Abstract
Posttraumatic epilepsy (PTE) is a severe complication arising from a traumatic brain injury caused by various violent actions on the brain. The underlying mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PTE are complex and have not been fully defined. Approximately, one-third of patients with PTE are resistant to antiepileptic therapy. Recent research evidence has shown that neuroinflammation is critical in the development of PTE. This article reviews the immune-inflammatory mechanisms regarding microglial activation, astrocyte proliferation, inflammatory signaling pathways, chronic neuroinflammation, and intestinal flora. These mechanisms offer novel insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms of PTE and have groundbreaking implications in the prevention and treatment of PTE.
Graphical Abstract
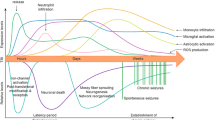
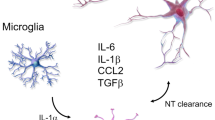
Immunoinflammatory cross-talk between glial cells and gut microbiota in posttraumatic epilepsy. This graphical abstract depicts the roles of microglia and astrocytes in posttraumatic epilepsy, highlighting the influence of the gut microbiota on their function. TBI traumatic brain injury, AQP4 aquaporin-4, Kir4.1 inward rectifying K channels


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Alyenbaawi H, Kanyo R, Locskai LF, Kamali-Jamil R, DuVal MG, Bai Q, Wille H, Burton EA, Allison WT (2021) Seizures are a druggable mechanistic link between TBI and subsequent tauopathy. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.58744
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Williamson A, Palomba M, Eid T, de Lanerolle NC, Nagelhus EA, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Agre P, Ottersen OP (2003) Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophin-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13615–13620. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2336064100
Badimon A, Strasburger HJ, Ayata P, Chen X, Nair A, Ikegami A, Hwang P, Chan AT, Graves SM, Uweru JO, Ledderose C, Kutlu MG, Wheeler MA, Kahan A, Ishikawa M, Wang YC, Loh YE, Jiang JX, Surmeier DJ, Robson SC, Junger WG, Sebra R, Calipari ES, Kenny PJ, Eyo UB, Colonna M, Quintana FJ, Wake H, Gradinaru V, Schaefer A (2020) Negative feedback control of neuronal activity by microglia. Nature 586(7829):417–423. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2777-8
Balosso S, Liu J, Bianchi ME, Vezzani A (2014) Disulfide-containing high mobility group box-1 promotes N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function and excitotoxicity by activating Toll-like receptor 4-dependent signaling in hippocampal neurons. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(12):1726–1740. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5349
Binder DK, Steinhäuser C (2021) Astrocytes and epilepsy. Neurochem Res 46(10):2687–2695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03236-x
Braganza O, Bedner P, Hüttmann K, von Staden E, Friedman A, Seifert G, Steinhäuser C (2012) Albumin is taken up by hippocampal NG2 cells and astrocytes and decreases gap junction coupling. Epilepsia 53(11):1898–1906. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03665.x
Burda JE, Bernstein AM, Sofroniew MV (2016) Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.03.020
Cho SJ, Park E, Telliyan T, Baker A, Reid AY (2020) Zebrafish model of posttraumatic epilepsy. Epilepsia 61(8):1774–1785. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16589
Cruz SL, Armenta-Reséndiz M, Carranza-Aguilar CJ, Galván EJ (2020) Minocycline prevents neuronal hyperexcitability and neuroinflammation in medial prefrontal cortex, as well as memory impairment caused by repeated toluene inhalation in adolescent rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 395:114980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.114980
D’Ambrosio R, Maris DO, Grady MS, Winn HR, Janigro D (1999) Impaired K(+) homeostasis and altered electrophysiological properties of post-traumatic hippocampal glia. J Neurosci 19(18):8152–8162. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.19-18-08152.1999
Darch H, McCafferty CP (2022) Gut microbiome effects on neuronal excitability & activity: Implications for epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 165:105629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105629
Diamond ML, Ritter AC, Failla MD, Boles JA, Conley YP, Kochanek PM, Wagner AK (2015) IL-1β associations with posttraumatic epilepsy development: a genetics and biomarker cohort study. Epilepsia 56(7):991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13100
