Abstract
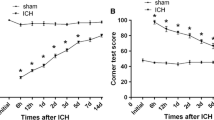
Somatostatins are peptide hormones that regulate diverse cellular processes, such as neurotransmission, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and endocrine signaling as well as inhibiting the release of many hormones and other secretory proteins. SSTR1 is a member of the superfamily of somatostatin receptors possessing seven-transmembrane segments. Aberrant expression of SSTR1 has been implicated in several human diseases, including pseudotumor cerebri, and oncogenic osteomalacia. In this study, we investigated a potential role of SSTR1 in the regulation of neuronal apoptosis in the course of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). A rat ICH model in the caudate putamen was established and subjected to behavioral tests. Western blot and immunohistochemistry indicated a remarkable up-regulation of SSTR1 expression surrounding the hematoma after ICH. Double-labeled immunofluorescence showed that SSTR1 was mostly co-localized with neurons, and was rarely distributed in activated astrocytes and microglia. Additionally, SSTR1 co-localized with active-caspase-3 and bcl-2 around the hematoma. The expression of active-caspase-3 was parallel with that of SSTR1 in a time-dependent manner. In addition, SSTR1 knockdown specifically resulted in reduced neuronal apoptosis in PC12 cells. All our findings suggested that up-regulated SSTR1 contributed to neuronal apoptosis after ICH, which was accompanied with reduced expression of bcl-2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akopian A, Johnson J, Gabriel R, Brecha N, Witkovsky P (2000) Somatostatin modulates voltage-gated K(+) and Ca(2+) currents in rod and cone photoreceptors of the salamander retina. J Neurosci 20:929–936
Aronowski J, Zhao X (2011) Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: secondary brain injury. Stroke 42:1781–1786
Bradl M, Lassmann H (2010) Oligodendrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119:37–53
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:e331–e339
Chatterjee S et al (2007) Prolonged somatostatin therapy may cause down-regulation of SSTR-like GPCRs on Schistosoma mansoni. J Vector Borne Dis 44:164–180
Cregan SP, MacLaurin JG, Craig CG, Robertson GS, Nicholson DW, Park DS, Slack RS (1999) Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis in neurons. J Neurosci 19:7860–7869
Epelbaum J, Dournaud P, Fodor M, Viollet C (1994) The neurobiology of somatostatin. Crit Rev Neurobiol 8:25–44
Hu C et al (2004) The effect of somatostatin and SSTR3 on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 3:726–730
Hua Y, Schallert T, Keep RF, Wu J, Hoff JT, Xi G (2002) Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 33:2478–2484
Huan W et al (2012) Spatiotemporal patterns and essential role of TNF receptor-associated factor 5 expression after rat spinal cord Injury. J Mol Histol 43:527–533
Ikram MA, Wieberdink RG, Koudstaal PJ (2012) International epidemiology of intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr Atheroscler Rep 14:300–306
Jiang H, Li J, Zhou T, Wang C, Zhang H, Wang H (2014) Colistin-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells: involvement of the mitochondrial apoptotic and death receptor pathways. Int J Mol Med 33:1298–1304
Karabiyikoglu M, Hua Y, Keep RF, Ennis SR, Xi G (2004) Intracerebral hirudin injection attenuates ischemic damage and neurologic deficits without altering local cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:159–166
Karwacki Z et al (2005) Apoptosis in the course of experimental intracerebral haemorrhage in the rat. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 64:248–252
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Li L et al (2013) Up-regulation of NFATc4 involves in neuronal apoptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:893–905
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X (1996) Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 86:147–157
Liu X, Yuan D, Nie X, Shen J, Yan Y, Zhang D, Gu J (2014) BTEB2 prevents neuronal apoptosis via promoting bad phosphorylation in rat intracerebral hemorrhage model. J Mol Neurosci
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92–101
Papadaki T, Tsilimbaris M, Pallikaris I, Thermos K (2010) Somatostatin receptor activation (sst(1) -sst(5)) differentially influences human retinal pigment epithelium cell viability. Acta Ophthalmol 88:e228–e233
