Summary
1. During the course of studies directed to determine the transport of Angiotensin II AT2 receptors in the rat brain, we found that stab wounds to the brain revealed a binding site recognized by the AT2 receptor ligand CGP42112 but not by Angiotensin II.
2. We localized this novel site to macrophages/microglia associated with physical or chemical injuries of the brain.
3. The non-Angiotensin II site was also highly localized to inflammatory lesions of peripheral arteries.
4. In rodent tissues, high binding expression was limited to the spleen and to circulating monocytes. A high-affinity binding site was also characterized in human monocytes.
5. Lack of affinity for many ligands binding to known macrophage receptors indicated the possibility that the non-Angiotensin II CGP42112 binding corresponds to a novel site.
6. CGP42112 enhanced cell attachment to fibronectin and collagen and metalloproteinase-9 secretion from human monocytes incubated in serum-free medium but did not promote cytokine secretion.
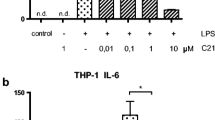
7. When added in the presence of lipopolysaccharide, CGP42112 reduced the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1, IL-1 ß, and IL-6, and increased protein kinase A.
8. Molecular modeling revealed that a CGP42112 derivative was selective for the novel macrophage site and did not recognize the Angiotensin II AT2 receptor.
9. These results demonstrate that CGP42112, previously considered as a selective Angiotensin II AT2 ligand, recognizes an additional non-Angiotensin II site different from AT2 receptors.
10. Our observations indicate that CGP42112 or related molecules could be considered of interest as potential anti-inflammatory compounds.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, H., Zhou, J., Macova, M., Imboden, H., and Saavedra, J. M. (2004). Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade reverses pathological hypertrophy and inflammation in brain microvessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 35:1726–1731.
Chancel, D., Bizet, T., Vandermeersch, S., Pham, P., Levy, B., and Ardaillou, R. (1994). Differential regulation of angiotensin II and losartan binding sites in glomeruli and mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 266:F384–F393.
Braun-Menéndez, E., Fasciolo, J. C., Leloir, L. F., and Muñoz, J. M. (1940). The substance causing renal hypertension. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 98:283–298.
Ciuffo, G. M., and Saavedra, J. M. (1995). Selective peptide and non-peptide ligands differentially bind to angiotensin II AT2 receptor and a non-angiotensin II CGP 42112 binding site. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 274:1129–1134.
De Gasparo, M., Catt, K. J., Inagami, T., Wright, J. W., and Unger, T. H. (2000). International Union of Pharmacology: XXIII. The angiotensin receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 52:415–472.
De Oliveira, A. M., Viswanathan, M., Heemskerk, F. M. J., Correa, F. M. A., and Saavedra, J. M. (1994). Specific, non-angiotensin, [125I]CGP 42112 binding sites in rat spleen macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 200:1049–1058.
Egidy, G., Friedman, J., Viswanathan, M., Wahl, L. M., and Saavedra, J. M. (1997). CGP 42112 partially activates human monocytes and reduces their stimulation by lipopolysaccharides. Am. J. Physiol. 273:C826–C833.
Giulian, D., Chen, J., Ingeman, J. E., George, J. K., and Noponen, M. (1989). The role of mononuclear phagocytes in wound healing after traumatic injury to adult mammalian brain. J. Neurosci. 9:4416–4429.
Heemskerk, F. M. J., and Saavedra, J. M. (1995). Quantitative autoradiography of angiotensin II AT2 receptors with [125I] CGP 42112. Brain Res. 677:29–38.
Heemskerk, F. M. J., Zorad, S., Seltzer, A., and Saavedra, J. M. (1993). Characterization of brain angiotensin II AT2 receptor subtype using [125I] CGP42112A. Neuroreport 4:103–105.
Jöhren, O., Häuser, W., and Saavedra, J. M. (1998). Chemical lesion of the inferior olive reduces [125I]sarcosine1-angiotensin II binding to AT2 receptors in the cerebellar cortex of young rats. Brain Res. 793:176–186.
Jöhren, O., Inagami, T., and Saavedra, J. M. (1995a). AT1A, AT1B, and AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtype gene expression in rat brain. Neuroreport 6:2549–2552.
Jöhren, O., and Saavedra, J. M. (1996). Gene expression of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the cerebellar cortex of young rats. Neuroreport 7:1349–1352.