Dohgu S, Takata F, Yamauchi A, Nakagawa S, Egawa T, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Sawada Y, Niwa M, Kataoka Y (2005) Brain pericytes contribute to the induction and up-regulation of blood-brain barrier functions through transforming growth factor-beta production. Brain Res 1038(2):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.01.027
Erny D, Hrabě de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mahlakoiv T, Jakobshagen K, Buch T, Schwierzeck V, Utermöhlen O, Chun E, Garrett WS, McCoy KD, Diefenbach A, Staeheli P, Stecher B, Amit I, Prinz M (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 18(7):965–977. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4030
Evans LP, Woll AW, Wu S, Todd BP, Hehr N, Hedberg-Buenz A, Anderson MG, Newell EA, Ferguson PJ, Mahajan VB, Harper MM, Bassuk AG (2020) Modulation of post-traumatic immune response using the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra for improved visual outcomes. J Neurotrauma 37(12):1463–1480. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2019.6725
Feigin VL, Theadom A, Barker-Collo S, Starkey NJ, McPherson K, Kahan M, Dowell A, Brown P, Parag V, Kydd R, Jones K, Jones A, Ameratunga S (2013) Incidence of traumatic brain injury in New Zealand: a population-based study. Lancet Neurol 12(1):53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70262-4
Fu R, Shen Q, Xu P, Luo JJ, Tang Y (2014) Phagocytosis of microglia in the central nervous system diseases. Mol Neurobiol 49(3):1422–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8620-6
Gibbs-Shelton S, Benderoth J, Gaykema RP, Straub J, Okojie KA, Uweru JO, Lentferink DH, Rajbanshi B, Cowan MN, Patel B, Campos-Salazar AB, Perez-Reyes E, Eyo UB (2023) Microglia play beneficial roles in multiple experimental seizure models. Glia 71(7):1699–1714. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24364
Goodwin GH, Sanders C, Johns EW (1973) A new group of chromatin-associated proteins with a high content of acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem 38(1):14–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03026.x
Henning L, Unichenko P, Bedner P, Steinhäuser C, Henneberger C (2023) Overview article astrocytes as initiators of epilepsy. Neurochem Res 48(4):1091–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03773-z
Hesam S, Khoshkholgh-Sima B, Pourbadie HG, Babapour V, Zendedel M, Sayyah M (2018) Monophosphoryl lipid A and Pam3Cys prevent the increase in seizure susceptibility and epileptogenesis in rats undergoing traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Res 43(10):1978–1985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2619-3
Hu Y, Yao Y, Qi H, Yang J, Zhang C, Zhang A, Liu X, Zhang C, Gan G, Zhu X (2023) Microglia sense and suppress epileptic neuronal hyperexcitability. Pharmacol Res 195:106881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106881
Ivens S, Kaufer D, Flores LP, Bechmann I, Zumsteg D, Tomkins O, Seiffert E, Heinemann U, Friedman A (2007) TGF-beta receptor-mediated albumin uptake into astrocytes is involved in neocortical epileptogenesis. Brain 130(Pt 2):535–547. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl317
Jiang JY, Gao GY, Feng JF, Mao Q, Chen LG, Yang XF, Liu JF, Wang YH, Qiu BH, Huang XJ (2019) Traumatic brain injury in China. Lancet Neurol 18(3):286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30469-1
Kierdorf K, Prinz M (2013) Factors regulating microglia activation. Front Cell Neurosci 7:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00044
Korgaonkar AA, Li Y, Sekhar D, Subramanian D, Guevarra J, Swietek B, Pallottie A, Singh S, Kella K, Elkabes S, Santhakumar V (2020) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in neurons enhances calcium-permeable α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor currents and drives post-traumatic epileptogenesis. Ann Neurol 87(4):497–515. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25698
Kumar A, Alvarez-Croda DM, Stoica BA, Faden AI, Loane DJ (2016) Microglial/Macrophage polarization dynamics following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 33(19):1732–1750. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2015.4268
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, Münch AE, Chung WS, Peterson TC, Wilton DK, Frouin A, Napier BA, Panicker N, Kumar M, Buckwalter MS, Rowitch DH, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Stevens B, Barres BA (2017) Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541(7638):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21029
