Abstract
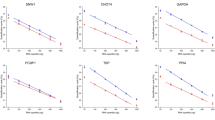
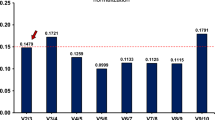
Relative quantification of in vitro gene expression using real-time PCR requires stably expressed reference gene for normalisation. In this study, total RNA from MCF7, HCT116 and HepG2 cells were extracted and converted to cDNA using commercially available kit, and real-time PCR was then performed to analyse the expression levels of twelve reference genes to select the most ideal reference gene for accurate normalisation in gene expression study. geNorm and NormFinder software were used to analyse the stabilities of the reference genes, which showed a wide range of Ct values. The geNorm analysis showed the following ranking for stability of genes: UBC, YWHAZ > RPLP > TBP > ACTB > HPRT1 > PPIA > GAPDH > GUSB > B2M > TUBB > RRN18S. A similar ranking of reference genes was obtained by NormFinder, and the four most stable reference genes were identical using both approaches. UBC and YWHAZ were proposed to be the two most suitable reference genes based on the above analyses. To further assess the stabilities of the UBC and YWHAZ in a formal experiment, MCF7, HCT116 and HepG2 cell lines were subjected to treatments with 5-aza-dC and TSA. Both UBC and YWHAZ exhibited stable expression levels across control and treatment groups. Therefore, we propose that UBC and YWHAZ are the two most suitable reference genes for our gene expression studies using MCF7, HCT116 and HepG2 cell lines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Arukwe A (2006) Toxicological housekeeping genes: do they really keep the house? Environ Sci Technol 40:7944–7949
Bracke ME, Vyncke BM, Bruynee EA, Vermeulen SJ, De Bruyne GK, Van Larebeke NA, Vleminckx K, Van Roy FM, Mareel MM (1993) Insulin-like growth factor I activates the invasion suppressor function of E-cadherin in MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 68:282–289
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25:169–193
Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW (2005) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR—a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol 34:597–601
Carlyle WC, Toher CA, Vandervelde JR, McDonald KM, Homans DC, Cohn JN (1996) Changes in beta-actin mRNA expression in remodeling canine myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 28:53–63
Cicinnati VR, Shen Q, Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Gerken G, Beckebaum S (2008) Validation of putative reference genes for gene expression studies in human hepatocellular carcinoma using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Cancer 8:350
de Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA, Pennings JL, Waas ET, Feuth T, Swinkels DW, Span PN (2005) Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest 85:154–159
Dobosy J, Roberts J, Fu V, Jarrard D (2007) The expanding role of epigenetics in the development, diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 177:822–831
Dong H, Lin W, Wu J, Chen T (2010) Flavonoids activate pregnane X receptor mediated CYP3A4 gene expression by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases in HepG2 liver carcinoma cells. BMC Biochem 11:23
Eleaume H, Jabbouri S (2004) Comparison of two standardisation methods in real-time quantitative RT-PCR to follow Staphylococcus aureus genes expression during in vitro growth. J Microbiol Meth 59:363–370
Foss DL, Baarsch MJ, Murtaugh MP (1998) Regulation of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and beta-actin mRNA expression in porcine immune cells and tissues. Anim Biotechnol 9:67–78
Fukuda R, Kelly B, Semenza GL (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in colon cancer cells exposed to prostaglandin E2 is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res 63:2330–2334
Gao Y, Hannan NR, Wanyonyi S, Konstantopolous N, Pagnon J, Feng HC, Jowett JB, Kim KH, Walder K, Collier GR (2006) Activation of the selenoprotein SEPS1 gene expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines in HepG2 cells. Cytokine 33:246–251
Garson JA, Grant PR, Ayliffe U, Ferns RB, Tedder RS (2005) Real-time PCR quantitation of hepatitis B virus DNA using automated sample preparation and murine cytomegalovirus internal control. J Virol Methods 126:207–213
Ginzinger DG (2002) Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: an emerging technology hits the mainstream. Exp Hematol 30:503–512
Goossens K, Van Poucke M, Van Soom A, Vandesompele J, Van Zeveren A, Peelman LJ (2005) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in bovine preimplantation embryos. BMC Dev Biol 5:27
Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Engeli S, Sharma AM (2001) Validation of endogenous controls for gene expression studies in human adipocytes and preadipocytes. Horm Metab Res 33:625–627
Huang H, Zhang ZX, Xu YJ, Shao JF (2003) HDAC1 expression and effect of TSA on proliferation and apoptosis of A549 cells. Ai Zheng 22:922–926
Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun 6:279–284
Jian B, Liu B, Bi Y, Hou W, Wu C, Han T (2008) Validation of internal control for gene expression study in soybean by quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 9:59
