Abstract
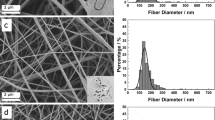
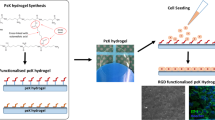
Cell-based therapies have been emerged to find innovative solutions for corneal endothelial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to investigate the suitability of a blended scaffold containing human platelet lysate (HPL) and fibrin not only for cultivating human corneal endothelial cells (HCECs) but also for serving as a scaffold for the respected cells. We isolated HCECs from human donors and encapsulated the cells with three concentrations of HPL/Fibrin scaffold, namely HPL/Fibrin 1, HPL/Fibrin 2 and HPL/Fibrin 3, by adding 28.9, 57.8 and 86.7 mg/dl of fibrinogen to HPL to obtain a final percentage of 10, 20 and 30 % of fibrinogen, respectively. SEM imaging and swelling test were done to characterize the scaffolds. Cell viability assay and cell counting were performed on the cells. HCECs were characterized by morphology and immunocytochemistry. SEM imaging on freeze-dried scaffolds showed higher porosity of HPL/Fibrin 1 and HPL/Fibrin 2 than HPL/Fibrin 3, but larger pores were observed only in HPL/Fibrin 1. Cellular attachment and morphology on HPL/Fibrin 1 were appropriate by SEM imaging. A higher swelling rate was observed in HPL/Fibrin 1. After 3 and 5 days, higher numbers of cells were observed specifically in HPL/Fibrin 1. A higher expression of Na+/K+-ATPase, ZO-1 and vimentin proteins was detected in the HPL/Fibrin 1-cultured HCECs as compared with control (no scaffold). HPL/Fibrin can be used as a suitable scaffold for HCECs while preserving the cells viability. Further investigations are necessitated to approve the beneficial effects of the suggested scaffold for delivering and transplantation of cultivated HCECs into the anterior chamber of the eye.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Annabi N, Nichol JW, Zhong X, Ji C, Koshy S, Khademhosseini A, Dehghani F (2010) Controlling the porosity and microarchitecture of hydrogels for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 16:371–383
Bagheri-Hosseinabadi Z, Salehinejad P, Mesbah-Namin SA (2017) Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells in fibrin scaffold by a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Biomed Eng Online 16:134
Balagholi S, Rezaei Kanavi M, Alizadeh S, Dabbaghi R, Karami S, Kheiri B, Daftarian N (2018) Effects of fibrin glue as a three-dimensional scaffold in cultivated adult human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Biomater Appl 33:514–526
Barsotti MC, Felice F, Balbarini A, Di Stefano R (2011) Fibrin as a scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 58:301–310
Bayat N, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Ardakan MMM, Ai J (2015) Differentiation of human endometrial stem cells into Schwann cells in fibrin hydrogel as 3D culture. Mol Neurobiol 53:7177
Bhat S, Tripathi A, Kumar A (2011) Supermacroprous chitosan–agarose–gelatin cryogels: in vitro characterization and in vivo assessment for cartilage tissue engineering. J R Soc Interface 8:540–554
Blombäck B, Bark N (2004) Fibrinopeptides and fibrin gel structure. Biophys Chem 112:147–151
Carducci A et al (2016) GMP-grade platelet lysate enhances proliferation and migration of tenon fibroblasts. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 8:84–99
Chamani T, Javadi MA, Kanavi MR (2019) Trephine-and dye-free technique for eye bank preparation of pre-stripped descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty tissue. Cell Tissue Bank 20:321–326
Chou M-L, Burnouf T, Wang T-J (2014) Ex vivo expansion of bovine corneal endothelial cells in xeno-free medium supplemented with platelet releasate. PloS one 9:e99145
Duong H, Wu B, Tawil B (2009) Modulation of 3D fibrin matrix stiffness by intrinsic fibrinogen–thrombin compositions and by extrinsic cellular activity. Tissue Eng Part A 15:1865–1876
Fagerholm P et al (2010) A biosynthetic alternative to human donor tissue for inducing corneal regeneration: 24-month follow-up of a phase 1 clinical study. Sci Transl Med 2:46ra61