Liu SJ, Zheng P, Wright DK, Dezsi G, Braine E, Nguyen T, Corcoran NM, Johnston LA, Hovens CM, Mayo JN, Hudson M, Shultz SR, Jones NC, O’Brien TJ (2016) Sodium selenate retards epileptogenesis in acquired epilepsy models reversing changes in protein phosphatase 2A and hyperphosphorylated tau. Brain 139(Pt 7):1919–1938. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww116
Liu L, Tong F, Li H, Bin Y, Ding P, Peng L, Liu Z, Dong X (2023) Maturation, morphology, and function: the decisive role of intestinal flora on microglia: a review. J Integr Neurosci 22(3):70. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.jin2203070
Loane DJ, Kumar A, Stoica BA, Cabatbat R, Faden AI (2014) Progressive neurodegeneration after experimental brain trauma: association with chronic microglial activation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 73(1):14–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/nen.0000000000000021
Lowenstein DH (2009) Epilepsy after head injury: an overview. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 2):4–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.02004.x
Lu DC, Zador Z, Yao J, Fazlollahi F, Manley GT (2021) Aquaporin-4 reduces post-traumatic seizure susceptibility by promoting astrocytic glial scar formation in mice. J Neurotrauma 38(8):1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.2114
Lum GR, Olson CA, Hsiao EY (2020) Emerging roles for the intestinal microbiome in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 135:104576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104576
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Liu J, Aronica E, Iyer AM, Rossetti C, Molteni M, Casalgrandi M, Manfredi AA, Bianchi ME, Vezzani A (2010) Toll-like receptor 4 and high-mobility group box-1 are involved in ictogenesis and can be targeted to reduce seizures. Nat Med 16(4):413–419. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2127
Medel-Matus JS, Lagishetty V, Santana-Gomez C, Shin D, Mowrey W, Staba RJ, Galanopoulou AS, Sankar R, Jacobs JP, Mazarati AM (2022a) Susceptibility to epilepsy after traumatic brain injury is associated with preexistent gut microbiome profile. Epilepsia 63(7):1835–1848. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.17248
Medel-Matus JS, Simpson CA, Ahdoot AI, Shin D, Sankar R, Jacobs JP, Mazarati AM (2022b) Modification of post-traumatic epilepsy by fecal microbiota transfer. Epilepsy Behav 134:108860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.108860
Mukherjee S, Arisi GM, Mims K, Hollingsworth G, O’Neil K, Shapiro LA (2020) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of post-traumatic epilepsy. J Neuroinflamm 17(1):193. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01854-w
Nicholson SE, Watts LT, Burmeister DM, Merrill D, Scroggins S, Zou Y, Lai Z, Grandhi R, Lewis AM, Newton LM, Eastridge BJ, Schwacha MG (2019) Moderate traumatic brain injury alters the gastrointestinal microbiome in a time-dependent manner. Shock 52(2):240–248. https://doi.org/10.1097/shk.0000000000001211
Paolicelli RC, Sierra A, Stevens B, Tremblay ME, Aguzzi A, Ajami B, Amit I, Audinat E, Bechmann I, Bennett M, Bennett F, Bessis A, Biber K, Bilbo S, Blurton-Jones M, Boddeke E, Brites D, Brône B, Brown GC, Butovsky O, Carson MJ, Castellano B, Colonna M, Cowley SA, Cunningham C, Davalos D, De Jager PL, de Strooper B, Denes A, Eggen BJL, Eyo U, Galea E, Garel S, Ginhoux F, Glass CK, Gokce O, Gomez-Nicola D, González B, Gordon S, Graeber MB, Greenhalgh AD, Gressens P, Greter M, Gutmann DH, Haass C, Heneka MT, Heppner FL, Hong S, Hume DA, Jung S, Kettenmann H, Kipnis J, Koyama R, Lemke G, Lynch M, Majewska A, Malcangio M, Malm T, Mancuso R, Masuda T, Matteoli M, McColl BW, Miron VE, Molofsky AV, Monje M, Mracsko E, Nadjar A, Neher JJ, Neniskyte U, Neumann H, Noda M, Peng B, Peri F, Perry VH, Popovich PG, Pridans C, Priller J, Prinz M, Ragozzino D, Ransohoff RM, Salter MW, Schaefer A, Schafer DP, Schwartz M, Simons M, Smith CJ, Streit WJ, Tay TL, Tsai LH, Verkhratsky A, von Bernhardi R, Wake H, Wittamer V, Wolf SA, Wu LJ, Wyss-Coray T (2022) Microglia states and nomenclature: a field at its crossroads. Neuron 110(21):3458–3483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.020
Pingue V, Mele C, Nardone A (2021) Post-traumatic seizures and antiepileptic therapy as predictors of the functional outcome in patients with traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep 11(1):4708. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84203-y
Roh JS, Sohn DH (2018) Damage-associated molecular patterns in inflammatory diseases. Immune Netw 18(4):e27. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2018.18.e27
