Abstract
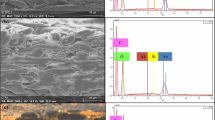
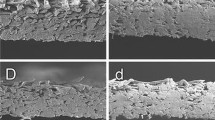
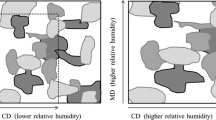
In museums, libraries and archives, some of the paper relics, upon ageing, are very brittle and even cannot be handled without destroying the material. This is because of the depolymerization of cellulose and, consequently, the loss of mechanical strength. To prolong the life expectancy of paper relics, the poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate-co-styrene) (MMA-BA-ST) was used to strengthen the fragile paper fibers in this work. The relation between the mass concentration of MMA-BA-ST emulsion and the specific properties of papers (e.g., folding endurance, tensile strength, tearing strength, whiteness and glossiness) and the ageing resistance were investigated. In addition, the effect of MMA-BA-ST on different types of paper was also studied. Furthermore, the reinforcing mechanism of MMA-BA-ST on paper was also investigated by dissipative particle dynamics simulations. The results showed that MMA-BA-ST could significantly improve the mechanical properties and ageing resistance of papers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amornkitbamrung L, Mohan T, Hribernik S, Reichel V, Faivre D (2015) Polysaccharide stabilized nanoparticles for deacidification and strengthening of paper. RSC Adv 5:32950–32961
ASTM standard D6819-02e2 (2002) Standard test method for accelerated temperature aging of printing and writing paper by dry oven exposure apparatus. Annu B ASTM Stand 15:1–4
ASTM standard D643-97 (2007) Standard test method for folding endurance of paper by the schopper tester. Annu B ASTM Stand 14:1–6
Bai L, Hu H, Xu J (2012) Influences of configuration and molecular weight of hemicelluloses on their paper-strengthening effects. Carbohydr Polym 88:1258–1263
Burguiere C et al (2001) Block copolymers of poly(styrene) and poly(acrylic acid) of various molar masses, topologies, and compositions prepared via controlled/living radical polymerization. Application as stabilizers in emulsion polymerization. Macromolecules 34:4439–4450
Burguiere C, Chassenieux C, Charleux B (2003) Characterization of aqueous micellar solutions of amphiphilic block copolymers of poly(acrylic acid) and polystyrene prepared via ATRP. Toward the control of the number of particles in emulsion polymerization. Polymer 44:509–518
Chen Y, Knappe DRU, Barlaz MA (2004) Effect of cellulose/hemicellulose and lignin on the bioavailability of toluene sorbed to waste paper. Environ Sci Technol 38:3731–3736
Cheng F et al (2015) Characteristic of core materials in polymeric micelles effect on their micellar properties studied by experimental and dpd simulation methods. Int J Pharm 492:152–160
Chunhong Y, Malak ST, Kesong H, Weibin W, Tsukruk VV (2015) Cellulose nanocrystal microcapsules as tunable cages for nano- and microparticles. ACS Nano 9:10887–10895
Dorenbos G (2014) Pore network design: DPD-Monte Carlo study of solvent diffusion dependence on side chain location. J Power Sources 270:536–546
Dupont AL, Souguir Z, Mortha G, Cheradame H, Ipert S (2012) Simultaneous deacidification and reinforcement of very degraded papers using polysiloxanes. In: Sciences des Matériaux du Patrimoine Culturel, 2nd edn, vol 1. pp 1–2
Fan CF, Olafson BD, Blanco M, Hsu SL (1992) Application of molecular simulation to derive phase diagrams of binary mixtures. Macromolecules 25:3667–3676
Ferruti P (2013) Poly(amidoamine)s: past, present, and perspectives. J Polym Sci Polym Chem 51:2319–2353
Giorgi R, Baglioni M, Berti D, Baglioni P (2010) New methodologies for the conservation of cultural heritage: micellar solutions, microemulsions, and hydroxide nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 43:695–704
