Abstract
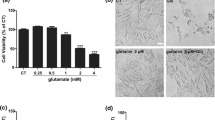
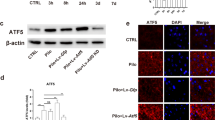
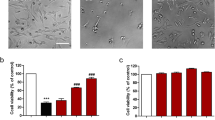
Oxidative stress has been identified as the significant mediator in epilepsy, which is a chronic disorder in central nervous system. About 30% of epilepsy patients are refractory to antiepileptic drug treatment. However, the underlying mechanism of oxidative damage in epilepsy needs further investigation. In our study, we first find that ubiquitin-specific peptidase 15 (USP15) expression was upregulated in a pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) kindled rat model of epilepsy. Silencing USP15 protected against glutamate-mediated neuronal cell death, and inhibited the high expression levels of cleaved caspase-3. Knockout of USP15 significantly reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and enhanced superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in HT22 cells under the exposure to glutamate treatment. Furthermore, USP15 inhibition induced nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-related factor2 (Nrf2) nuclear translocation and promoted protein expression level of heme oxygenase (HO-1). Taken together, our findings first reveal a role of USP15 in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, and silencing USP15 in vitro protects against glutamate-mediated cytotoxicity in HT22 cells. Pharmacological inhibition of USP15 may alleviate epileptic seizures via fighting against oxidative damage, providing a novel antiepileptic target.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akanda MR, Kim MJ, Kim IS, Ahn D, Tae HJ, Rahman MM, Park YG, Seol JW, Nam HH, Choo BK, Park BY (2018) Neuroprotective effects of sigesbeckia pubescens extract on glutamate-induced oxidative stress in HT22 cells via downregulation of MAPK/caspase-3 pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(2):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0496-y
Baker RT, Wang XW, Woollatt E, White JA, Sutherland GR (1999) Identification, functional characterization, and chromosomal localization of USP15, a novel human ubiquitin-specific protease related to the UNP oncoprotein, and a systematic nomenclature for human ubiquitin-specific proteases. Genomics 59(3):264–274. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1999.5879
Bao F, Tao L, Zhang H (2019) Neuroprotective effect of natural alkaloid fangchinoline against oxidative glutamate toxicity: involvement of Keap1-Nrf2 axis regulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00711-6
Baohai X, Shi F, Yongqi F (2019) Inhibition of ubiquitin specific protease 17 restrains prostate cancer proliferation by regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via ROS production. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 118:108946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108946
Caldeira MV, Salazar IL, Curcio M, Canzoniero LM, Duarte CB (2014) Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe? Progress Neurobiol 112:50–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.003
Cardenas-Rodriguez N, Huerta-Gertrudis B, Rivera-Espinosa L, Montesinos-Correa H, Bandala C, Carmona-Aparicio L, Coballase-Urrutia E (2013) Role of oxidative stress in refractory epilepsy: evidence in patients and experimental models. Int J Mol Sci 14(1):1455–1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011455
Chen L, Li K, Liu Q, Quiles JL, Filosa R, Kamal MA, Wang F, Kai G, Zou X, Teng H, Xiao J (2019) Protective effects of raspberry on the oxidative damage in HepG2 cells through Keap1/Nrf2-dependent signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110781
Corda MG, Giorgi O, Longoni B, Orlandi M, Biggio G (1990) Decrease in the function of the gamma-aminobutyric acid-coupled chloride channel produced by the repeated administration of pentylenetetrazol to rats. J Neurochem 55(4):1216–1221. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03127.x
Cotto-Rios XM, Bekes M, Chapman J, Ueberheide B, Huang TT (2012) Deubiquitinases as a signaling target of oxidative stress. Cell Rep 2(6):1475–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.011
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, O'Brien TJ, Jette N, Scheffer IE, de Curtis M, Perucca P (2018) Epilepsy. Nature Rev Dis Primers 4:18024. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.24
Eichhorn PJ, Rodon L, Gonzalez-Junca A, Dirac A, Gili M, Martinez-Saez E, Aura C, Barba I, Peg V, Prat A, Cuartas I, Jimenez J, Garcia-Dorado D, Sahuquillo J, Bernards R, Baselga J, Seoane J (2012) USP15 stabilizes TGF-beta receptor I and promotes oncogenesis through the activation of TGF-beta signaling in glioblastoma. Nature Med 18(3):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2619
