Abstract
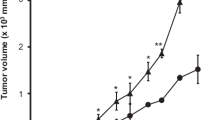
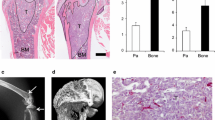
Bone metastases impair general health status, quality of life and survival of patients. Electrochemotherapy (ECT), which combines electroporation (EP) and the administration of anticancer drugs, has been recently introduced into clinical practice for the local treatment of solid tumours. In the present study, the ability of EP with bleomycin (Bleo) to induce MRMT-1 rat breast cancer cell death was investigated in vitro. Then, an in vivo model for bone metastases was set up by the inoculation of MRMT-1 cells in rat proximal tibia. 7 days after tumour induction the animals were treated with Bleo, EP, Bleo followed by EP (ECT), or left untreated. ECT eliminated the tumour in 6 out of 8 (75 %) treated metastases. Radiological evaluation showed that the Honore score in ECT-treated animals was significantly lower when compared with the other groups (p < 0.0005) and not significantly different from healthy controls. Bone morphology in ECT-treated animals, evaluated by histological and microtomographical analyses, showed intact cortical and trabecular bone structure with new bone apposition. Histomorphometric evaluation showed that ECT-treated metastases had significantly higher bone volume, trabecular number, trabecular thickness and bone mineral density compared with those of untreated metastases (respectively p < 0.0005 for BV/TV, Tb.N and BMD; p < 0.05 for Tb.Th) or metastases treated with Bleo (p < 0.05 for BV/TV, Tb.N, p < 0.005 for BMD) or EP (p < 0.005 for BV/TV, Tb.N; p < 0.0005 for BMD). These findings suggest that early ECT treatment of bone metastases is minimally invasive, safe and effective, thus providing pre-clinical evidence for its use in the treatment of human bone metastases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escoffre JM, Dean DS, Hubert M, Rols MP, Favard C (2007) Membrane perturbation by an external electric field: a mechanism to permit molecular uptake. Eur Biophys J 36:973–983. doi:10.1007/s00249-007-0194-7
Gissel H, Lee RC, Gehl J (2011) Electroporation and cellular physiology. In: Kee ST, Gehl J, Lee EW (eds) Clinical Aspects of Electroporation. Springer, New York, pp 9–17
Orlowski S, Belehradek J Jr, Paoletti C, Mir LM (1988) Transient electropermeabilization of cells in culture. Increase of the cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs. Biochem Pharmacol 37(24):4727–4733
Pron G, Mahrour N, Orlowski S, Tounekti O, Poddevin B, Belehradek J Jr, Mir LM (1999) Internalisation of the bleomycin molecules responsible for bleomycin toxicity: a receptor-mediated endocytosis mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol 57(1):45–56. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(98)00282-2
Escoffre JM, Rols MP (2012) Electrochemotherapy: progress and prospects. Curr Pharm Des 18(23):3406–3415. doi:10.2174/138161212801227087
Silve A, Mir LM (2011) Cell electropermeabilization and cellular uptake of small molecules: the electrochemotherapy concept. In: Kee ST, Gehl J, Lee EW (eds) Clinical aspects of electroporation. Springer, New York, pp 69–82
Spugnini EP, Dotsinsky I, Mudrov N, Citro G, D’Avino A, Baldi A (2008) Biphasic pulses enhance bleomycin efficacy in a spontaneous canine genital tumour model of chemoresistance: sticker sarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:58. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-27-58
Spugnini EP, Citro G, Dotsinsky I, Mudrov N, Mellone P, Baldi A (2008) Ganglioneuroblastoma in a cat: a rare neoplasm treated with electrochemotherapy. Vet J 178:291–293. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.08.014
Cemazar M, Tamzali Y, Sersa G, Tozon N, Mir LM, Miklavcic D, Lowe R, Teissie J (2008) Electrochemotherapy in veterinary oncology. J Vet Intern Med 22:826–831. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2008.0117.x
Mir LM, Orlowski S, Belehradek J Jr, Paoletti C (1991) Electrochemotherapy potentiation of antitumour effect of bleomycin by local electric pulses. Eur J Cancer 27(1):68–72. doi:10.1016/0277-5379(91)90064-K
Sersa G, Cemazar M, Miklavcic D, Chaplin DJ (1999) Tumour blood flow modifying effect of electrochemotherapy with bleomycin. Anticancer Res 19:4017–4022
