of phospholipase C-Υ1 with villin regulates epithelial cell migration. J Biol Chem 281:31972–31986
Vashisht M, Rani P, Onteru SK, Singh D (2017) Curcumin encapsulated in milk exosomes resists human digestion and possesses enhanced intestinal permeability in vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s12010-017-2478-4
Velge P, Kaeffer B, Bottreau E, Langendonck N (1995) The loss of contact inhibition and anchorage-dependent growth are key steps in the acquisition of Listeria monocytogenes susceptibility phenotype by non-phagocytic cells. Biol Cell 85:55–66
Vij R, Reddi S, Kapila S, Kapila R (2016) Transepithelial transport of milk derived bioactive peptide VLPVPQK. Food Chem 190:681–688
Wang Y, Srinivasan K, Siddiqui MR, George SP, Tomar A, Khurana S (2008) A novel role for villin in intestinal epithelial cell survival and homeostasis. J Biol Chem 283:9454–9464
Weng XH, Beyenbach KW, Quaroni A (2005) Cultured monolayers of the dog jejunum with the structural and functional properties resembling the normal epithelium. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G705–G717
Whitehead RH, Demmler K, Rockman SP, Watson NK (1999) Clonogenic growth of epithelial cells from normal colonic mucosa from both mice and humans. Gastroenterology 117:858–865
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR-NDRI for providing infrastructure to carry out the present study. This research work was financially supported by Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, India (Grant No. 102/IFD/SAN/3670/2014-15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, N., Agrawal, H., Pandey, M. et al. Development and characterization of 2-dimensional culture for buffalo intestinal cells. Cytotechnology 70, 361–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0151-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0151-y