Groot RD (2003) Electrostatic interactions in dissipative particle dynamics—simulation of polyelectrolytes and anionic surfactants. J Chem Phys 119:10454
Groot R, Rabone K (2001) Mesoscopic simulation of cell membrane damage, morphology change and rupture by nonionic surfactants. Biophys J 81:725–736
Groot RD, Warren PB (1997) Dissipative particle dynamics: bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J Chem Phys 107:4423–4429
Guerfali M, Saidi A, Gargouri A, Belghith H (2015) Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of waste paper for ethanol production using separate saccharification and fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:25–42
Guo H, Cui J, Sun D, Zhou J (2012) Dissipative particle dynamics simulation on phase behavior of thermo-responsive amphiphilic copolymer PCL-PNIPAM-PCL. CIESC J 63:3707–3715
Guo H, Qiu X, Zhou J (2013) Self-assembled core–shell and Janus microphase separated structures of polymer blends in aqueous solution. J Chem Phys 139:8323–8331
Hoogerbrugge P, Koelman J (1992) Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. EPL (Europhys Lett) 19:155–158
Ipert Rousset S, Cheradame EH (2016) Mass deacidification of papers and books III: study of a paper strengthening and deacidification process with amino alkyl alkoxy silanes. Restaur Int J Preserv Libr Arch Mater 26:250–264
Ipert S, Dupont AL, Lavédrine B, Bégin P, Rousset E, Cheradame H (2006a) Mass deacidification of papers and books. IV—a study of papers treated with aminoalkylalkoxysilanes and their resistance to ageing. Polym Degrad Stab 91:3448–3455
Ipert S, Dupont AL, Lavedrine B, Begin P, Rousset E, Cheradame H (2006b) Mass deacidification of papers and books. IV—a study of papers treated with aminoalkylalkoxysilanes and their resistance to ageing. Polym Degrad Stabil 91:3448–3455
Isca C, D’Avorgna S, Graiff C, Montanari M, Ugozzoli F, Predieri G (2016) Paper preservation with polyamidoamines: a preliminary study. Cellulose 23:1415–1432
Khan AK, Ray BC, Maiti J, Dolui SK (2009) Preparation of core-shell latex from co-polymer of styrene-butyl acrylate-methyl methacrylate and their paint properties. Pigm Resin Technol 38:159–164
Li S, Zhang X, Dong W, Wang W (2008) Computer simulations of solute exchange using micelles by a collision-driven fusion process. Langmuir 24:9344–9353
Li Y, Zhang X, Cao D (2015) Nanoparticle hardness controls the internalization pathway for drug delivery. Nanoscale 7:2758–2769
Liu HY, Guo HY, Zhou J (2012) Computer simulations on the anticancer drug delivery system of docetaxel and PLGA-PEG copolymer. Acta Chim Sin 70:2445–2450
Mai J, Sun D, Li L, Zhou J (2016a) Phase behavior of an amphiphilic block copolymer in ionic liquid: a dissipative particle dynamics study. J Chem Eng Data 24:3999–4005
Mai JL, Sun DL, Quan XB, Li LB, Zhou J (2016b) Mesoscopic structure of nafion-ionic liquid membrane using dissipative particle dynamics simulations. Acta Phys Chim Sin 32:1649–1657
Mather BD, Viswanathan K, Miller KM, Long TE (2006) Michael addition reactions in macromolecular design for emerging technologies. Prog Polym Sci 31:487–531
Meshram MW, Patil VV, Mhaske ST, Thorat BN (2009) Graft copolymers of starch and its application in textiles. Carbohydr Polym 75:71–78
Nie S, Zhang X, Gref R, Couvreur P, Qian Y, Zhang L (2015) Multilamellar nanoparticles self-assembled from opposite charged blends: insights from mesoscopic simulation. J Phys Chem C 119:20649–20661
Piovesan C, Fabre-Francke I, Fichet O, Dupont AL, Lavédrine B (2013) Conservation Treatment of Newsprint Paper by Polysiloxanes. Study of interpenetrating networks for strengthening and deacidification (CoMPresSil project). In: Cultural heritage conservation science and sustainable development: experience, research, innovation, vol 12. pp 118–126
Piovesan C, Dupont A-L, Fabre-Francke I, Fichet O, Lavédrine B, Chéradame H (2014a) Paper strengthening by polyaminoalkylalkoxysilane copolymer networks applied by spray or immersion: a model study. Cellulose 21:705–715
