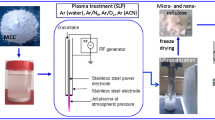
Abstract
The development of biodegradable food packaging materials continues to be of significant interest because of its benefits. Among these materials, cellulose-based composites are candidates to replace conventional, petroleum-based food packaging materials. However, incomplete dissolution of cellulose has hindered its large-scale application. Since undissolved cellulose can affect the mechanical properties of the film, full dissolution is preferred. This work explores the use of plasma irradiation as a pretreatment step before the dissolution of cellulose in lithium chloride–N,N-dimethylacetamide (LiCl–DMAc) solvent. Prior to swelling, the cellulose was exposed to subatmospheric oxygen (O\(_2\)) plasma to initiate glycosidic bond cleavage without intense degradation of cellulose. Fourier transform infrared, Raman, and X-ray photoelectron spectral analyses revealed decrystallization and oxidation of the surface after plasma treatment which enhanced the dissolution of cellulose in LiCl–DMAc. Mechanical tests of drop-casted films revealed that plasma-treated cellulose greatly enhanced the mechanical strength of the film compared to that of untreated cellulose whose film was too weak for the tensile test. This work showed that exposure to O\(_2\) plasma as a pretreatment step can improve the dissolution of cellulose via decrystallization and thereby can be coupled with other natural materials as alternative to food packaging materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acda MN, Devera EE, Cabangon RJ, Ramos HJ (2012) Effects of plasma modification on adhesion properties of wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 32:70–75
Agarwal UP (2017) Raman spectroscopy in the analysis of cellulose nanomaterials. In: Nanocelluloses: their preparation, properties, and applications, ACS symposium series, vol 1251. American Chemical Society, Providence, pp 4–75
Agarwal UP, Ralph SA (1997) FT-Raman spectroscopy of wood: identifying contributions of lignin and carbohydrate polymers in the spectrum of black spruce (Picea mariana). Appl Spectrosc 51:1648–1655
Agarwal UP, Reiner RS, Ralph SA (2010) Cellulose I crystallinity determination using FT-Raman spectroscopy: univariate and multivariate methods. Cellulose 17:721–733
Alanis A, Valdés JH, Mará Guadalupe NV, Lopez R, Mendoza R, Mathew AP, Diaz de León R, Valencia L (2019) Plasma surface-modification of cellulose nanocrystals: a green alternative towards mechanical reinforcement of ABS. RSC Adv 9:17417–17424
Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Lyapin A, Militz H, Viol W, Wolkenhauer A (2009) Plasma treatment of wood and wood-based materials to generate hydrophilic or hydrophobic surface characteristics. Wood Mater Sci Eng 4:52–60
Balu B, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2008) Fabrication of “roll-off” and “sticky” superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces via plasma processing. Langmuir 24:4785–4790
Bhat N, Netravali A, Gore A, Sathianarayanan M, Arolkar G, Deshmukh R (2011) Surface modification of cotton fabrics using plasma technology. Text Res J 81:1014–1026
Cagomoc CMD, Vasquez MR (2016) Enhanced chromium adsorption capacity via plasma modification of natural zeolites. Jpn J Appl Phys 56:01AF02
Cagomoc CMD, Leon MJDD, Ebuen ASM, Gilos MNR, Vasquez MR (2017) RF plasma cleaning of silicon substrates with high-density polyethylene contamination. Jpn J Appl Phys 57(1S):01AB04
Calvimontes A, Mauersberger P, Nitschke M, Dutschk V, Simon F (2011) Effects of oxygen plasma on cellulose surface. Cellulose 18:803–809
Chu P, Chen J, Wang L, Huang N (2002) Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 36:143–206
Dam S, Thakur A, Das D, Amarendra G, Hussain S (2018) Temperature dependent Raman studies of free standing thin films of cellulose. Mater Res Exp 5:126401
Denes F, Young RA (1998) Surface modification of polysaccharides under cold plasma conditions. In: Dumitriu S (ed) Polysaccharides: structural diversity and functional versatility. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 1087–1136
Dupont AL (2003) Cellulose in lithium chloride/N,N-dimethylacetamide, optimisation of a dissolution method using paper substrates and stability of the solutions. Polymer 44:4117–4126
Fang Q, Cui HW, Du GB (2016) Surface wettability, surface free energy, and surface adhesion of microwave plasma-treated Pinus yunnanensis wood. Wood Sci Technol 50:285–296