Patel YC (1999) Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 20:157–198
Patel YC, Srikant CB (1994) Subtype selectivity of peptide analogs for all five cloned human somatostatin receptors (hsstr 1-5). Endocrinology 135:2814–2817
Qiu CZ, Wang C, Huang ZX, Zhu SZ, Wu YY, Qiu JL (2006) Relationship between somatostatin receptor subtype expression and clinicopathology, Ki-67, bcl-2 and p53 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12:2011–2015
Qureshi AI, Mendelow AD, Hanley DF (2009) Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 373:1632–1644
Reubi JC (1992) Somatostatin receptors in the gastrointestinal tract in health and disease. Yale J Biol Med 65:493–503 discussion 531-496
Rochaix P et al (1999) Gene therapy for pancreatic carcinoma: local and distant antitumor effects after somatostatin receptor sst2 gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther 10:995–1008
Rui Y et al (2013) Up-regulated expression of Bnip3L after intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. J Mol Histol 44:497–505
Sharma K, Srikant CB (1998) G protein coupled receptor signaled apoptosis is associated with activation of a cation insensitive acidic endonuclease and intracellular acidification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242:134–140
Sharma K, Patel YC, Srikant CB (1996) Subtype-selective induction of wild-type p53 and apoptosis, but not cell cycle arrest, by human somatostatin receptor 3. Mol Endocrinol 10:1688–1696
Stetak A, Lankenau A, Vantus T, Csermely P, Ullrich A, Keri G (2001) The antitumor somatostatin analogue TT-232 induces cell cycle arrest through PKCdelta and c-Src. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285:483–488
Teijeiro R, Rios R, Costoya JA, Castro R, Bello JL, Devesa J, Arce VM (2002) Activation of human somatostatin receptor 2 promotes apoptosis through a mechanism that is independent from induction of p53. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:31–38
Tsai CF, Thomas B, Sudlow CL (2013) Epidemiology of stroke and its subtypes in Chinese vs white populations: a systematic review. Neurology 81:264–272
Vaux DL (2011) Apoptogenic factors released from mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:546–550
Wang J, Dore S (2007) Inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:894–908
War SA, Kumar U (2012) Coexpression of human somatostatin receptor-2 (SSTR2) and SSTR3 modulates antiproliferative signaling and apoptosis. J Mol Signal 7:5
War SA, Somvanshi RK, Kumar U (2011) Somatostatin receptor-3 mediated intracellular signaling and apoptosis is regulated by its cytoplasmic terminal. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:390–402
Watt HL, Kharmate GD, Kumar U (2009) Somatostatin receptors 1 and 5 heterodimerize with epidermal growth factor receptor: agonist-dependent modulation of the downstream MAPK signalling pathway in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 21:428–439
Xi G, Fewel ME, Hua Y, Thompson BG Jr, Hoff JT, Keep RF (2004) Intracerebral hemorrhage: pathophysiology and therapy. Neurocrit Care 1:5–18
Xue M, Del Bigio MR (2003) Comparison of brain cell death and inflammatory reaction in three models of intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 12:152–159
Yoon JH, Lee HH, Yi ES, Baek SG (2013) Age-dependent effect of treadmill exercise on hemorrhage-induced neuronal cell death in rats. J Exerc Rehabil 9:506–510
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81371367, No. 31370803), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2009156, No. BK2009157, No. BK2009161), Nantong City Social Development Projects Fund (No. HS2012032), Development Fund for Collaborative Innovation Center of Glycoscience of Shandong University and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Damin Yuan and Janhong Shen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, D., Shen, J., Yan, Y. et al. Upregulated Expression of SSTR1 is Involved in Neuronal Apoptosis and is Coupled to the Reduction of bcl-2 Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adult Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 951–961 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0081-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0081-6