Abstract
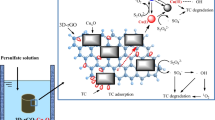
The advanced oxidation process of perdisulfate (PDS) presents strong oxidation ability for different kinds of industrial wastewater treatments. Graphene is a stable and loss-free PDS catalyst that can be doped using S atoms to improve the catalytic activity of PDS. Thus, sulfur-doped graphene (S@RGO) was prepared and applied to catalyze PDS for bisphenol A (BPA) and complex microbial flora destruction given the threat of both refractory organism and complex microbial flora. The characterization indicated that S doping is beneficial to increase the defect degree of graphene and enhance the catalytic activity. BPA can be degraded rapidly without disturbance of complex microbial flora during the reaction. Fluorescent substances, proteins and polysaccharides in different layers of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), and even the tightly-bound extracellular polymeric substances TB-EPS layer closely bound to the microbial flour can be decomposed and result in the breakdown of microbial flora without the protection of EPS. Leaching of LDH and DNA confirmed the destruction of cell membrane for microbial flora breakdown. Dominant microbial floras of Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Bacteroidetes, Nitrospirae, and Acidobacteria were effectively destroyed. The mechanism analysis indicated that not only strong free radicals (SO4−·, ·OH and 1O2) contributed to the disintegration of EPS skeleton and inactivation of microbial flour and electron transference among “S@RGO-PDS-complex microbial flora” is also a critical factor. The synergetic system of S@RGO/PDS showed high application potential as a complicated wastewater treatment.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J, Wang S (2018) Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem Eng J 334:1502–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.059
Zhou L, Richard C, Ferronato C, Chovelon J, Sleiman M (2018) Investigating the performance of biomass-derived biochars for the removal of gaseous ozone, adsorbed nitrate and aqueous bisphenol A. Chem Eng J 334:2098–2104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.145
Ullah S, Shi Q, Zhou J, Yang X, Ta HQ, Hasan M, Ahmad NM, Fu L, Bachmatiuk A, Rümmeli MH (2020) Advances and trends in chemically doped graphene. Adv Mater Interfaces 7(24):2000999. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.20200099
Zheng W, Xiao X, Chen B (2019) A nonradical reaction-dominated phenol degradation with peroxydisulfate catalyzed by nitrogen-doped graphene. Sci Total Environ 667:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.173
Sun P, Liu H, Feng M, Guo L, Zhai Z, Fang Y, Zhang X, Sharma VK (2019) Nitrogen-sulfur co-doped industrial graphene as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator: singlet oxygen-dominated catalytic degradation of organic contaminants. Appl Catal B 251:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.085
Kang J, Zhou L, Duan X, Sun H, Wang S (2020) Catalytic degradation of antibiotics by metal-free catalysis over nitrogen-doped graphene. Catal Today 357:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.12.002
Ren X, Feng J, Si P, Zhang L, Lou J, Ci L (2018) Enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxydisulfate by S, N co-doped graphene via controlling S, N functionalization for the catalytic decolorization of dyes in water. Chemosphere 210:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.011
Liu S, Lai C, Li B, Zhang C, Zhang M, Huang D, Qin L, Yi H, Liu X, Huang F, Zhou X, Chen L (2020) Role of radical and non-radical pathway in activating persulfate for degradation of p-nitrophenol by sulfur-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. Chem Eng J 384:123304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123304
Liu H, Liu Y, Tang L, Wang J, Yu J, Zhang H, Yu M, Zou J, Xie Q (2020) Egg shell biochar-based green catalysts for the removal of organic pollutants by activating persulfate. Sci Total Environ 745:141095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141095
Wang Z, Chen Y, Xie P, Shang R, Ma J (2016) Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa by UV-activated persulfate: Performance and characteristics. Chem Eng J 300:245–253
Zhang L, Jin H, Ma H, Gregory K, Qi Z, Wang C, Wu W, Cang D, Li Z (2020) Oxidative damage of antibiotic resistant E. coli and gene in a novel sulfidated micron zero-valent activated persulfate system. Chem Eng J 381:122787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122787