Rothhammer V, Mascanfroni ID, Bunse L, Takenaka MC, Kenison JE, Mayo L, Chao CC, Patel B, Yan R, Blain M, Alvarez JI, Kébir H, Anandasabapathy N, Izquierdo G, Jung S, Obholzer N, Pochet N, Clish CB, Prinz M, Prat A, Antel J, Quintana FJ (2016) Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat Med 22(6):586–597. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4106
Russo E (2022) The gut microbiota as a biomarker in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 163:105598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105598
Samuelsson C, Kumlien E, Flink R, Lindholm D, Ronne-Engström E (2000) Decreased cortical levels of astrocytic glutamate transport protein GLT-1 in a rat model of posttraumatic epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 289(3):185–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01284-2
Sano F, Shigetomi E, Shinozaki Y, Tsuzukiyama H, Saito K, Mikoshiba K, Horiuchi H, Cheung DL, Nabekura J, Sugita K, Aihara M, Koizumi S (2021) Reactive astrocyte-driven epileptogenesis is induced by microglia initially activated following status epilepticus. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.135391
Sanz P, Garcia-Gimeno MA (2020) Reactive glia inflammatory signaling pathways and epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114096
Schilling T, Eder C (2003) Effects of kinase inhibitors on TGF-beta induced upregulation of Kv13 K+ channels in brain macrophages. Pflugers Archiv 447(3):312–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1155-3
Semple BD, O’Brien TJ, Gimlin K, Wright DK, Kim SE, Casillas-Espinosa PM, Webster KM, Petrou S, Noble-Haeusslein LJ (2017) Interleukin-1 receptor in seizure susceptibility after traumatic injury to the pediatric brain. J Neurosci 37(33):7864–7877. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0982-17.2017
Small C, Dagra A, Martinez M, Williams E, Lucke-Wold B (2022) Examining the role of astrogliosis and JNK signaling in post-traumatic epilepsy. Egypt J Neurosur. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-021-00141-x
Steinhäuser C, Grunnet M, Carmignoto G (2016) Crucial role of astrocytes in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 323:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.12.047
Sun Y, Ma J, Li D, Li P, Zhou X, Li Y, He Z, Qin L, Liang L, Luo X (2019) Interleukin-10 inhibits interleukin-1β production and inflammasome activation of microglia in epileptic seizures. J Neuroinflamm 16(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1452-1
Sun L, Shan W, Yang H, Liu R, Wu J, Wang Q (2021) The role of neuroinflammation in post-traumatic epilepsy. Front Neurol 12:646152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.646152
Szu JI, Chaturvedi S, Patel DD, Binder DK (2020) Aquaporin-4 dysregulation in a controlled cortical impact injury model of posttraumatic epilepsy. Neuroscience 428:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.12.006
Therajaran P, Hamilton JA, O’Brien TJ, Jones NC, Ali I (2020) Microglial polarization in posttraumatic epilepsy: potential mechanism and treatment opportunity. Epilepsia 61(2):203–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16424
Tomkins O, Shelef I, Kaizerman I, Eliushin A, Afawi Z, Misk A, Gidon M, Cohen A, Zumsteg D, Friedman A (2008) Blood-brain barrier disruption in post-traumatic epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(7):774–777. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.126425
van Vliet EA, da Costa AS, Redeker S, van Schaik R, Aronica E, Gorter JA (2007) Blood-brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain J Neurol 130(Pt 2):521–534. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl318
Verellen RM, Cavazos JE (2010) Post-traumatic epilepsy: an overview. Therapy 7(5):527–531. https://doi.org/10.2217/thy.10.57
Walker PA, Bedi SS, Shah SK, Jimenez F, Xue H, Hamilton JA, Smith P, Thomas CP, Mays RW, Pati S, Cox CS Jr (2012) Intravenous multipotent adult progenitor cell therapy after traumatic brain injury: modulation of the resident microglia population. J Neuroinflamm 9:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-228
Wang F, Wang X, Shapiro LA, Cotrina ML, Liu W, Wang EW, Gu S, Wang W, He X, Nedergaard M, Huang JH (2017) NKCC1 up-regulation contributes to early post-traumatic seizures and increased post-traumatic seizure susceptibility. Brain Struct Funct 222(3):1543–1556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1292-z
Webster KM, Sun M, Crack P, O’Brien TJ, Shultz SR, Semple BD (2017) Inflammation in epileptogenesis after traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflamm 14(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0786-1