Piovesan C, Dupont AL, Fabre-Francke I, Fichet O, Lavédrine B, Cheradame H (2014) A new conservation treatment for strengthening and deacidification of paper using polysiloxane networks. In: ChemCH 2014—third international congress on chemistry for cultural heritage, vol 15. pp 121–126
Poggi G, Toccafondi N, Melita LN, Knowles JC, Bozec L, Giorgi R, Baglioni P (2014) Calcium hydroxide nanoparticles for the conservation of cultural heritage: new formulations for the deacidification of cellulose-based artifacts. Appl Phys A 114:685–693
Potthast A, Henniges U, Banik G (2008) Iron gall ink-induced corrosion of cellulose: aging, degradation and stabilization. Part 1: model paper studies. Cellulose 15:849–859
Seaton MA, Anderson RL, Metz S, Smith W (2013) DL_MESO: highly scalable mesoscale simulations. Mol Simul 39:796–821
Soto-Figueroa C, Rodriguez-Hidalgo MdR, Vicente L (2012) Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of the micellization-demicellization process and micellar shuttle of a diblock copolymer in a biphasic system (water/ionic-liquid). Soft Matter 8:1871–1877
Souguir Z, Dupont AL, d’Espinose de Lacaillerie JB, Lavedrine B, Cheradame H (2011) Chemical and physicochemical investigation of an aminoalkylalkoxysilane as strengthening agent for cellulosic materials. Biomacromol 12:2082–2091
Souguir Z, Dupont A-L, Fatyeyeva K, Mortha G, Cheradame H, Ipert S, Lavédrine B (2012) Strengthening of degraded cellulosic material using a diamine alkylalkoxysilane. RSC Adv 2:7470–7478
Stuart MA et al (2010) Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat Mater 9:101–113
Sun DL, Zhou J (2012) Dissipative particle dynamics simulations on mesoscopic structures of nafion and PVA/nafion blend membranes. Acta Phys Chim Sin 28:909–916
Wang S, Sun Y, Kong F, Yang G, Fatehi P (2016) Preparation and characterization of lignin-acrylamide copolymer as a paper strength additive. BioResources 11:1765–1783
Wu B, Taylor CM, Knappe DR, Nanny MA, Barlaz MA (2001) Factors controlling alkylbenzene sorption to municipal solid waste. Environ Sci Technol 35:4569–4576
Xiong R et al (2016) Ultrarobust transparent cellulose nanocrystal-graphene membranes with high electrical conductivity. Adv Mater 28:1501–1509
Zhang RL, Huang YD, Liu L, Tang YR, Su D, Xu LW (2011) Effect of the molecular weight of sizing agent on the surface of carbon fibres and interface of its composites. Appl Surf Sci 257:3519–3523
Zhang L, Feng Q, Wang J, Sun J, Shi X, Jiang X (2015a) Microfluidic synthesis of rigid nanovesicles for hydrophilic reagents delivery. Angew Chem 54:3952–3956
Zhang RL, Zhang JS, Zhao LH, Sun YL (2015b) Sizing agent on the carbon fibers surface and interface properties of its composites. Fibers Polym 16:657–663
Zhu K, Li X, Wang H, Fei G, Li J (2016) Properties and paper sizing application of waterborne polyurethanemicroemulsions: effects of extender, cross-linker, and polyol. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43201–43211
Acknowledgments
Support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91334202, 21376089), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB733500), Guangdong Science Foundation (No. 2014A030312007) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SCUT-2015ZP033) are gratefully acknowledged. An allocation time from the SCUT Grid at South China University of Technology is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, L., Chen, K., Zhao, D. et al. The application of poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate-co-styrene) in reinforcing fragile papers: experiments and computer simulations. Cellulose 24, 5157–5171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1470-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1470-z