Xia D, Li Y, Huang G, Yin R, An T, Li G, Zhao H, Lu A, Wong PK (2017) Activation of persulfates by natural magnetic pyrrhotite for water disinfection: efficiency, mechanisms, and stability. Water Res 112:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.052
Chen Y, Duan X, Zhang C, Wang S, Ren N, Ho S (2020) Graphitic biochar catalysts from anaerobic digestion sludge for nonradical degradation of micropollutants and disinfection. Chem Eng J 384:123244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123244
Wang X, Sun G, Routh P, Kim D, Huang W, Chen P (2014) Heteroatom-doped graphene materials: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev 43(20):7067–7098. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00141A
Meka Chufa B, Abdisa Gonfa B, Yohannes Anshebo T, Adam Workneh G (2021) A novel and simplest green synthesis method of reduced graphene oxide using methanol extracted vernonia amygdalina: large-scale production. Adv Cond Matter Phys 2021:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6681710
Qiao Y, Wang B, Zong P, Tian Y, Xu F, Li D, Li F, Tian Y (2019) Thermal behavior, kinetics and fast pyrolysis characteristics of palm oil: analytical TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS study. Energ Convers Manage 199:111964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.111964
Boudjellal A, Trache D, Bekhouche S, Khimeche K, Razali MS, Guettiche D (2021) Preparation and characterization of Alfa fibers/graphene nanoplatelets hybrid for advanced applications. Mater Lett 289:129379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129379
Zhang Q, Wang BX, Chen S, Zhang SY, Hong J (2020) S edge/center-selectively doped graphene oxide for bisphenol A electro-degradation: preparation, efficiency and mechanism. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127669
Cai G, Darmawan P, Cui M, Wang J, Chen J, Magdassi S, Lee PS (2016) Highly stable transparent conductive silver Grid/PEDOT:PSS electrodes for integrated bifunctional flexible electrochromic supercapacitors. Adv Energy Mater 6(4):1501882. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201501882
Hu T, Chen S, Zhang Q, Hong J (2022) Efficiency and mechanism analysis of bisphenol A degradation by sulfur-doped graphene-catalyzed peroxydisulfate. Appl Surf Sci 572:151429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151429
Wang K, Yang L, Wei W, Zhang L, Chang G (2018) Phosphoric acid-doped poly(ether sulfone benzotriazole) for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. J Membrane Sci 549:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.067
Duan X, Sun H, Ao Z, Zhou L, Wang G, Wang S (2016) Unveiling the active sites of graphene-catalyzed peroxymonosulfate activation. Carbon 107:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.06.016
Yin H, Yao F, Pi Z, Zhong Y, He L, Hou K, Fu J, Chen S, Tao Z, Wang D, Li X, Yang Q (2021) Efficient degradation of bisphenol A via peroxydisulfate activation using in-situ N-doped carbon nanoparticles: structure-function relationship and reaction mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 586:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.120
Guo Y, Zeng Z, Li Y, Huang Z, Cui Y (2018) In-situ sulfur-doped carbon as a metal-free catalyst for persulfate activated oxidation of aqueous organics. Catal Today 307:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.080
Xiong B, Zhou Y, O’Hayre R, Shao Z (2013) Facile single-step ammonia heat-treatment and quenching process for the synthesis of improved Pt/N-graphene catalysts. Appl Surf Sci 266:433–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.053
Wang Q, Li L, Luo L, Yang Y, Yang Z, Li H, Zhou Y (2019) Activationof persulfate with dual-doped reduced graphene oxide for degradation of alkylphenols. Chem Eng J 376:120891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.170
Sevilla M, Fuertes AB (2012) Highly porous S-doped carbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 158:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.02.029
Cao B, Zhang W, Wang Q, Huang Y, Meng C, Wang D (2016) Interaction mechanisms of activated sludge particles and different speciation of hydroxy aluminum with implication to sludge conditioning. Water Res 105:615–624
Yu G, He P, Shao L, He P (2008) Stratification structure of sludge flocs with implications to dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):7944–7949. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8016717
Zhen G, Lu X, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang B, Song Y, Chai X, Niu D, Cao X (2012) Novel insights into enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation. Bioresource Technol 119:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.115