Jaroszeski MJ, Coppola D, Pottinger C, Benson K, Gilbert RA, Heller R (2001) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in a rat model using electrochemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 37(3):422–430. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00412-3
Engstrom PE, Ivarsson K, Tranberg KG, Stenram U, Salford LG, Persson BR (2001) Electrically mediated drug delivery for treatment of an adenocarcinoma transplanted into rat liver. Anticancer Res 21:1817–1822
Mitsui K, Kato K, Nakamura K, Yamada Y, Honda N, Fukatsu H, Yoshikawa K (2002) Effective treatment of bladder tumour-bearing mice by direct delivery of bleomycin using electrochemotherapy. Drug Deliv 9:249–252. doi:10.1080/10717540260397864
Miyazaki S, Gunji Y, Matsubara H, Shimada H, Uesato M, Suzuki T, Kouzu T, Ochiai T (2003) Possible involvement of antitumour immunity in the eradication of colon 26 induced by low-voltage electrochemotherapy with bleomycin. Surg Today 33:39–44. doi:10.1007/s005950300006
Zheng MH, Feng B, Li JW, Lu AG, Wang ML, Hu WG, Ma JJ, Yu BM (2005) Effects and possible anti-tumour immunity of electrochemotherapy with bleomycin on human colon cancer xenografts in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol 11:2426–2430
Kitamura A (2003) Bleomycin-mediated electrochemotherapy in mouse NR-S1 carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 51:359–362
Ivanov MA, Lamrihi B, Szyf M, Scherman D, Bigey P (2003) Enhanced antitumour activity of a combination of MBD2-antisense electrotransfer gene therapy and bleomycin electrochemotherapy. J Gene Med 5:893–899
Soden DM, Larkin JO, Collins CG, Tangney M, Aarons S, Piggott J, Morrissey A, Dunne C, O’Sullivan GC (2006) Successful application of targeted electrochemotherapy using novel flexible electrodes and low dose bleomycin to solid tumours. Cancer Lett 232(2):300–310. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.057
Torrero MN, Henk WG, Li S (2006) Regression of high-grade malignancy in mice by bleomycin and interleukin-12 electrochemogenetherapy. Clin Cancer Res 12:257–263. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1514
Agerholm-Larsen B, Iversen HK, Ibsen P, Moller JM, Mahmood F, Jensen KS, Gehl J (2011) Preclinical validation of electrochemotherapy as an effective treatment for brain tumours. Cancer Res 71:3753–3762. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0451
Marty M, Sersa G, Garbay JR, Gehl J, Collins CG, Snoj M, Billarda V, Geertsenc PF, Larkind JO, Miklavcice D, Pavlovice I, Paulin-Kosirb SM, Cemazarb M, Morslia N, Sodend DM, Rudolfb Z, Roberta C, O’Sullivand GC, Mir LM (2006) Electrochemotherapy: an easy, highly effective and safe treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases: results of ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) study. EJC Suppl 4:3–13. doi:10.1016/j.ejcsup.2006.08.002
Giardino R, Fini M, Bonazzi V, Cadossi R, Nicolini A, Carpi A (2006) Electrochemotherapy a novel approach to the treatment of metastatic nodules on the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Biomed Pharmacother 60:458–462. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2006.07.016
Belehradek M, Domenge C, Luboinski B, Orlowski S, Belehradek J Jr, Mir LM (1993) Electrochemotherapy, a new antitumour treatment. First clinical phase I–II trial. Cancer 72:3694–3700. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19931215)72:12<3694:AID-CNCR2820721222>3.0.CO;2-2
Gehl J, Geertsen PF (2000) Efficient palliation of haemorrhaging malignant melanoma skin metastases by electrochemotherapy. Melanoma Res 10:585–589. doi:10.1097/00008390-200012000-00011
Mir LM, Glass LF, Sersa G, Teissie J, Domenge C, Miklavcic D, Jaroszeski MJ, Orlowski S, Reintgen DS, Rudolf Z, Belehradek M, Gilbert R, Rols MP, Belehradek J Jr, Bachaud JM, DeConti R, Stabuc B, Cemazar M, Coninx P, Heller R (1998) Effective treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous malignant tumours by electrochemotherapy. Br J Cancer 77:2336–2342. doi:10.1038/bjc.1998.388
