Abstract
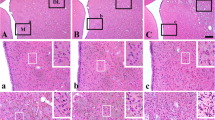
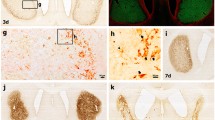
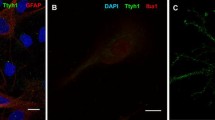
The extent of neuronal damage/death in some brain regions is highly correlated to duration time of transient ischemia. In the present study, we carried out neuronal degeneration/death and glial changes in the septum 4 days after 5, 10, 15, and 20 min of transient cerebral ischemia using gerbils. To examine neuronal damage, Fluoro-Jade B (F-J B, a marker for neuronal degeneration) histofluorescence staining was used. F-J B positive (+) cells were detected in the septo-hippocampal nucleus (SHN) of the septum only in the 20 min ischemia-group; the mean number of F-J B+ neurons was 14.9 ± 2.5/400 μm2 in a section. Gliosis of astrocytes and microglia was examined using anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and anti-ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1), respectively. In all the ischemia-groups, GFAP- and Iba-1-immunoreactive astrocytes and microglia, respectively, were increased in number, and apparently tended to be increased in their immunoreactivity. Especially, in the 20 min ischemia-group, the number and immunoreactivity of Iba-immunoreactive microglia was highest and strongest in the ischemic SHN 4 days after ischemia–reperfusion. In brief, our findings showed that neuronal damage/death in the SHN occurred and gliosis was apparently increased in the 20 min ischemia-group at 4 days after ischemia–reperfusion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron KD (1995) The microglial cell. A historical review. J Neurol Sci 134(Suppl):57–68
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Cavanaugh K, Eveleth D, Carriero DL, Lynch G (1995) Time-related neuronal changes following middle cerebral artery occlusion: implications for therapeutic intervention and the role of calpain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15(6):969–979
Brashear HR, Zaborszky L, Heimer L (1986) Distribution of GABAergic and cholinergic neurons in the rat diagonal band. Neuroscience 17(2):439–451
Buchan AM, Pulsinelli WA (1990) Septo-hippocampal deafferentation protects CA1 neurons against ischemic injury. Brain Res 512(1):7–14
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N, Leon OS (2003) Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils. Neurosci Res 47(2):245–253
Crain BJ, Westerkam WD, Harrison AH, Nadler JV (1988) Selective neuronal death after transient forebrain ischemia in the Mongolian gerbil: a silver impregnation study. Neuroscience 27(2):387–402
de Araujo FL, Bertolino G, Goncalves RB, Marini Lde C, Coimbra NC, de Araujo JE (2012) Neuropathology and behavioral impairments after three types of global ischemia surgery in Meriones unguiculatus: evidence in motor cortex, hippocampal CA1 region and the neostriatum. J Neurol Sci 312(1–2):73–78
DeFrance JF, Kitai ST, Shimono T (1973) Electrophysiological analysis of the hippocampal-septal projections. I. Response and topographical characteristics. Exp Brain Res 17(5):447–462
Freund TF, Antal M (1988) GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus. Nature 336(6195):170–173
Fukuchi T, Katayama Y, Kamiya T, McKee A, Kashiwagi F, Terashi A (1998) The effect of duration of cerebral ischemia on brain pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, energy metabolites, and blood flow during reperfusion in gerbil brain. Brain Res 792(1):59–65
Gallyas F, Zoltay G, Dames W (1992) Formation of “dark” (argyrophilic) neurons of various origin proceeds with a common mechanism of biophysical nature (a novel hypothesis). Acta Neuropathol 83(5):504–509
Gehrmann J, Banati RB, Wiessner C, Hossmann KA, Kreutzberg GW (1995) Reactive microglia in cerebral ischaemia: an early mediator of tissue damage? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 21(4):277–289
Giulian D, Vaca K (1993) Inflammatory glia mediate delayed neuronal damage after ischemia in the central nervous system. Stroke 24(12 Suppl):I84–I90
Guo X, Nakamura K, Kohyama K, Harada C, Behanna HA, Watterson DM, Matsumoto Y, Harada T (2007) Inhibition of glial cell activation ameliorates the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Res 59(4):457–466
Hailer NP, Jarhult JD, Nitsch R (1996) Resting microglial cells in vitro: analysis of morphology and adhesion molecule expression in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Glia 18(4):319–331