Jung M, Ramankulov A, Roigas J, Johanssen M, Ringsdorf M, Kristiansen G, Jung K (2007) In search of suitable reference genes for gene expression studies of human renal cell carcinoma by real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 8:47
Krishnan V, Wang X, Safe S (1994) Estrogen receptor-Spl complexes mediate estrogen-induced cathepsin D gene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 269:15912–15917
Krussel JS, Huang HY, Simon C, Behr B, Pape AR, Wen Y, Bielfeld P, Polan ML (1998) Single blastomeres within human preimplantation embryos express different amounts of messenger ribonucleic acid for beta-actin and interleukin-1 receptor type I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:953–959
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−ΔΔ C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lyng MB, Laenkholm AV, Pallisgaard N, Ditzel HJ (2008) Identification of genes for normalization of real-time RT-PCR data in breast carcinomas. BMC Cancer 8:20
Mori R, Wang Q, Danenberg KD, Pinski JK, Danenberg PV (2008) Both actin and GAPDH are useful reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in human FFPE tissue samples of prostate cancer. Prostate 68:1555–1560
Ohl F, Jung M, Radonic A, Sachs M, Loening SA, Jung K (2006) Identification and validation of suitable endogenous reference genes for gene expression studies of human bladder cancer. J Urol 175:1915–1920
Perez S, Royo LJ, Astudillo A, Escudero D, Alvarez F, Rodriguez A, Gomez E, Otero J (2007) Identifying the most suitable endogenous control for determining gene expression in hearts from organ donors. BMC Mol Biol 8:114
Revillion F, Pawlowski V, Hornez L, Peyrat JP (2000) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 36:1038–1042
Rivard GE, Momparler RL, Demers J, Benoit P, Raymond R, Lin K-T, Momparler LF (1987) Phase I study on 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in children with acute leukemia. Leuk Res 11:319–325
Rondinelli RH, Epner DE, Tricoli JV (1997) Increased glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression in late pathological stage human prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 1:66–72
Schek N, Hall BL, Finn OJ (1988) Increased glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 48:6354–6359
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA (2000) Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods 46:69–81
Selvey S, Thompson EW, Matthaei K, Lea RA, Irving MG, Griffiths LR (2001) Beta-actin—an unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Mol Cell Probes 15:307–311
Singh R, Green MR (1993) Sequence-specific binding of transfer RNA by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science 259:365–368
Su RY, Chi KH, Huang DY, Tai MH, Lin WW (2008) 15-deoxy-Delta12, 14-prostaglandin J2 up-regulates death receptor 5 gene expression in HCT116 cells: involvement of reactive oxygen species and C/EBP homologous transcription factor gene transcription. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3429–3440
Tanic N, Perovic M, Mladenovic A, Ruzdijic S, Kanazir S (2007) Effects of aging, dietary restriction and glucocorticoid treatment on housekeeping gene expression in rat cortex and hippocampus-evaluation by real time RT-PCR. J Mol Neurosci 32:38–46
Thellin O, Zorzi W, Lakaye B, De Borman B, Coumans B, Hennen G, Grisar T, Igout A, Heinen E (1999) Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J Biotechnol 75:291–295
Tricarico C, Pinzani P, Bianchi S, Paglierani M, Distante V, Pazzagli M, Bustin SA, Orlando C (2002) Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction: normalization to rRNA or single housekeeping genes is inappropriate for human tissue biopsies. Anal Biochem 309:293–300
Valenti MT, Bertoldo F, Dalle Carbonare L, Azzarello G, Zenari S, Zanatta M, Balducci E, Vinante O, Lo Cascio V (2006) The effect of bisphosphonates on gene expression: GAPDH as a housekeeping or a new target gene? BMC Cancer 6:49
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Zajchowski DA, Bartholdi MF, Gong Y, Webster L, Liu HL, Munishkin A, Beauheim C, Harvey S, Ethier SP, Johnson PH (2001) Identification of gene expression profiles that predict the aggressive behavior of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:5168–5178
Zhang X, Ding L, Sandford AJ (2005) Selection of reference genes for gene expression studies in human neutrophils by real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 6:4
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a Fundamental Research Grant (203/PPSK/6171103) from the Ministry of Higher Education, and Chua Siang Ling was supported by a fellowship from the Institute of Postgraduate Studies, Universiti Sains Malaysia. We also thank the technical support from UPMS, Culture and Biomedicine Laboratories, School of Health Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chua, S.L., See Too, W.C., Khoo, B.Y. et al. UBC and YWHAZ as suitable reference genes for accurate normalisation of gene expression using MCF7, HCT116 and HepG2 cell lines. Cytotechnology 63, 645–654 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-011-9383-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-011-9383-4