Gupta NV, Shivakumar HJIjoprI (2012) Investigation of swelling behavior and mechanical properties of a pH-sensitive superporous hydrogel composite. Iran J Pharm Res 11:481–493
Hassan W, Dong Y, Wang W (2013) Encapsulation and 3D culture of human adipose-derived stem cells in an in-situ crosslinked hybrid hydrogel composed of PEG-based hyperbranched copolymer and hyaluronic acid. Stem Cell Res Ther 4:32
Ho W, Tawil B, Dunn JC, Wu BM (2006) The behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D fibrin clots: dependence on fibrinogen concentration and clot structure. Tissue Eng 12:1587–1595
Hokugo A, Takamoto T, Tabata Y (2006) Preparation of hybrid scaffold from fibrin and biodegradable polymer fiber. Biomaterials 27:61–67
Ishino Y, Sano Y, Nakamura T, Connon CJ, Rigby H, Fullwood NJ, Kinoshita S (2004) Amniotic membrane as a carrier for cultivated human corneal endothelial cell transplantation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:800–806
Janmey PA, Winer JP, Weisel JW (2009) Fibrin gels and their clinical and bioengineering applications. J R Soc Interface 6:1–10
Joyce NC (2003) Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog Retin Eye Res 22:359–389
Kennedy S, Lace R, Carserides C, Gallagher AG, Wellings DA, Williams RL, Levis HJ (2019) Poly-ε-lysine based hydrogels as synthetic substrates for the expansion of corneal endothelial cells for transplantation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 30:102
Khademhosseini A, Langer R, Borenstein J, Vacanti JP (2006) Microscale technologies for tissue engineering and biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2480–2487
Kharkar PM, Kiick KL, Kloxin AM (2013) Designing degradable hydrogels for orthogonal control of cell microenvironments. Chem Soc Rev 42:7335–7372
Kim EY, Tripathy N, Cho SA, Joo C-K, Lee D, Khang G (2015) Bioengineered neo-corneal endothelium using collagen type-I coated silk fibroin film. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 136:394–401
Kim DK, Sim BR, Khang G (2016) Nature-derived aloe vera gel blended silk fibroin film scaffolds for cornea endothelial cell regeneration and transplantation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:15160–15168
Kim EY, Tripathy N, Cho SA, Lee D, Khang G (2017) Collagen type I–PLGA film as an efficient substratum for corneal endothelial cells regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 11:2471–2478
Kim DK, Sim BR, Kim JI, Khang G (2018) Functionalized silk fibroin film scaffold using β-Carotene for cornea endothelial cell regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 164:340–346
Kinoshita S et al (2018) Injection of cultured cells with a ROCK inhibitor for bullous keratopathy. N Engl J Med 378:995–1003
Koizumi N et al (2007) Cultivated corneal endothelial cell sheet transplantation in a primate model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:4519–4526
Komeri R, Thankam FG, Muthu J (2015) Influence of matrix and bulk behaviour of an injectable hydrogel on the survival of encapsulated cardiac cells. RSC Adv 5:31439–31449
Konings J et al (2011) Factor XIIa regulates the structure of the fibrin clot independently of thrombin generation through direct interaction with fibrin. Blood 118:3942–3951
Kopsachilis N, Tsinopoulos I, Tourtas T, Kruse FE, Luessen UW (2012) Descemet’s membrane substrate from human donor lens anterior capsule. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 40:187–194
Kopsachilis N, Tsaousis KT, Tsinopoulos IT, Kruse FE, Welge-Lüssen U (2013) Human anterior lens capsule serving as a substrate for human trabecular meshwork cells cultivation. Cell Tissue Bank 14:407–412
Kubota K, Kogure H, Masuda Y, Toyama Y, Kita R, Takahashi A, Kaibara M (2004) Gelation dynamics and gel structure of fibrinogen. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 38:103–109
Lai J-Y, Ma DH-K, Lai M-H, Li Y-T, Chang R-J, Chen L-M (2013) Characterization of cross-linked porous gelatin carriers and their interaction with corneal endothelium: biopolymer concentration effect. PLoS One 8:e54058