Hashimoto M, Nitta A, Fukumitsu H, Nomoto H, Shen L, Furukawa S (2005) Involvement of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in activation processes of rodent macrophages. J Neurosci Res 79(4):476–487
Horn M, Schlote W (1992) Delayed neuronal death and delayed neuronal recovery in the human brain following global ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 85(1):79–87
Hu Z, Zeng L, Xie L, Lu W, Zhang J, Li T, Wang X (2007) Morphological alteration of Golgi apparatus and subcellular compartmentalization of TGF-beta1 in Golgi apparatus in gerbils following transient forebrain ischemia. Neurochem Res 32(11):1927–1931
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DW, Choi SY, Kang TC, Kim YS, Won MH (2006) Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 immunoreactive cells change in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region after ischemia/reperfusion. Neurochem Res 31(7):957–965
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DO, Lee BH, Kwon YG, Won MH (2007) Time course of changes in pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (vitamin B6 active form) and its neuroprotection in experimental ischemic damage. Exp Neurol 206(1):114–125
Janac B, Radenovic L, Selakovic V, Prolic Z (2006) Time course of motor behavior changes in Mongolian gerbils submitted to different durations of cerebral ischemia. Behav Brain Res 175(2):362–373
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239(1):57–69
Kirino T, Sano K (1984) Selective vulnerability in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 62(3):201–208
Kiss J, Patel AJ, Freund TF (1990) Distribution of septohippocampal neurons containing parvalbumin or choline acetyltransferase in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 298(3):362–372
Kraig RP, Dong LM, Thisted R, Jaeger CB (1991) Spreading depression increases immunohistochemical staining of glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Neurosci 11(7):2187–2198
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19(8):312–318
Kriz J (2006) Inflammation in ischemic brain injury: timing is important. Crit Rev Neurobiol 18(1–2):145–157
Kumar K, Evans AT (1997) Effect of hypothermia on microglial reaction in ischemic brain. NeuroReport 8(4):947–950
Lascola C, Kraig RP (1997) Astroglial acid-base dynamics in hyperglycemic and normoglycemic global ischemia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21(2):143–150
Laurenzi MA, Arcuri C, Rossi R, Marconi P, Bocchini V (2001) Effects of microenvironment on morphology and function of the microglial cell line BV-2. Neurochem Res 26(11):1209–1216
Levine S, Sohn D (1969) Cerebral ischemia in infant and adult gerbils. Relation to incomplete circle of Willis. Arch Pathol 87(3):315–317
Levy DE, Brierley JB (1974) Communications between vertebro-basilar and carotid arterial circulations in the gerbil. Exp Neurol 45(3):503–508
Lin CS, Polsky K, Nadler JV, Crain BJ (1990) Selective neocortical and thalamic cell death in the gerbil after transient ischemia. Neuroscience 35(2):289–299
Lorrio S, Negredo P, Roda JM, Garcia AG, Lopez MG (2009) Effects of memantine and galantamine given separately or in association, on memory and hippocampal neuronal loss after transient global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Brain Res 1254:128–137
Lu YZ, Lin CH, Cheng FC, Hsueh CM (2005) Molecular mechanisms responsible for microglia-derived protection of Sprague-Dawley rat brain cells during in vitro ischemia. Neurosci Lett 373(2):159–164
Manns ID, Alonso A, Jones BE (2000) Discharge profiles of juxtacellularly labeled and immunohistochemically identified GABAergic basal forebrain neurons recorded in association with the electroencephalogram in anesthetized rats. J Neurosci 20(24):9252–9263
Matsushima K, Schmidt-Kastner R, Hogan MJ, Hakim AM (1998) Cortical spreading depression activates trophic factor expression in neurons and astrocytes and protects against subsequent focal brain ischemia. Brain Res 807(1–2):47–60
McRae A, Gilland E, Bona E, Hagberg H (1995) Microglia activation after neonatal hypoxic-ischemia. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 84(2):245–252
Meibach RC, Siegel A (1977) Efferent connections of the septal area in the rat: an analysis utilizing retrograde and anterograde transport methods. Brain Res 119(1):1–20