Engel T, Martinez-Villarreal J, Henke C, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Sanz-Rodriguez A, Alves M, Hernandez-Santana Y, Brennan GP, Kenny A, Campbell A, Lucas JJ, Henshall DC (2017) Spatiotemporal progression of ubiquitin-proteasome system inhibition after status epilepticus suggests protective adaptation against hippocampal injury. Mol Neurodegener 12(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0163-2
Fao L, Mota SI, Rego AC (2019) Shaping the Nrf2-ARE-related pathways in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Ageing Res Rev 54:100942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2019.100942
Fiest KM, Sauro KM, Wiebe S, Patten SB, Kwon CS, Dykeman J, Pringsheim T, Lorenzetti DL, Jette N (2017) Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of international studies. Neurology 88(3):296–303. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000003509
Folbergrova J, Jesina P, Kubova H, Druga R, Otahal J (2016) Status epilepticus in immature rats is associated with oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Front Cell Neurosci 10:136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00136
Fukui M, Song JH, Choi J, Choi HJ, Zhu BT (2009) Mechanism of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 mouse hippocampal cells. Eur J Pharmacol 617(1–3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.059
Geronzi U, Lotti F, Grosso S (2018) Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 18(5):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1465410
Grewal GK, Kukal S, Kanojia N, Saso L, Kukreti S, Kukreti R (2017) Effect of oxidative stress on ABC transporters: contribution to epilepsy pharmacoresistance. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365
Hoang TT, Johnson DA, Raines RT, Johnson JA (2019) Angiogenin activates the astrocytic Nrf2/ARE pathway and thereby protects murine neurons from oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008491
Huang OW, Cochran AG (2013) Regulation of deubiquitinase proteolytic activity. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23(6):806–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2013.07.012
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (1999) Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev 13(1):76–86. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.1.76
Jarrett SG, Liang LP, Hellier JL, Staley KJ, Patel M (2008) Mitochondrial DNA damage and impaired base excision repair during epileptogenesis. Neurobiol Dis 30(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2007.12.009
Jiang X, Yu M, Ou Y, Cao Y, Yao Y, Cai P, Zhang F (2017) Downregulation of USP4 promotes activation of microglia and subsequent neuronal inflammation in rat spinal cord after injury. Neurochem Res 42(11):3245–3253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2361-2
Kaur H, Bal A, Sandhir R (2014) Curcumin supplementation improves mitochondrial and behavioral deficits in experimental model of chronic epilepsy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 125:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.08.001
Khan M, Rutten BPF, Kim MO (2019) MST1 regulates neuronal cell death via JNK/Casp3 signaling pathway in HFD mouse brain and HT22 cells. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102504
Kim JE, Lee DS, Kim MJ, Kang TC (2019) PLPP/CIN-mediated NEDD4-2 S448 dephosphorylation regulates neuronal excitability via GluA1 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis 10(8):545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1781-0
Kovac S, Domijan AM, Walker MC, Abramov AY (2014) Seizure activity results in calcium- and mitochondria-independent ROS production via NADPH and xanthine oxidase activation. Cell Death Dis 5:e1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.390
Kudin AP, Zsurka G, Elger CE, Kunz WS (2009) Mitochondrial involvement in temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Neurol 218(2):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.02.014
Lin Y, Han Y, Xu J, Cao L, Gao J, Xie N, Zhao X, Jiang H, Chi Z (2010) Mitochondrial DNA damage and the involvement of antioxidant defense and repair system in hippocampi of rats with chronic seizures. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30(6):947–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9524-x
Liu J, Ye J, Zou X, Xu Z, Feng Y, Zou X, Chen Z, Li Y, Cang Y (2014) CRL4A(CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase restricts BK channel activity and prevents epileptogenesis. Nature Commun 5:3924. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4924
