Abstract
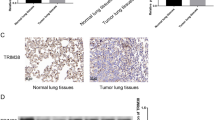
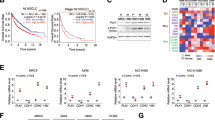
Nuclear factor (NF)-κB is frequently over-expressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but the exact role of this observation remains unclear. In this regard, activation of the transcription factor may govern distinct steps of NSCLC progression, such as carcinogenesis, angiogenesis, and metastasis. In these studies we attempted to dissect the effects of two proteins of the NF-κB pathway (p65/RelA and IκΒα) on experimental metastasis of murine NSCLC, using a novel approach of bioluminescent detection of NF-κB activation in tumor cells. Stable integration of a NF-κΒ reporter confirmed high basal activation of the transcription factor in mouse NSCLC cells in vitro and during experimental metastasis to the lungs, like human NSCLC. In the mouse model of NSCLC metastasis, NF-κΒ-dependent luciferase expression served as a reliable indicator of tumor cell delivery to the lungs, establishment of metastatic tumors, and lung tumor burden. In vitro transient p65/RelA and IκΒα gene transfer to mouse NSCLC cells resulted, respectively, in significant NF-κB activation and inhibition, without affecting cell growth. However, p65/RelA overexpression in NSCLC cells drastically reduced in vivo metastasis to the lungs, while overexpression of IκΒα had no effect. In conclusion, using bioluminescent detection of NF-κB activation in mouse lug adenocarcinoma cells, we found a negative impact of p65/RelA on NSCLC metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- IκB:
-
Inhibitor of NF-κB
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- LLC:
-
Lewis lung cancer
- pNGL :
-
NF-κB.GFP.LUC reporter plasmid
- MOI:
-
Multiplicity of infection
- pfu:
-
Plaque forming units
- Ad:
-
Adenoviral vector
- IκBα-DN:
-
Dominant inhibitor of NF-κB
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- Luc:
-
Luciferase
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- βgal:
-
β-Galactosidase
References
Blackwell TS, Christman JW (1997) The role of nuclear factor-κB in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:3–9
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6853–6866
Sadikot RT, Han W, Everhart MB et al (2003) Selective IκB Kinase expression in airway epithelium generates neutrophilic lung inflammation. J Immunol 170:1091–1098
Chen FE, Ghosh G (1999) Regulation of DNA binding by Rel/NF-kB transcription factors: structural views. Oncogene 18:6845–6852
Mercurio F, Zhu H, Murray BW et al (1997) IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IκB kinases essential for NF-κB activation. Science 278:860–866
Karin M (1999) How NF-κB is activated: the role of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex. Oncogene 18:6867–6874
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:106–130
Mukhopadhyay T, Roth JA, Maxwell SA (1995) Altered expression of the p50 subunit of the NF-κB transcription factor complex in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene 11:999–1003
Tang X, Liu D, Shishodia S et al (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is frequently expressed in lung cancer and preneoplastic lesions. Cancer 107:2637–2646
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420:860–867
Mountain CF (1997) Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest 111:1710–1717
Stathopoulos GT, Zhu Z, Everhart MB et al (2006) Nuclear factor-κB activation affects tumor progression in a mouse model of malignant pleural effusion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 34:142–150
Sadikot RT, Zeng H, Joo M et al (2006) Targeted immunomodulation of the NF-κB pathway in airway epithelium impacts host defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Immunol 176:4923–4930
Sadikot RT, Zeng H, Yull FE et al (2004) p47phox deficiency impairs NF-κΒ activation and host defense in Pseudomonas pneumonia. J Immunol 172:1801–1808
Fidler IJ (1970) Metastasis: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2’-deoxyuridine. J Natl Cancer Inst 45:773–782
Jiang Y, Cui L, Yie TA et al (2001) Inhibition of anchorage-independent growth and lung metastasis of A549 lung carcinoma cells by IkBb. Oncogene 20:2254–2263
Kim D-M, Koo S-Y, Jeon K et al (2003) Rapid induction of apoptosis by combination of flavopiridol and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 63:621–626
Andela VB, Schwarz EM, Puzas JE et al (2000) Tumor metastasis and the reciprocal regulation of prometastatic and antimetastatic factors by nuclear factor-κB. Cancer Res 60:6557–6562
Ricca A, Biroccio A, Trisciuoglio D et al (2001) RelA over-expression reduces tumorigenicity and activates apoptosis in human cancer cells. Br J Cancer 85:1914–1921
Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB (2001) Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 107:135–142
Dajee M, Lazarov M, Zhang JY et al (2003) NF-κB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature 421:639–643
Dong G, Chen Z, Kato T et al (1999) The host environment promotes the constitutive activation of nuclear factor-κB and proinflammatory cytokine expression during metastatic tumor progression of murine squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 59:3495–3504
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR et al (2002) NF-κB in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2:301–310
Rollins BJ, Sunday ME (1991) Suppression of tumor formation in vivo by expression of the JE gene in malignant cells. Mol Cell Biol 11:3125–3131
Nokihara H, Yanagawa H, Nishioka Y et al (2000) Natural killer cell-dependent suppression of systemic spread of human lung adenocarcinoma cells by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene transfection in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res 60:7002–7007
Luo J-L, Maeda S, Hsu L-C et al (2004) Inhibition of NF-κB in cancer cells converts inflammation-induced tumor growth mediated by TNF-α to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell 6:297–305
Voorhees PM, Dees EC, O’Neil B et al (2003) The proteasome as a target for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 9:6316–6325
Lenz HJ (2003) Clinical update: proteasome inhibitors in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 29S1:41–48
Collett GP, Campbell FC (2006) Overexpression of p65/RelA potentiates curcumin-induced apoptosis in HCT116 human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 27:1285–1291
Weissleder R (2002) Scaling down imaging: molecular mapping of cancer in mice. Nat Rev Cancer 2:1–8
Contag CH, Bachmann MH (2002) Advances in in vivo bioluminescence imaging of gene expression. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4:235–260
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by NIH HL66196 (TSB), NIH HL61419 (TSB), the Department of Veterans Affairs (TSB), the Ingram Charitable Fund (FEY) and Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center (FEY). GTS was supported by a scholarship by the Greek State Scholarship Foundation (IKY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stathopoulos, G.T., Sherrill, T.P., Han, W. et al. Use of bioluminescent imaging to investigate the role of nuclear factor-κΒ in experimental non-small cell lung cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 25, 43–51 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9100-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9100-z