Heller R, Jaroszeski MJ, Reintgen DS, Puleo CA, DeConti RC, Gilbert RA, Glass LF (1998) Treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumours with electrochemotherapy using intralesional bleomycin. Cancer 83:148–157. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980701)83:1<148:AID-CNCR20>3.0.CO;2-W
Byrne CM, Thompson JF, Johnston H, Hersey P, Quinn MJ, Michael Hughes T, McCarthy WH (2005) Treatment of metastatic melanoma using electroporation therapy with bleomycin (electrochemotherapy). Melanoma Res 15:45–51. doi:10.1097/00008390-200502000-00008
Shimizu T, Nikaido T, Gomyo H, Yoshimura Y, Horiuchi A, Isobe K, Ebara S, Takaoka K (2003) Electrochemotherapy for digital chondrosarcoma. J Orthop Sci 8:248–251
Glass LF, Jaroszeski M, Gilbert R, Reintgen DS, Heller R (1997) Intralesional bleomycin-mediated electrochemotherapy in 20 patients with basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 37:596–599. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(97)70178-6
Testori A, Rossi CR, Tosti G (2012) Utility of electrochemotherapy in melanoma treatment. Curr Opin Oncol 24:155–161. doi:10.1097/CCO.0b013e32834fcaa8
Richetta AG, Curatolo P, D’Epiro S, Mancini M, Mattozzi C, Giancristoforo S, Rotunno R, Calvieri S (2011) Efficacy of electrochemotherapy in ulcerated basal cell carcinoma. Clin Ter 162:443–445
Marenco F, Nardò T, Savoia P, Bernengo MG (2011) Effectiveness of electrochemotherapy in treatment of a recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the scalp. Eur J Dermatol 21:618–619
Kis E, Oláh J, Ócsai H, Baltas E, Gyulai R, Kemény L, Horvath AR (2011) Electrochemotherapy of cutaneous metastases of melanoma: a case series study and systematic review of the evidence. Dermatol Surg 37:816–824. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.01951.x
Testori A, Tosti G, Martinoli C, Spadola G, Cataldo F, Verrecchia F, Baldini F, Mosconi M, Soteldo J, Tedeschi I, Passoni C, Pari C, Di Pietro A, Ferrucci PF (2010) Electrochemotherapy for cutaneous and subcutaneous tumour lesions: a novel therapeutic approach. Dermatol Ther 23:651–661. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01370.x
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA, McCauley LK (2011) Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer 11(6):411–425. doi:10.1038/nrc3055
Mundy GR (2002) Metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2(8):584–593. doi:10.1038/nrc867
Desantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P, Jemal A (2011) Breast cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:409–418. doi:10.3322/caac.20134
Fini M, Tschon M, Ronchetti M, Cavani F, Bianchi G, Mercuri M, Alberghini M, Cadossi R (2010) Ablation of bone cells by electroporation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:1614–1620. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.92B11.24664
Honore P, Rogers SD, Schwei MJ, Salak-Johnson JL, Luger NM, Sabino MC, Clohisy DR, Mantyh PW (2000) Murine models of inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer pain each generates a unique set of neurochemical changes in the spinal cord and sensory neurons. Nat Neurosci 98:585–595. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00110-X
Otsu N (1979) Threshold selection method from grey level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern SMC 9:62–66
Parfitt AM (1988) Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols and units. Summary of proposed system. Bone Miner 4:1–5. doi:10.1016/8756-3282(88)90029-4
Hahn M, Vogel M, Pompesius-KempaM Delling G (1992) Trabecular bone pattern factor: a new parameter for simple quantification of bone microarchitecture. Bone 13:327–330. doi:10.1016/8756-3282(92)90078-B
Hildebrand T, Ruegsegger P (1997) A new method for the model independent assessment of thickness in three dimensionel images. J Microsc 185:67–75
Jaroszeski MJ, Dang V, Pottinger C, Hickey J, Gilbert R, Heller R (2000) Toxicity of anticancer agents mediated by electroporation in vitro. Anticancer Drugs 11:201–208. doi:10.1097/00001813-200003000-00008
Gehl J, Skovsgaard T, Mir LM (1998) Enhancement of cytotoxicity by electropermeabilization: an improved method for screening drugs. Anticancer Drugs 9:319–325. doi:10.1097/00001813-199804000-00005