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation−emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034354c
Michael-Kordatou I, Iacovou M, Frontistis Z, Hapeshi E, Dionysiou DD, Fatta-Kassinos D (2015) Erythromycin oxidation and ERY-resistant Escherichia coli inactivation in urban wastewater by sulfate radical-based oxidation process under UV-C irradiation. Water Res 85:346–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.050
Guo S, Lin J, Wang Q, Megharaj M, Chen Z (2018) The toxicity of graphene and its impacting on bioleaching of metal ions from sewages sludge by Acidithiobacillus sp. Chemosphere 195:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.073
Dignac MF, Urbain V, Rybacki D, Bruchet A, Snidaro D, Scribe P (1998) Chemical description of extracellular polymers: implication on activated sludge floc structure. Water Sci Technol 8(38):45–53
Liu Y, Wang L, Ma J, Zhao X, Huang Z, Mahadevan GD, Qi J (2016) Improvement of settleability and dewaterability of sludge by newly prepared alkaline ferrate solution. Chem Eng J 287:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.037
Wu S, Luo G, Sun J, Wei W, Song L, Ni B (2021) Medium chain fatty acids production from anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. J Clean Prod 279:123482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123482
Rizzatti G, Lopetuso LR, Gibiino G, Binda C, Gasbarrini A (2017) Proteobacteria: a common factor in human diseases. Biomed Res Int 2017:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9351507
Tsolis RM (2002) Comparative genome analysis of the alpha-proteobacteria: relationships between plant and animal pathogens and host specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(20):12503–12505. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.212508599
Luo J, Du W, Chu S, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Cheng X, Huang W, Cao J, Su Y (2022) Effects of persulfate treatment on the fates of antibiotic resistance genes in waste activated sludge fermentation process and the underlying mechanism. Bioresource Technol 345:126474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126474
Xu LS, Sun XB, Hong J, Zhang Q (2021) Peroxymonosulfate activation by α-MnO2/MnFe2O4 for norfloxacin degradation: efficiency and mechanism. J Phys Chem Solids 153:110029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110029
Sun F, Chen T, Liu H, Zou X, Zhai P, Chu Z, Shu D, Wang H, Chen D (2021) The pH-dependent degradation of sulfadiazine using natural siderite activating PDS: the role of singlet oxygen. Sci Total Environ 784:147117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147117
Zhang Z, Fan J, Du J, Peng X (2021) Two-channel responsive luminescent chemosensors for dioxygen species: molecular oxygen, singlet oxygen and superoxide anion. Coordin Chem Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213575
Guo J, Jia X, Gao Q (2020) Insight into the improvement of dewatering performance of waste activated sludge and the corresponding mechanism by biochar-activated persulfate oxidation. Sci Total Environ 744:140912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140912
Wang H, Guo W, Liu B, Wu Q, Luo H, Zhao Q, Si Q, Sseguya F, Ren N (2019) Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: an electron transfer mechanism. Water Res 160:405–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.059
Lee H, Kim H, Weon S, Choi W, Hwang YS, Seo J, Lee C, Kim J (2016) Activation of persulfates by graphitized nanodiamonds for removal of organic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 50(18):10134–10142. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02079
Jiang L, Wang Q, Zhou M, Liang L, Li K, Yang W, Lu X, Zhang Y (2020) Role of adsorption and oxidation in porous carbon aerogel/persulfate system for non-radical degradation of organic contaminant. Chemosphere 241:125066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125066
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under grant 51978291, Fujian province Science and Technology project Foundation (2021J01311, 2022I0030), Xiamen Science and Technology project Foundation (3502Z20226012) and Scientific Research Funds of Huaqiao University. The authors would like to acknowledge the Testing center of Huaqiao University for the TEM and LC-MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Hu, Tf., Huang, Z. et al. Sulfur-Doped Graphene-Activated Perdisulfate for Synergetic Destruction of Bisphenol A and Complex Microbial Flora. Catal Lett 153, 2057–2073 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04133-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04133-w