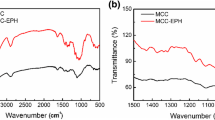
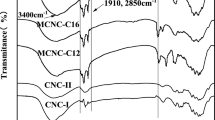
Abstract
A cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) based adsorbent was synthesized by modifying pristine CNC with various amounts of a positively-charged surfactant (CTAB) and was used to study the adsorption behavior of Congo red (CR) in aqueous medium. The interaction of CTAB with CNCs, and potential alterations on the chemical and physical structure of CNCs are studied, and the synthesized adsorbent, modified cellulose nanocrystal (MCNC) was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, elemental and zeta potential analysis. The amount of surfactant used for modification was optimized to maximize the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent. Furthermore, it was found that the amount of surfactant affects the CR-MCNC interactions and determines the mechanism of adsorption. The kinetics followed a pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion model implying that the rate-controlling step of the adsorption process was first dominated by film-diffusion, and consequently by intra-particle diffusion. Thermodynamic studies on the system suggested that the adsorption process is spontaneous and exothermic. Characterization of the adsorbent, before and after adsorption, coupled with the kinetic and isotherm studies indicated that electrostatic attraction, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic attraction are the main mechanisms/interactions of adsorption. The adsorbent is highly stable in water and retains its original adsorption capacity after successive dialysis cycles.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Khalil HPS, Davoudpour Y, Islam MN et al (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.069
Alila S, Boufi S, Belgacem MN, Beneventi D (2005) Adsorption of a cationic surfactant onto cellulosic fibers I. Surface charge effects. Langmuir 21:8106–8113. https://doi.org/10.1021/LA050367N
Bai L, Liu Y, Ding A et al (2019) Fabrication and characterization of thin-film composite (TFC) nanofiltration membranes incorporated with cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) for enhanced desalination performance and dye removal. Chem Eng J 358:1519–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2018.10.147
Batmaz R, Mohammed N, Zaman M et al (2014) Cellulose nanocrystals as promising adsorbents for the removal of cationic dyes. Cellulose 21:1655–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0168-8
Beyki MH, Bayat M, Shemirani F (2016) Fabrication of core-shell structured magnetic nanocellulose base polymeric ionic liquid for effective biosorption of Congo red dye. Bioresour Technol 218:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.069
Boczkaj G, Fernandes A (2017) Wastewater treatment by means of advanced oxidation processes at basic pH conditions: a review. Chem Eng J 320:608–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2017.03.084
Chatterjee S, Chatterjee T, Lim SR, Woo SH (2011) Effect of surfactant Impregnation into chitosan hydrogel beads formed by sodium dodecyl sulfate gelation for the removal of Congo red. Sep Sci Technol 46:2022–2031. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2011.592520
Dashtian K, Ghaedi M, Shirinzadeh H et al (2018) Achieving enhanced blue-light-driven photocatalysis using nanosword-like VO2/CuWO4type II n–n heterojunction. Chem Eng J 339:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.107
Dhar N, Au D, Berry RC, Tam KC (2012) Interactions of nanocrystalline cellulose with an oppositely charged surfactant in aqueous medium. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 415:310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2012.09.010
Ding F, Gao M, Shen T et al (2018) Comparative study of organo-vermiculite, organo-montmorillonite and organo-silica nanosheets functionalized by an ether-spacer-containing Gemini surfactant: Congo red adsorption and wettability. Chem Eng J 349:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.095
Domingues RMA, Gomes ME, Reis RL (2014) The potential of cellulose nanocrystals in tissue engineering strategies. Biomacromol 15:2327–2346. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500524s
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gao Y, Deng S, Jin X et al (2019) The construction of amorphous metal-organic cage-based solid for rapid dye adsorption and time-dependent dye separation from water. Chem Eng J 357:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.124
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110:3479–3500. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900339w
Hu Z, Ballinger S, Pelton R, Cranston ED (2015) Surfactant-enhanced cellulose nanocrystal Pickering emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 439:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.10.034
Jana S, Pradhan SS, Tripathy T (2018) Poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) grafted hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel: a useful Congo red dye remover. J Polym Environ 26:2730–2747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1168-1