Wei Y, Chen T, Bosco DB, Xie M, Zheng J, Dheer A, Ying Y, Wu Q, Lennon VA, Wu LJ (2021) The complement C3–C3aR pathway mediates microglia-astrocyte interaction following status epilepticus. Glia 69(5):1155–1169. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23955
Weissberg I, Wood L, Kamintsky L, Vazquez O, Milikovsky DZ, Alexander A, Oppenheim H, Ardizzone C, Becker A, Frigerio F, Vezzani A, Buckwalter MS, Huguenard JR, Friedman A, Kaufer D (2015) Albumin induces excitatory synaptogenesis through astrocytic TGF-β/ALK5 signaling in a model of acquired epilepsy following blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Neurobiol Dis 78:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.02.029
Witcher KG, Eiferman DS, Godbout JP (2015) Priming the inflammatory pump of the CNS after traumatic brain injury. Trends Neurosci 38(10):609–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2015.08.002
Wu W, Li Y, Wei Y, Bosco DB, Xie M, Zhao MG, Richardson JR, Wu LJ (2020) Microglial depletion aggravates the severity of acute and chronic seizures in mice. Brain Behav Immun 89:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.06.028
Xu S, Sun Q, Fan J, Jiang Y, Yang W, Cui Y, Yu Z, Jiang H, Li B (2019) Role of astrocytes in post-traumatic epilepsy. Front Neurol 10:1149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.01149
Yamamoto M, Kim M, Imai H, Itakura Y, Ohtsuki G (2019) Microglia-triggered plasticity of intrinsic excitability modulates psychomotor behaviors in acute cerebellar inflammation. Cell Rep 28(11):2923-2938.e2928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.078
Yu C, Deng XJ, Xu D (2023) Microglia in epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 185:106249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106249
Zhang S, Chen F, Zhai F, Liang S (2022) Role of HMGB1/TLR4 and IL-1β/IL-1R1 signaling pathways in epilepsy. Front Neurol 13:904225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.904225
Zhao X, Liao Y, Morgan S, Mathur R, Feustel P, Mazurkiewicz J, Qian J, Chang J, Mathern GW, Adamo MA, Ritaccio AL, Gruenthal M, Zhu X, Huang Y (2018) Noninflammatory changes of microglia are sufficient to cause epilepsy. Cell Rep 22(8):2080–2093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.004
Zheng P, Shultz SR, Hovens CM, Velakoulis D, Jones NC, O’Brien TJ (2014) Hyperphosphorylated tau is implicated in acquired epilepsy and neuropsychiatric comorbidities. Mol Neurobiol 49(3):1532–1539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8601-9
Zhou Y, Dhaher R, Parent M, Hu QX, Hassel B, Yee SP, Hyder F, Gruenbaum SE, Eid T, Danbolt NC (2019) Selective deletion of glutamine synthetase in the mouse cerebral cortex induces glial dysfunction and vascular impairment that precede epilepsy and neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int 123:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2018.07.009
Zhu G, Okada M, Yoshida S, Mori F, Ueno S, Wakabayashi K, Kaneko S (2006) Effects of interleukin-1beta on hippocampal glutamate and GABA releases associated with Ca2+-induced Ca2+ releasing systems. Epilepsy Res 71(2–3):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.05.017
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Gansu Provincial Key Talents Program in 2023, A Study on the Sleep Structure in Refractory Epilepsy Treated with the Addition of AMPA Receptor Antagonists (grant number 2022SHFZ0014), Science and Technology Program (Key Research and Development Program) of Gansu Province (Grant Number 21YF1FA171), Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (Grant Number CY2019-MS13), Lanzhou Science and Technology Program (Grant Number 2018-1-111), and 2017 Cuiying Graduate Research Mentorship Cultivation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (Grant Number 201701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. TW was responsible for conducting feasibility analysis, ensuring quality control, and overseeing the supervision and management of articles. YD proposed the idea for the article, conducted literature retrieval and collection, wrote the original draft, and revised it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
No ethical approval was needed, as no data were generated and used in the review.
Consent for Publication
All the authors have granted their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, Y., Wang, T. Research Progress on the Immune-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Posttraumatic Epilepsy. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 4059–4069 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01429-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01429-2