Liu C, Liu C, Liu H, Gong L, Tao T, Shen Y, Zhu S, Shen A (2017) Increased expression of ubiquitin-specific protease 4 participates in neuronal apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(3):427–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0375-y
Mazhar F, Malhi SM, Simjee SU (2017) Comparative studies on the effects of clinically used anticonvulsants on the oxidative stress biomarkers in pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling model of epileptogenesis in mice. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 28(1):31–42. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2016-0034
Mendez-Armenta M, Nava-Ruiz C, Juarez-Rebollar D, Rodriguez-Martinez E, Gomez PY (2014) Oxidative stress associated with neuronal apoptosis in experimental models of epilepsy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:293689. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/293689
Mevissen TET, Komander D (2017) Mechanisms of deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 86:159–192. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044916
Munguia-Martinez MF, Nava-Ruiz C, Ruiz-Diaz A, Diaz-Ruiz A, Yescas-Gomez P, Mendez-Armenta M (2019) Immunohistochemical study of antioxidant enzymes regulated by Nrf2 in the models of epileptic seizures (KA and PTZ). Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2019:1327986. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1327986
Nagai H, Noguchi T, Homma K, Katagiri K, Takeda K, Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2009) Ubiquitin-like sequence in ASK1 plays critical roles in the recognition and stabilization by USP9X and oxidative stress-induced cell death. Mol Cell 36(5):805–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.016
Paemka L, Mahajan VB, Ehaideb SN, Skeie JM, Tan MC, Wu S, Cox AJ, Sowers LP, Gecz J, Jolly L, Ferguson PJ, Darbro B, Schneider A, Scheffer IE, Carvill GL, Mefford HC, El-Shanti H, Wood SA, Manak JR, Bassuk AG (2015) Seizures are regulated by ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9 X-linked (USP9X), a de-ubiquitinase. PLoS Genet 11(3):e1005022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005022
Pansani AP, Cysneiros RM, Colugnati DB, Janjoppi L, Ferrari D, de Lima E, Ghazale PP, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Scorza FA (2018) Long-term monotherapy treatment with vitamin E reduces oxidative stress, but not seizure frequency in rats submitted to the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 88:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.027
Pardillo-Diaz R, Carrascal L, Barrionuevo G, Nunez-Abades P (2017) Oxidative stress induced by cumene hydroperoxide produces synaptic depression and transient hyperexcitability in rat primary motor cortex neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 82:204–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2017.06.002
Pauletti A, Terrone G, Shekh-Ahmad T, Salamone A, Ravizza T, Rizzi M, Pastore A, Pascente R, Liang LP, Villa BR, Balosso S, Abramov AY, van Vliet EA, Del Giudice E, Aronica E, Patel M, Walker MC, Vezzani A (2019) Targeting oxidative stress improves disease outcomes in a rat model of acquired epilepsy. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz130
Pearson JN, Rowley S, Liang LP, White AM, Day BJ, Patel M (2015) Reactive oxygen species mediate cognitive deficits in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 82:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.07.005
Perucca P, Gilliam FG (2012) Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol 11(9):792–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70153-9
Rajalingam K, Dikic I (2016) SnapShot: expanding the ubiquitin code. Cell 164(5):1074–1074.e1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.019
Rowley S, Patel M (2013) Mitochondrial involvement and oxidative stress in temporal lobe epilepsy. Free Radical Biol Med 62:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.02.002
Sesti F, Liu S, Cai SQ (2010) Oxidation of potassium channels by ROS: a general mechanism of aging and neurodegeneration? Trends Cell Biol 20(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2009.09.008
Shalem O, Sanjana NE, Hartenian E, Shi X, Scott DA, Mikkelson T, Heckl D, Ebert BL, Root DE, Doench JG, Zhang F (2014) Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 343(6166):84–87. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1247005
Shao YY, Li B, Huang YM, Luo Q, Xie YM, Chen YH (2017) Thymoquinone attenuates brain injury via an anti-oxidative pathway in a status epilepticus rat model. Transl Neurosci 8:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2017-0003