Jin L, Li W, Xu Q, Sun Q (2015a) Amino-functionalized nanocrystalline cellulose as an adsorbent for anionic dyes. Cellulose 22:2443–2456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0649-4
Jin L, Sun Q, Xu Q, Xu Y (2015b) Adsorptive removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using microgel based on nanocellulose and polyvinylamine. Bioresour Technol 197:348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2015.08.093
Kaboorani A, Riedl B (2015) Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) by a cationic surfactant. Ind Crops Prod 65:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INDCROP.2014.11.027
Kargarzadeh H, Mariano M, Gopakumar D et al (2018) Advances in cellulose nanomaterials. Cellulose 25:2151–2189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1723-5
Khan M, Lo IMC (2016) A holistic review of hydrogel applications in the adsorptive removal of aqueous pollutants: recent progress, challenges, and perspectives. Water Res 106:259–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.008
Kumar KV, Sivanesan S (2005) Comparison of linear and non-linear method in estimating the sorption isotherm parameters for safranin onto activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 123:288–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2005.03.040
Kumari S, Mankotia D, Chauhan GS (2016) Crosslinked cellulose dialdehyde for Congo red removal from its aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 4:1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.01.008
Lin N, Huang J, Dufresne A (2012) Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: a review. Nanoscale 4:3274. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30260h
Lin F, You Y, Yang X et al (2017) Microwave-assisted facile synthesis of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads with high adsorption capacity for organic dyes. Cellulose 24:5025–5040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1473-9
Ling Z, Wang T, Makarem M et al (2019) Effects of ball milling on the structure of cotton cellulose. Cellulose 26:305–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-02230-x
Liu S, Ding Y, Li P et al (2014) Adsorption of the anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution onto natural zeolites modified with N,N-dimethyl dehydroabietylamine oxide. Chem Eng J 248:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.026
Marco-brown JL, Guz L, Olivelli MS et al (2018) New insights on crystal violet dye adsorption on montmorillonite: kinetics and surface complexes studies. Chem Eng J 333:495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.172
Meza-Contreras JC, Manriquez-Gonzalez R, Gutiérrez-Ortega JA, Gonzalez-Garcia Y (2018) XRD and solid state 13C-NMR evaluation of the crystallinity enhancement of 13C-labeled bacterial cellulose biosynthesized by Komagataeibacter xylinus under different stimuli: a comparative strategy of analyses. Carbohydr Res 461:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2018.03.005
Notley SM (2009) Direct visualization of cationic surfactant aggregates at a cellulose − water interface. J Phys Chem B 113:13895–13897. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9078234
Olusegun SJ, de Sousa Lima LF, Mohallem NDS (2018) Enhancement of adsorption capacity of clay through spray drying and surface modification process for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 334:1719–1728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.084
Pan Y, Wang F, Wei T et al (2016) Hydrophobic modification of bagasse cellulose fibers with cationic latex: adsorption kinetics and mechanism. Chem Eng J 302:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.022
Penfold J, Tucker I, Petkov J, Thomas RK (2007) Surfactant adsorption onto cellulose surfaces. Langmuir 23:8357–8364. https://doi.org/10.1021/LA700948K
Prathapan R, Thapa R, Garnier G, Tabor RF (2016) Modulating the zeta potential of cellulose nanocrystals using salts and surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 509:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2016.08.075
Qiao H, Zhou Y, Yu F et al (2015) Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 141:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.078
Raeiszadeh M, Hakimian A, Shojaei A, Molavi H (2018) Nanodiamond-filled chitosan as an efficient adsorbent for anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 6:3283–3294. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.05.005
Rajeswari A, Vismaiya S, Pius A (2017) Preparation, characterization of nano ZnO-blended cellulose acetate-polyurethane membrane for photocatalytic degradation of dyes from water. Chem Eng J 313:928–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.124
Ranjbar D, Hatzikiriakos SG (2020) Effect of ionic surfactants on the viscoelastic properties of chiral nematic cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Langmuir 36:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03437
Salajková M, Berglund LA, Zhou Q (2012) Hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals modified with quaternary ammonium salts. J Mater Chem 22:19798. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34355j