Fei P, Liao L, Cheng B, Song J (2017) Quantitative analysis of cellulose acetate with a high degree of substitution by ftir and its application. Analyt Methods 9:6194–6201
Ghasemi M, Alexandridis P, Tsianou M (2017) Cellulose dissolution: insights on the contributions of solvent-induced decrystallization and chain disentanglement. Cellulose 24:571–590
Ghasemi M, Alexandridis P, Tsianou M (2018) Dissolution of cellulosic fibers: impact of crystallinity and fiber diameter. Biomacromolecules 19:640–651
Gupta B (2013) 1—Manufacture, types and properties of biotextiles for medical applications. In: King MW, Gupta BS, Guidoin R (eds) Biotextiles as medical implants, Woodhead Publishing series in textiles. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 3–47
Hidzir NM, Hill DJ, Taran E, Martin D, Grandahl L (2013) Argon plasma treatment-induced grafting of acrylic acid onto expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) membranes. Polymer 54:6536–6546
Hubilla FAD, Panghulan GR, Pechardo J, Vasquez MR (2017) Mechanical properties of epoxy composites with plasma-modified rice-husk-derived nanosilica. Jpn J Appl Phys 57:01AG07
Jiao C, Zhang Z, Tao J, Zhang D, Chen Y, Lin H (2017) Synthesis of a poly(amidoxime-hydroxamic acid) cellulose derivative and its application in heavy metal ion removal. RSC Adv 7:27787–27795
Kang X, Kuga S, Wang L, Wu M, Huang Y (2016) Dissociation of intra/inter-molecular hydrogen bonds of cellulose molecules in the dissolution process: a mini review. J Bioresour Bioprod 1:58–63
Kondo T (1997) The assignment of IR absorption bands due to free hydroxyl groups in cellulose. Cellulose 4(4):281
Kuzmina O, Heinze T, Wawro D (2012) Blending of cellulose and chitosan in alkyl imidazolium ionic liquids. ISRN Polym Sci 2012:251950
Kan CW (2015) Application of plasma in the pretreatment of textiles. In: A novel green treatment for textiles: plasma treatment as a sustainable technology, chap 5. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 101–103
Lao TLB, Diaz LJL (2020) Thermoformability of montmorillonite reinforced chitin–cellulose nanocomposite film. Master’s thesis, University of the Philippines, Quezon City, Philippines, unpublished Master’s thesis
Lao TL, Pengson LT, Placido J, Diaz LJ (2019) Synthesis of montmorillonite nanoclay reinforced chitin–cellulose nanocomposite film, vol 540
Latag GV, Vasquez MR (2018) Effects of RF plasma modification on the thermal and mechanical properties of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber mats. J Vac Sci Technol B 36(4):04I101
Lee KR, Song KH (2014) Effect of plasma power on degradation of chitosan. Korean J Chem Eng 31:162–165
Lee KY, Aitomaki Y, Berglund LA, Oksman K, Bismarck A (2014) On the use of nanocellulose as reinforcement in polymer matrix composites. Compos Sci Technol 105:15–27
Liebert TF (2010) Cellulose solvents—remarkable history, bright future. In: Liebert TF, Heinze TJ, Edgar KJ (eds) Cellulose solvents: for analysis, shaping and chemical modification, American Chemical Society, pp 3–54
Lindman B, Karlström G, Stigsson L (2010) On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J Mol Liq 156:76–81
Medronho B, Lindman B (2015) Brief overview on cellulose dissolution/regeneration interactions and mechanisms. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 222:502–508
Montallana ADS, Lai BZ, Chu JP, Vasquez MR (2020) Enhancement of photodegradation efficiency of PVA/TiO\(_2\) nanofiber composites via plasma treatment. Mater Today Commun 24:101183
Morales J, Olayo MG, Cruz GJ, Herrera-Franco P, Olayo R (2006) Plasma modification of cellulose fibers for composite materials. J Appl Polym Sci 101:3821–3828
Oehr C (2003) Plasma surface modification of polymers for biomedical use. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 208:40–47
Oh SY, Yoo DI, Shin Y, Seo G (2005) FTIR analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide. Carbohydr Res 340:417–428
Pabelina KG, Lumban CO, Ramos HJ (2012) Plasma impregnation of wood with fire retardants. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 272:365–369
Pan M, Zhou X, Chen M (2013) Cellulose nanowhiskers isolation and properties from acid hydrolysis combined with high pressure homogenization. Bioresources 8:933–943
Parviainen H, Parviainen A, Virtanen T, Kilpeläinen I, Ahvenainen P, Serimaa R, Grönqvist S, Maloney T, Maunu SL (2014) Dissolution enthalpies of cellulose in ionic liquids. Carbohydr Polym 113:67–76