Horikoshi T, Naganuma H, Ohashi Y, Ueno T, Nukui H (2000) Enhancing effect of electric stimulation on cytotoxicity of anticancer agents against rat and human glioma cells. Brain Res Bull 51:371–378. doi:10.1016/S0361-9230(99)00247-6
Byrnes RW, Petering DH (1991) Inhibition of bleomycin-induced cellular DNA strand scission by 1,10-phenanthroline. Biochem Pharmacol 41:1241–1248. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(91)90664-Q
Ehrenfeld GM, Rodriguez LO, Hecht SM, Chang C, Basus VJ, Oppenheimer NJ (1985) Copper(I)-bleomycin: structurally unique complex that mediates oxidative DNA strand scission. Biochemistry 24(1):81–92. doi:10.1021/bi00322a013
Kénani A, Bailly C, Houssin R, Hénichart JP (1994) Comparative subcellular distribution of the copper complexes of bleomycin-A2 and deglycobleomycin-A2. Anticancer Drugs 5:199–201. doi:10.1097/00001813-199404000-00010
Lazo JS, Schisselbauer JC, Meandzija B, Kennedy KA (1989) Initial single-strand DNA damage and cellular pharmacokinetics of bleomycin A2. Biochem Pharmacol 38:2207–2213. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(89)90078-6
Medhurst SJ, Walker K, Bowes M, Kidd BL, Glatt M, Muller M, Hattenberger M, Vaxelaire J, O’Reilly T, Wotherspoon G, Winter J, Green J, Urban (2002) A rat model of bone cancer pain. Pain 96:129–140. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00437-7
Manthey CL, Johnson DL, Illig CR, Tuman RW, Zhou Z, Baker JF, Chaikin MA, Donatelli RR, Franks CF, Zeng L, Crysler C, Chen Y, Yurkow EJ, Boczon L, Meegalla SK, Wilson KJ, Wall MJ, Chen J, Ballentine SK, Ott H, Baumann C, Lawrence D, Tomczuk BE, Molloy CJ (2009) JNJ-28312141, a novel orally active colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor/FMS-related receptor tyrosine kinase-3 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potential utility in solid tumours, bone metastases, and acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 8(11):3151–3161. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0255
Ogawa K, Mukai T, Asano D, Kawashima H, Kinuya S, Shiba K, Hashimoto K, Mori H, Saji H (2007) Therapeutic effects of a 186Re-complex-conjugated bisphosphonate for the palliation of metastatic bone pain in an animal model. J Nucl Med 48(1):122–127
Salamanna F, Martini L, Pagani S, Parrilli A, Giavaresi G, Maltarello MC, Fini M (2012) MRMT-1 rat breast carcinoma cells and models of bone metastases: in vitro systems to mimic the in vivo conditions. Acta Histochem 115(1):76–85. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2012.05.005
Miklavcic D, Beravs K, Semrov D, Cemazar M, Demsar F, Sersa G (1998) The importance of electric field distribution for effective in vivo electroporation of tissues. Biophys J 74(5):2152–2158
Puc M, Corović S, Flisar K, Petkovsek M, Nastran J, Miklavcic D (2004) Techniques of signal generation required for electropermeabilization. Survey of electropermeabilization devices. Bioelectrochemistry 64(2):113–124
Miklavčič D, Serša G, Brecelj E, Gehl J, Soden D, Bianchi G, Ruggieri P, Rossi CR, Campana LG, Jarm T (2012) Electrochemotherapy: technological advancements for efficient electroporation-based treatment of internal tumors. Med Biol Eng Comput 50(12):1213–1225. doi:10.1007/s11517-012-0991-8
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Prof. Mario Mercuri († 7/05/2011), an inspiring guide and example who has contributed to this study with his enthusiasm, incitement and support. Moreover, this study would not have been the same without the valuable and constructive assistance of Dr. Marco Alberghini († 27/06/2012), who helped the authors with his knowledge and friendship during histology and data analysis. The authors are grateful to Fondazione Carisbo for their financial support. The research was also financed by Istituto Ortopedico Rizzoli and funds 5 × 1,000 (year 2008–2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fini, M., Salamanna, F., Parrilli, A. et al. Electrochemotherapy is effective in the treatment of rat bone metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 30, 1033–1045 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9601-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9601-x