Jöhren, O., Viswanathan, M., and Saavedra, J. M. (1995b). Expression of non-angiotensin II [125I]CGP 42112 binding sites on activated microglia after kainic acid induced neurodegeneration. Brain Res. 207:153–161.
Page, I. H. (1987). Hypertension mechanisms. Grune & Stratton. New York, pp. 1–1102.
Page, I. H., and Helmer, O. M. (1940). A crystalline pressor substance (angiotensin) resulting from the reaction between renin and renin activator. J. Exp. Med. 71:29–42.
Roulston, C. L., Lawrence, A. J., Jarrott, B., and Widdop, R. E. (2003). Localization of AT2 receptors in the nucleus of the solitary tract of spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar Kyoto rats using [125I]CGP42112: Upregulation of a non-angiotensin II binding site following unilateral nodose ganglionectomy. Brain Res. 968:139–155.
Roulston, C. L., Lawrence, A. J., Jarrott, B., and Widdop, R. E. (2004). Non-angiotensin II [125I] CGP42112 binding is a sensitive marker of neuronal injury in brainstem following unilateral nodose ganglionectomy: Comparison with markers for activated microglia. Neuroscience 127:753–767.
Roulston, C. L., Lawrence, A. J., Widdop, R. E., and Jarrott, B. (2005). Minocycline treatment attenuates microglia activation and non-angiotensin II [125I]CGP42112 binding in brainstem following nodose ganglionectomy. Neuroscience 135:1241–1253.
Saavedra, J. M. (1992). Brain and pituitary angiotensin. Endocr. Rev. 13:329–380.
Saavedra, J. M. (2005). Brain angiotensin II: New developments, unanswered questions and therapeutic opportunities. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 25:485–512.
Saavedra, J. M., Ando, H., Armando, I., Baiardi, G., Bregonzio, C., Juorio, A., and Macova, M. (2005). Anti-stress and anti-anxiety effects of centrally acting angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonists. Reg. Pept. 128:227–238.
Tsutsumi, K., and Saavedra, J. M. (1991a). Characterization and development of angiotensin II receptor subtypes (AT1 and AT2) in rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. 261:R209–R216.
Tsutsumi, K., and Saavedra, J. M. (1991b). Differential development of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain. Endocrinology 128:630–632.
Tsutsumi, K., and Saavedra, J. M. (1991c). Quantitative autoradiography reveals different angiotensin II receptor subtypes in selected rat brain nuclei. J. Neurochem. 56:348–351.
Tsutsumi, K., Strömberg, C., and Saavedra, J. M. (1992). Characterization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat spleen. Peptides 13:291–296.
Viswanathan, M., de Oliveira, A. M., Correa, F. M. A., and Saavedra, J. M. (1994a). Expression of a novel non-angiotensin II [125I] CGP 42112 binding site in healing wounds of the rat brain. Brain Res. 658:265–270.
Viswanathan, M., de Oliveira, A. M., Wu, R. -M., Chiueh, C. C., and Saavedra, J. M. (1994b). [125I]CGP 42112 reveals a non-angiotensin II binding site in 1-Methyl–4- phenylpyridine (MPP+)-induced brain injury. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:99–104.
Viswanathan, M., Jöhren, O., de Oliveira, A. M., and Saavedra, J. M. (1996). Increased non-angiotensin II [125I]CGP 42112 binding in rat carotid artery after balloon injury. Peptides 17:695–699.
Viswanathan, M., Strömberg, C., Seltzer, A., and Saavedra, J. M. (1992). Balloon angioplasty enhances the expression of angiotensin II AT1 receptors in neointima of rat aorta. J. Clin. Invest. 909:1707–1712.
Whitebread, S., Mele, M., Kamber, B., and De Gasparo, M. (1989). Preliminary biochemical characterization of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163:284–291.
Zhou, J., Ando, H., Macova, M., Dou, J., and Saavedra, J. M. (2005). Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade abolishes brain microvascular inflammation and heat shock protein responses in hypertensive rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25:878–886.
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by the Division of Intramural Research Programs, National Institute of Mental Health, NIH, DHHS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saavedra, J.M., Pavel, J. The Discovery of a Novel Macrophage Binding Site. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 507–524 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9044-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9044-x