Ohk TG, Yoo KY, Park SM, Shin BN, Kim IH, Park JH, Ahn HC, Lee YJ, Kim MJ, Kim TY, Won MH, Cho JH (2012) Neuronal damage using fluoro-jade B histofluorescence and gliosis in the striatum after various durations of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurochem Res 37(4):826–834
Ordy JM, Wengenack TM, Bialobok P, Coleman PD, Rodier P, Baggs RB, Dunlap WP, Kates B (1993) Selective vulnerability and early progression of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell degeneration and GFAP-positive astrocyte reactivity in the rat four-vessel occlusion model of transient global ischemia. Exp Neurol 119(1):128–139
Panula P, Revuelta AV, Cheney DL, Wu JY, Costa E (1984) An immunohistochemical study on the location of GABAergic neurons in rat septum. J Comp Neurol 222(1):69–80
Petito CK, Halaby IA (1993) Relationship between ischemia and ischemic neuronal necrosis to astrocyte expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein. Int J Dev Neurosci 11(2):239–247
Petito CK, Feldmann E, Pulsinelli WA, Plum F (1987) Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorespiratory arrest. Neurology 37(8):1281–1286
Petito CK, Morgello S, Felix JC, Lesser ML (1990) The two patterns of reactive astrocytosis in postischemic rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10(6):850–859
Raisman G (1966) The connexions of the septum. Brain 89(2):317–348
Risold PY, Swanson LW (1997) Connections of the rat lateral septal complex. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 24(2–3):115–195
Rodrigo R, Fernandez-Gajardo R, Gutierrez R, Matamala JM, Carrasco R, Miranda-Merchak A, Feuerhake W (2013) Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets [Epub ahead of print]
Salazar-Colocho P, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2008) Neuroprotective effects of serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor activation against ischemic cell damage in gerbil hippocampus: involvement of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit and BDNF. Brain Res 1199:159–166
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874(2):123–130
Schwartz M, Butovsky O, Bruck W, Hanisch UK (2006) Microglial phenotype: is the commitment reversible? Trends Neurosci 29(2):68–74
Selakovic V, Korenic A, Radenovic L (2011) Spatial and temporal patterns of oxidative stress in the brain of gerbils submitted to different duration of global cerebral ischemia. Int J Dev Neurosci 29(6):645–654
Stensaas SS, Edwards CQ, Stensaas LJ (1972) An experimental study of hyperchromic nerve cells in the cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol 36(3):472–487
Steward O, Torre ER, Tomasulo R, Lothman E (1992) Seizures and the regulation of astroglial gene expression. Epilepsy Res Suppl 7:197–209
Stoll G, Jander S, Schroeter M (1998) Inflammation and glial responses in ischemic brain lesions. Prog Neurobiol 56(2):149–171
Sugawara T, Lewen A, Noshita N, Gasche Y, Chan PH (2002) Effects of global ischemia duration on neuronal, astroglial, oligodendroglial, and microglial reactions in the vulnerable hippocampal CA1 subregion in rats. J Neurotrauma 19(1):85–98
Swanson LW, Cowan WM (1979) The connections of the septal region in the rat. J Comp Neurol 186(4):621–655
Winson J (1978) Loss of hippocampal theta rhythm results in spatial memory deficit in the rat. Science 201(4351):160–163
Yoshida K, Oka H (1995) Topographical projections from the medial septum-diagonal band complex to the hippocampus: a retrograde tracing study with multiple fluorescent dyes in rats. Neurosci Res 21(3):199–209
Yu DK, Yoo KY, Shin BN, Kim IH, Park JH, Lee CH, Choi JH, Cho YJ, Kang IJ, Kim YM, Won MH (2012) Neuronal damage in hippocampal subregions induced by various durations of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils using Fluoro-Jade B histofluorescence. Brain Res 1437:50–57
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A1A2001404), and by 2012 Kangwon National University Hospital Grant.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chan Woo Park and Jae-Chul Lee contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C.W., Lee, JC., Ahn, J.H. et al. Neuronal Damage Using Fluoro-Jade B Histofluorescence and Gliosis in the Gerbil Septum Submitted to Various Durations of Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 991–1001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9967-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9967-y