Poblete MRS, Diaz LJL (2014) Synthesis of biodegradable cellulose–chitin polymer blend from Portunus pelagicus. In: Al-Douri Y (ed) Advanced materials research, vol 925. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, Zurich, pp 379–384. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.925.379
Poletto M, Ornaghi H, Zattera A (2014) Native cellulose: structure, characterization and thermal properties. Materials 7:6105–6119
Potthast A, Rosenau T, Buchner R, Röder T, Ebner G, Bruglachner H, Sixta H, Kosma P (2002) The cellulose solvent system N,N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chloride revisited: the effect of water on physicochemical properties and chemical stability. Cellulose 9:41–53
Ramos HJ, Monasterial JLC, Blantocas GQ (2006) Effect of low energy ion beam irradiation on wettability of narra (Pterocarpus indicus) wood chips. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 242:41–44
Sahin HT (2009) RF-O\(_2\) plasma surface modification of kraft lignin derived from wood pulping. Wood Res 54:103–112
Schuchmann MN, Sonntag C (1978) The effect of oxygen on the OH-radical-induced scission of the glycosidic linkage of cellobiose. Int J Radiat Biol 34:397–400
Shepherd LM, Frey MW (2018) The degradation of cellulose by radio frequency plasma. Fibers 6:61
Swensson B, Larsson A, Hasani M (2020) Dissolution of cellulose using a combination of hydroxide bases in aqueous solution. Cellulose 27:101–112
Taaca KLM, Vasquez MR (2018) Hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility of pristine and plasma-treated silver–zeolite–chitosan composites. Appl Surf Sci 432:324–331
Taaca KLM, Nakajima H, Thumanu K, Janphuang P, Chanlek N, Vasquez MR (2020) Spectroscopic studies of plasma-modified silver-exchanged zeolite and chitosan composites. Mater Chem Phys 250:122980
Tumlos R, Ting J, Osorio E, Rosario L, Ramos H, Ulano A, Lee H, Regalado G (2011) Results of the study of chemical-, vacuum drying- and plasma-pretreatment of coconut (Cocos nucifera) lumber sawdust for the adsorption of methyl red in water solution. Surf Coat Technol 205:S425–S429
Valerio JKC, Nakajima H, Vasquez MR (2018) Grafting of acrylic acid onto microwave plasma-treated polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) substrates. Jpn J Appl Phys 58:SAAC02
Vasquez MR, Prieto EI, Wada M (2018) Radio-frequency plasma-induced biocompatibility of polyimide substrates. Plasma Med 8:35–44
Wiley JH, Atalla RH (1987) Band assignments in the Raman spectra of celluloses. Carbohydr Res 160:113–129
Wu J, Liang S, Dai H, Zhang X, Yu X, Cai Y, Zhang L, Wen N, Jiang B, Xu J (2010) Structure and properties of cellulose/chitin blended hydrogel membranes fabricated via a solution pre-gelation technique. Carbohydr Polym 79:677–684
Xu A, Zhang Y (2015) Insight into dissolution mechanism of cellulose in [C4mim][CH3COO]/DMSO solvent by 13C NMR spectra. J Mol Struct 1088:101–104
Xu F, Yu J, Tesso T, Dowell F, Wang D (2013) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared techniques: a mini-review. Appl Energy 104:801–809
Yuan X, Cheng G (2015) From cellulose fibrils to single chains: understanding cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:31592–31607
Zhang L, Ruan D, Gao S (2002) Dissolution and regeneration of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J Polym Sci B 40:1521–1529
Zhang C, Liu R, Xiang J, Kang H, Liu Z, Huang Y (2014) Dissolution mechanism of cellulose in N,N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chloride: revisiting through molecular interactions. J Phys Chem B 118:9507–9514
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Engineering Research and Development for Technology of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST-ERDT). The nanoQuench project (CHED PCARI IIID-2016-007) is acknowledged for the use of Raman Spectroscopy while Osaka University is also acknowledged for the XPS runs. Dr. N. Hideki is gratefully acknowledged for the assistance in the analysis of XPS data. M. Vasquez acknowledges the University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs BALIK-PhD Research Grant (OVPAA-BPhD-2014-01) and the Jardiolin Family Professorial Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lao, T.L.B., Cordura, S.L.A., Diaz, L.J.L. et al. Influence of plasma treatment on the dissolution of cellulose in lithium chloride–dimethylacetamide. Cellulose 27, 9801–9811 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03454-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03454-6