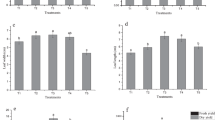
In this study, two wheat cultivars (cvs Demir 2000 and Konya 2002) were sprouted at 17°C and 85% relative humidity for 9 days. Then the wheat sprouts were dried and ground. The wheats and their sprouts were analyzed for α-tocopherol, some minerals, and fatty acid contents during the sprouting. The α-tocopherol contents of cvs Demir 2000 and Konya 2002 were 26.99 and 23.77 mg/kg, respectively, and these values reached 54.62 and 47.19 mg/kg for their sprouts, respectively. Mineral analyses showed that the mineral contents of the sprouts also increased with sprouting. Fatty acids, e.g., 4:0, 6:0, 8:0, and 10:0, could not be detected in the sprouts while some of them, e.g., cis-18:1 and cis,cis-18:2, were decreasing during sprouting, but an increase in 18:3 n3 (0-3) contents was noted. The results showed that sprouting of wheat grains leads to an increase in some significant functional components.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Lebiedzinska and P. Szefer, Food Chem., 95, 116 (2006).
P. R. Shewry, J. Cereal Sci., 46, 239 (2007).
T. V. Price, Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J., 21, 57 (1988).
F. Yang, T. K. Basu, and B. Ooraikul, Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr., 52, 319 (2001).
L. Plaza, B. Ancos, and M. P. Cano, Eur. Food Res. Technol., 216, 138 (2003).
S. D. Kulkarni, R. Acharya, A. G. C. Nair, N. S. Rajurkar, and A. V. R. Reddy, Food Chem., 95, 699 (2006).
P. L. Finney, Recent Adv. Phytochem., 17, 229 (1985).
P. K. Rudra, S. S. D. Nair, J. W. Leitch, and M. L. Garg, Handbook of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods, CRC Press, United States of America, 2001.
H. W. Lopez, V. Krespine, C. Guy, A. Messager, C. Demigne, and C. Remesy, J. Agr. Food Chem., 49, 2657 (2001).
M. Nabrzyski, Mineral Components in Foods, Taylor & Francis Group, CRC Press, New York, 2007.
Agilent Application Catalogue, 5989-3760 EN, www.agilent.com, 2008.
U. Sahin, S. Kartal, and A. Ulgen, Anal. Sci., 24,751 (2008).
H. G. Maier, Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, 1990.
M. Dogan and M. Soylak, Water Chemistry, Erciyes University Press, Turkey, 2006.
SAS: SAS/STAT User's guide (8.0); SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, North Carolina, 2000.
Acknowledgment
The financial support from the Scientific Research Project Unit of Erciyes University is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 6, pp. 770–772, November–December 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, I., Sagdic, O., Hayta, M. et al. Alteration in α-tocopherol, some minerals, and fatty acid contents of wheat through sprouting. Chem Nat Compd 47, 876–879 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-012-0092-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-012-0092-9