Shafiei Sabet S (2013) Shear rheology of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) aqueous suspensions. https://doi.org/10.14288/1.0165728
Shafiei-Sabet S, Hamad WY, Hatzikiriakos SG (2012) Rheology of nanocrystalline cellulose aqueous suspensions. Langmuir 28:17124–17133. https://doi.org/10.1021/la303380v
Shu D, Feng F, Han H, Ma Z (2017) Prominent adsorption performance of amino-functionalized ultra-light graphene aerogel for methyl orange and amaranth. Chem Eng J 324:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.136
Tang H, Zhou W, Zhang L (2012) Adsorption isotherms and kinetics studies of malachite green on chitin hydrogels. J Hazard Mater 209–210:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2012.01.010
Wang L, Wang A (2008) Adsorption properties of Congo red from aqueous solution onto surfactant-modified montmorillonite. J Hazard Mater 160:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.104
Wang Y, Zhao L, Peng H et al (2016) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by cellulose-based adsorbents: equilibrium. Kinet Thermodyn. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.6b00340
Wang T, He X, Li Y, Li J (2018a) Novel poly(piperazine-amide) (PA) nanofiltration membrane based poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) hollow fiber substrate for treatment of dye solutions. Chem Eng J 351:1013–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.165
Wang Y, Wang H, Peng H et al (2018b) Dye adsorption from aqueous solution by cellulose/chitosan composite: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Fibers Polym 19:340–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-7520-9
Wu Y, Luo H, Wang H et al (2013) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by graphene modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J Colloid Interface Sci 394:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2012.11.049
Wu Z, Zhong H, Yuan X et al (2014) Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by rhamnolipid-functionalized graphene oxide from wastewater. Water Res 67:330–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2014.09.026
Xhanari K, Syverud K, Chinga-Carrasco G et al (2011) Reduction of water wettability of nanofibrillated cellulose by adsorption of cationic surfactants. Cellulose 18:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9482-y
Xia C, Jing Y, Jia Y et al (2011) Adsorption properties of Congo red from aqueous solution on modified hectorite: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 265:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2010.07.035
Yu X, Wei C, Ke L et al (2010) Development of organovermiculite-based adsorbent for removing anionic dye from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 180:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.04.059
Zaman M, Xiao H, Chibante F, Ni Y (2012) Synthesis and characterization of cationically modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 89:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2012.02.066
Zeng G, Fu H, Zhong H et al (2007) Co-degradation with glucose of four surfactants, CTAB, Triton X-100, SDS and Rhamnolipid, in liquid culture media and compost matrix. Biodegradation 18:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-006-9064-8
Zhang SF, Yang MX, Qian LW et al (2018) Design and preparation of a cellulose-based adsorbent modified by imidazolium ionic liquid functional groups and their studies on anionic dye adsorption. Cellulose 25:3557–3569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1815-2
Zhong L, Fu S, Peng X et al (2012) Colloidal stability of negatively charged cellulose nanocrystalline in aqueous systems. Carbohydr Polym 90:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2012.05.091
Zhou Y, Hu X, Zhang M et al (2013) Preparation and characterization of modified cellulose for adsorption of Cd(II), Hg(II), and acid fuchsin from aqueous solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:876–884. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie301742h
Zhou C, Wu Q, Lei T, Negulescu II (2014) Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem Eng J 251:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.034
Zhu H-Y, Fu Y-Q, Jiang R et al (2011) Adsorption removal of Congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 173:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2011.08.020
Zhu W, Liu L, Liao Q et al (2016) Functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyethylenimine for selective dye adsorption and separation. Cellulose 23:3785–3797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1045-4
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided by the Canadian Network for Research and Innovation in Machining Technology and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbar, D., Raeiszadeh, M., Lewis, L. et al. Adsorptive removal of Congo red by surfactant modified cellulose nanocrystals: a kinetic, equilibrium, and mechanistic investigation. Cellulose 27, 3211–3232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03021-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03021-z