Abstract
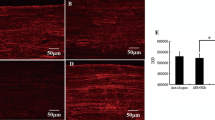
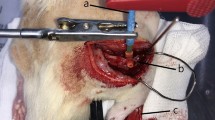
Objectives To observe the effect of ultrashortwave (USW) therapy on nerve regeneration after acellular nerve allografts(ANA) repairing the sciatic nerve gap of rats and discuss its acting mechanisms. Methods Sixteen Wistar rats weighing 180–220 g were randomly divided into four groups with four rats in each group: normal control group; acellular group (ANA, treated by hypotonic-chemical detergent, was applied for bridging a 10 mm-long sciatic nerve defect); USW group (After 24 h of ANA repairing the sciatic nerve gap, low dose USW was administrated for 7 min, once a day, 20 times a course of treatment, three courses of treatment in all); and autografts group. 12 weeks after operation, a series of examinations was performed, including electrophysiological methods, the restoring rate of tibialis anterior muscle wet weight, histopathological observation (myelinated nerve number, myelin sheath thickness, and axon diameter), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA expression of spinal cord, and muscle at injury site, and analyzed statistically. Results Compared to acellular nerve allografts alone, USW therapy can increase nerve conductive velocity, the restoring rate of tibialis anterior muscle wet weight, myelinated nerve number, axon diameter, VEGF mRNA expression of spinal cord, and muscle at injury site, the difference is significant. There were no differences between USW group and autografts group except myelin sheath thickness. Conclusions USW therapy can promote nerve axon regeneration and Schwann cells proliferation after ANA repairing the sciatic nerve gap of rats, the upregulation of VEGF mRNA expression of spinal cord and muscle may play an important role.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AI-Majed AA, Tam SL, Gordon T (2004) Electrical stimulation accelerates and enhances expression of regeneration-associated genes in regenerating rat femoral motoneurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24(3):379–402
Bervar M (2005) Effect of weak, interrupted sinusoidal low frequency magnetic field on neural regeneration in rats: functional evaluation. Bioelectromagnetics 26(5):351–356
English AW, Schwartz G, Meador W, et al (2007) Electrical stimulation promotes peripheral axon regeneration by enhanced neuronal neurotrophin signaling. Dev Neurobiol 67(2):158–172
Flores AJ, Lavernia CJ, Owens PW (2000) Anatomy and physiology of peripheral nerve injury repair. Am J Orthop 29(3):167–173
Hu I, Zhu QT, Liu XL, et al (2007) Repair of extended peripheral nerve lesions in rhesus monkeys using acellular allogenic nerve grafts implanted with autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Neurol 204(2):658–666
Kim BS, Yoo JJ, Atala A (2004) Peripheral nerve regeneration using acellular nerve grafts. J Biomed Mater Res A 68(2):201–209
Liao WJ, Zeng G (1995) Experimental study of effect of muscle weight and muscular tissue lipid peroxidation on injured peripheral nerve. J China Rehabil Med l0(5):209
Liu CHJ, Sun JZH, Tong XJ, et al (2003) The preparation of scaffolds from natural nerve by the method of tissue engineering. Prog Anat Sci 9(3):197–200
Nicolau RA, Martinez MS, Rigau J, et al (2004) Effect of low power 655 nm diode laser irradiation on the neuromuscular junctions of the mouse diaphragm. Lasers Surg Med 34(3):277–284
Raso VV, Barbieri CH, Mazzer N, et al (2005) Can therapeutic ultrasound influence the regeneration of peripheral nerves? J Neurosci Methods 142(2):185–192
Rui YJ, Zhang L, Wang J, et al (2006) Effects of ultra short wave on GAP-43 and CGRP expression in the spinal cord after sciatic nerve lesions in rats. Chin J Hand Sur Surg 22(6):370–372
Sondell M, Lundborg G, Kanje M (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates Schwann cell invasion and neovascularization of acellular nerve grafts. Brain Res 846(2):219–229
Sondell M, Sundler F, Kanje M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci 12(12):4243–4254
Strokebaum E, Lambrechts D, Carmeliet P (2004) VEGF:once regarded as a specific angiogenic factor, now implicated in neuroprotection. Bioessays 26(9):943–954
Tian DH, Mi LX, Zhao F (2004) Physical therapy of injured peripheral nerve. J China Rehabil Med 19(3):239–240
Tong XJ, Liu CHJ, Zhang CSH, et al (2004) Experimental study of the repairing effect of acellular nerve allografts on the sciatic nerve gap of rat. Acta Anat Sin 35(3):230–233
Zhang CHL, Hu SHY, Liu T (1996) Clinical and experimental study of two electricity therapy on peripheral nerve injury. SHIRONG Med J l2(6):406–407
Zhang ZHQ, Liu JX, Ren SHZH, et al (1991) Effects of ultra short wave on motor nerve conduction velocity after sciatic nerve injury in rats. J Chin Physiother 14(3):137–139
Zhang CSH, Tong XJ, Lin F, et al (2003) Experimental study of acellular nerve allografts promoting motor function on rats. Prog Anat Sci 1(1):16–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LX., Tong, XJ., Sun, XH. et al. Experimental Study of Low Dose Ultrashortwave Promoting Nerve Regeneration after Acellular Nerve Allografts Repairing the Sciatic Nerve Gap of Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28, 501–509 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-007-9226-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-007-9226-1