Lai J-Y (2015) Influence of pre-freezing temperature on the corneal endothelial cytocompatibility and cell delivery performance of porous hyaluronic acid hydrogel carriers. Int J Mol Sci 16:18796–18811
Lee BS, Stark WJ, Jun AS (2011) Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty: a successful alternative to repeat penetrating keratoplasty. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 39:195–200
Levis HJ et al (2012) Plastic compressed collagen as a novel carrier for expanded human corneal endothelial cells for transplantation. PloS one 7:e50993
Levis HJ, Menzel-Severing J, Drake RA, Daniels JT (2013) Plastic compressed collagen constructs for ocular cell culture and transplantation: a new and improved technique of confined fluid loss. Curr Eye Res 38:41–52
Li Y, Meng H, Liu Y, Lee BP (2015) Fibrin gel as an injectable biodegradable scaffold and cell carrier for tissue engineering. ScientificWorldJournal 2015:685690
Liu J, Xu HH, Zhou H, Weir MD, Chen Q, Trotman CA (2013a) Human umbilical cord stem cell encapsulation in novel macroporous and injectable fibrin for muscle tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 9:4688–4697
Liu Y et al (2013b) The application of hyaluronic acid hydrogels to retinal progenitor cell transplantation. Tissue Eng Part A 19:135–142
Lu L et al (2000) In vitro degradation of porous poly (L-lactic acid) foams. Biomaterials 21:1595–1605
Madden PW, Lai JN, George KA, Giovenco T, Harkin DG, Chirila TV (2011) Human corneal endothelial cell growth on a silk fibroin membrane. Biomaterials 32:4076–4084
Mallis P et al (2019) Short term results of fibrin gel obtained from cord blood units: a preliminary in vitro study. Bioengineering (Basel) 6:66
Mimura T et al (2004) Cultured human corneal endothelial cell transplantation with a collagen sheet in a rabbit model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:2992–2997
Niu G, Choi J-S, Wang Z, Skardal A, Giegengack M, Soker S (2014) Heparin-modified gelatin scaffolds for human corneal endothelial cell transplantation. Biomaterials 35:4005–4014
Okumura N, Ueno M, Koizumi N, Sakamoto Y, Hirata K, Hamuro J, Kinoshita S (2009) Enhancement on primate corneal endothelial cell survival in vitro by a ROCK inhibitor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:3680–3687
Okumura N, Koizumi N, Ueno M, Sakamoto Y, Takahashi H, Hamuro J, Kinoshita S (2011) The new therapeutic concept of using a rho kinase inhibitor for the treatment of corneal endothelial dysfunction. Cornea 30:S54–S59
Okumura N et al (2013) The ROCK inhibitor eye drop accelerates corneal endothelium wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2493–2502
Okumura N et al (2016) Rho kinase inhibitor enables cell-based therapy for corneal endothelial dysfunction. Scientific Rep 6:26113
Orwin EJ, Hubel A (2000) In vitro culture characteristics of corneal epithelial, endothelial, and keratocyte cells in a native collagen matrix. Tissue Eng 6:307–319
Pagani P, Campanile G, Bricola G, Csutak A, Traverso C (2006) A fibrin-based substrate for in vitro reconstruction of cultured corneal endothelial cells. Minerva Biotecnol 18:129–135
Parekh M, Ferrari S, Sheridan C, Kaye S, Ahmad S (2016) Concise review: an update on the culture of human corneal endothelial cells for transplantation. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:258–264
Park CH, Woo KM (2018) Fibrin-based biomaterial applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol 1064:253–261
Peh GS et al (2019) Functional evaluation of two corneal endothelial cell-based therapies: tissue-engineered construct and cell injection. Scientific Rep 9:6087
Pipparelli A, Arsenijevic Y, Thuret G, Gain P, Nicolas M, Majo F (2013) ROCK inhibitor enhances adhesion and wound healing of human corneal endothelial cells. PloS one 8:e62095
Redenti S et al (2009) Engineering retinal progenitor cell and scrollable poly (glycerol-sebacate) composites for expansion and subretinal transplantation. Biomaterials 30:3405–3414
Roura S, Gálvez-Montón C, Bayes‐Genis A (2017) Fibrin, the preferred scaffold for cell transplantation after myocardial infarction? An old molecule with a new life. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 11:2304–2313