Shekh-Ahmad T, Eckel R, Dayalan Naidu S, Higgins M, Yamamoto M, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Kovac S, Abramov AY, Walker MC (2018) KEAP1 inhibition is neuroprotective and suppresses the development of epilepsy. Brain 141(5):1390–1403. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy071
Shekh-Ahmad T, Lieb A, Kovac S, Gola L, Christian Wigley W, Abramov AY, Walker MC (2019) Combination antioxidant therapy prevents epileptogenesis and modifies chronic epilepsy. Redox Biol 26:101278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101278
Shi JX, Wang QJ, Li H, Huang Q (2016) Silencing of USP22 suppresses high glucose-induced apoptosis, ROS production and inflammation in podocytes. Mol BioSyst 12(5):1445–1456. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mb00722d
Shivakumar BR, Anandatheerthavarada HK, Ravindranath V (1991) Free radical scavenging systems in developing rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 9(2):181–185
Simeone KA, Matthews SA, Samson KK, Simeone TA (2014) Targeting deficiencies in mitochondrial respiratory complex I and functional uncoupling exerts anti-seizure effects in a genetic model of temporal lobe epilepsy and in a model of acute temporal lobe seizures. Exp Neurol 251:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.005
Singh N, Vijayanti S, Saha L, Bhatia A, Banerjee D, Chakrabarti A (2018) Neuroprotective effect of Nrf2 activator dimethyl fumarate, on the hippocampal neurons in chemical kindling model in rat. Epilepsy Res 143:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2018.02.011
Song JH, Lee HJ, Kang KS (2019) Procyanidin C1 activates the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway to prevent glutamate-induced apoptotic HT22 cell death. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010142
Takahashi M, Higuchi M, Matsuki H, Yoshita M, Ohsawa T, Oie M, Fujii M (2013) Stress granules inhibit apoptosis by reducing reactive oxygen species production. Mol Cell Biol 33(4):815–829. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00763-12
Tan S, Wood M, Maher P (1998) Oxidative stress induces a form of programmed cell death with characteristics of both apoptosis and necrosis in neuronal cells. J Neurochem 71(1):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71010095.x
Torre S, Polyak MJ, Langlais D, Fodil N, Kennedy JM, Radovanovic I, Berghout J, Leiva-Torres GA, Krawczyk CM, Ilangumaran S, Mossman K, Liang C, Knobeloch KP, Healy LM, Antel J, Arbour N, Prat A, Majewski J, Lathrop M, Vidal SM, Gros P (2017) USP15 regulates type I interferon response and is required for pathogenesis of neuroinflammation. Nature Immunol 18(1):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3581
Trotti D, Danbolt NC, Volterra A (1998) Glutamate transporters are oxidant-vulnerable: a molecular link between oxidative and excitotoxic neurodegeneration? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19(8):328–334
Villeneuve NF, Tian W, Wu T, Sun Z, Lau A, Chapman E, Fang D, Zhang DD (2013) USP15 negatively regulates Nrf2 through deubiquitination of Keap1. Mol Cell 51(1):68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.022
Wang L, Wu D, Xu Z (2019) USP10 protects against cerebral ischemia injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis through the inhibition of TAK1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(4):1272–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.042
Wen Y, Wu Q, Shi Q, Xie Y, Dan W, Chen Y, Ma L (2018) UCH-L1 inhibition aggravates mossy fiber sprouting in the pentylenetetrazole kindling model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(4):2312–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.154
Zhang SH, Liu D, Hu Q, Zhu J, Wang S, Zhou S (2019) Ferulic acid ameliorates pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures by reducing neuron cell death. Epilepsy Res 156:106183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2019.106183
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of this research by Shanghai Science & Technology Research Program (14411972200), Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (20134067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GB and XC conceived and designed the study. XC and FL performed the experiments. XC contributed to the statistical analyses. GB and XC wrote the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, (China) or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Bao, G. & Liu, F. Inhibition of USP15 Prevent Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in HT22 Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 999–1010 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00789-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00789-3