Abstract
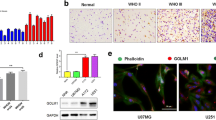
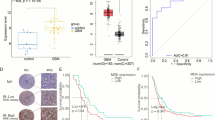
The KDEL (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) receptors (KDELRs), proteins with seven transmembrane domains, are primarily responsible for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis. Recent studies have found additional function of KDELRs in growth, cellular secretory traffic, immune response, and autophagy; however, its role in tumorigenesis is still poorly understood. Here, we showed that KDELR2 is highly expressed in glioblastoma (GBM) tissues. Reviewing the expression of KDELR2 in TCGA and REMBRANDT database, we found that higher expression of KDELR2 is associated with shorter survival of GBM patients. We explored the effect of KDELR2 on tumorigenesis in GBM cells and animal model (nude mice), and identified KDELR2 as oncogene promoting cell proliferation. Additionally, KDELR2 expression in GBM cells correlated positively with HIF1alpha (HIF1α) expression, and we demonstrated by ChIP-qPCR and luciferase reporter assay that the upstream region of the KDELR2 gene is directly targeted by HIF1alpha. Taken together, our data suggest that KDELR2 is a target gene downstream of HIF1-alpha driving the malignancy of GBM and could eventually serve as a therapeutic target for the treatment of GBM patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker FG II, Davis RL, Chang SM, Prados MD (1996) Necrosis as a prognostic factor in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer 77:1161–1166
Capitani M, Sallese M (2009) The KDEL receptor: new functions for an old protein. FEBS Lett 583:3863–3871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.053
Collins JE et al (2004) A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome. Genome Biol 5:R84. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84
Ghosh J, Kapur R (2017) Role of mTORC1-S6K1 signaling pathway in regulation of hematopoietic stem cell and acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol 50:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2017.02.004
Giannotta M et al (2012) The KDEL receptor couples to Galphaq/11 to activate Src kinases and regulate transport through the Golgi. EMBO J 31:2869–2881. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.134
Hsu VW, Shah N, Klausner RD (1992) A brefeldin A-like phenotype is induced by the overexpression of a human ERD-2-like protein, ELP-1. Cell 69:625–635
Hsu JB, Chang TH, Lee GA, Lee TY, Chen CY (2019) Identification of potential biomarkers related to glioma survival by gene expression profile analysis. BMC Med Genomics 11:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0479-6
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104819
Kamimura D et al (2015) KDEL receptor 1 regulates T-cell homeostasis via PP1 that is a key phosphatase for ISR. Nat Commun 6:7474. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8474
Kaur B, Khwaja FW, Severson EA, Matheny SL, Brat DJ, Van Meir EG (2005) Hypoxia and the hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol 7:134–153. https://doi.org/10.1215/S1152851704001115
Lewis MJ, Pelham HR (1990) A human homologue of the yeast HDEL receptor. Nature 348:162–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/348162a0
Lewis MJ, Pelham HR (1992) Sequence of a second human KDEL receptor. J Mol Biol 226:913–916
Li N et al (2016) Hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) recruits macrophage to activate pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060799
Raykhel I, Alanen H, Salo K, Jurvansuu J, Nguyen VD, Latva-Ranta M, Ruddock L (2007) A molecular specificity code for the three mammalian KDEL receptors. J Cell Biol 179:1193–1204. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200705180
Scheel AA, Pelham HR (1998) Identification of amino acids in the binding pocket of the human KDEL receptor. J Biol Chem 273:2467–2472
Semenza JC, Hardwick KG, Dean N, Pelham HR (1990) ERD2, a yeast gene required for the receptor-mediated retrieval of luminal ER proteins from the secretory pathway. Cell 61:1349–1357
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Tiwarekar V, Fehrholz M, Schneider-Schaulies J (2019) KDELR2 Competes with measles virus envelope proteins for cellular chaperones reducing their chaperone-mediated cell surface transport. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11010027
Touat M, Idbaih A, Sanson M, Ligon KL (2017) Glioblastoma targeted therapy: updated approaches from recent biological insights. Ann Oncol 28:1457–1472. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx106
Townsley FM, Wilson DW, Pelham HR (1993) Mutational analysis of the human KDEL receptor: distinct structural requirements for Golgi retention, ligand binding and retrograde transport. EMBO J 12:2821–2829
Trychta KA, Back S, Henderson MJ, Harvey BK (2018) KDEL receptors are differentially regulated to maintain the ER proteome under calcium deficiency. Cell Rep 25(1829–1840):e1826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.055
Wang P, Li B, Zhou L, Fei E, Wang G (2011) The KDEL receptor induces autophagy to promote the clearance of neurodegenerative disease-related proteins. Neuroscience 190:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.008
Watson CJ, Friend PJ, Jamieson NV, Frick TW, Alexander G, Gimson AE, Calne R (1999) Sirolimus: a potent new immunosuppressant for liver transplantation. Transplantation 67:505–509
Wilson DW, Lewis MJ, Pelham HR (1993) pH-dependent binding of KDEL to its receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem 268:7465–7468
Yamamoto K, Hamada H, Shinkai H, Kohno Y, Koseki H, Aoe T (2003) The KDEL receptor modulates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. J Biol Chem 278:34525–34532. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304188200
Zhao T et al (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha regulates chemotactic migration of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells through directly transactivating the CX3CR1 gene. PLoS ONE 7:e43399. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043399
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [81702481], National Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin [15JCQNJC44800].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS and LM conceived the project and designed the study; ZL and CS performed most of the experiments; ZS and XZ assisted in some in vitro experiments; PL, PW, and WL provided clinical samples; LM provided reagents and conceptual advice; ZL and CS wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital (China) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital (China) or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Z., She, C., Ma, L. et al. KDELR2 Promotes Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis Targeted by HIF1a via mTOR Signaling Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39, 1207–1215 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00715-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00715-2