Schek R, Michalek A, Iatridis J (2011) Genipin-crosslinked fibrin hydrogels as a potential adhesive to augment intervertebral disc annulus repair. Eur Cell Mater 21:373–383
Şeker Ş, Elçin AE, Elçin YM (2019) Autologous protein-based scaffold composed of platelet lysate and aminated hyaluronic acid. J Mater Sci Mater Med 30:127
Seow WY, Kandasamy K, Peh GS, Mehta JS, Sun W (2019) Ultrathin, strong, and cell-adhesive agarose-based membranes engineered as substrates for corneal endothelial cells. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:4067–4076
Shachar M, Tsur-Gang O, Dvir T, Leor J, Cohen S (2011) The effect of immobilized RGD peptide in alginate scaffolds on cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 7:152–162
Soleimannejad M et al (2018) Fibrin gel as a scaffold for photoreceptor cells differentiation from conjunctiva mesenchymal stem cells in retina tissue engineering. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:805–814
Sortwell CE, Pitzer MR, Collier TJ (2000) Time course of apoptotic cell death within mesencephalic cell suspension grafts: implications for improving grafted dopamine neuron survival. Exp Neurol 165:268–277
Spotnitz WD (2010) Fibrin sealant: past, present, and future: a brief review. World J Surg 34:632–634
Strandberg G, Sellberg F, Sommar P, Ronaghi M, Lubenow N, Knutson F, Berglund D (2017) Standardizing the freeze-thaw preparation of growth factors from platelet lysate. Transfusion 57:1058–1065
Tan C et al (2016) Feasibility and efficiency of human bone marrow stromal cell culture with allogeneic platelet lysate-supplementation for cell therapy against stroke. Stem Cells Int 2016:6104780
Teichmann J, Valtink M, Nitschke M, Gramm S, Funk RH, Engelmann K, Werner C (2013) Tissue engineering of the corneal endothelium: a review of carrier materials. J Funct Biomater 4:178–208
Thieme D, Reuland L, Lindl T, Kruse F, Fuchsluger T (2018) Optimized human platelet lysate as novel basis for a serum-, xeno‐, and additive‐free corneal endothelial cell and tissue culture. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 12:557–564
Van den Bogerd B, Ni Dhubhghaill S, Zakaria N (2018) Characterizing human decellularized crystalline lens capsules as a scaffold for corneal endothelial tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 12:e2020–e2028
Vázquez N et al (2017) Silk fibroin films for corneal endothelial regeneration: transplant in a rabbit descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58:3357–3365
Wang T-J, Wang I-J, Hu F-R, Young T-H (2016) Applications of biomaterials in corneal endothelial tissue engineering. Cornea 35:S25–S30
Wang T-J, Chen M-S, Chou M-L, Lin H-C, Seghatchian J, Burnouf T (2017) Comparison of three human platelet lysates used as supplements for in vitro expansion of corneal endothelium cells. Transfus Apher Sci 56:769–773
Yang L et al (2020) Improved mechanical properties by modifying fibrin scaffold with PCL and its biocompatibility evaluation. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 31:658–678
Yoeruek E, Saygili O, Spitzer MS, Tatar O, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Szurman P (2009) Human anterior lens capsule as carrier matrix for cultivated human corneal endothelial cells. Cornea 28:416–420
Young T-H, Wang I-J, Hu F-R, Wang T-J (2014) Fabrication of a bioengineered corneal endothelial cell sheet using chitosan/polycaprolactone blend membranes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 116:403–410
Zavizion B, Pistsov M, Bergel’son S, Miroshnichenko O, Trakht I (1990) Transformation of human corneal endothelial cells by micro-injection of oncogenes. Biull Eksp Biol Med 109:395–398
Zhao L, Xu Y, He M, Zhang W, Li M (2014) Preparation of spider silk protein bilayer small-diameter vascular scaffold and its biocompatibility and mechanism research. Compos Interfaces 21:869–884
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the Central Eye Bank of Iran for providing the donor eyes.
Funding
The manuscript was funded by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant number: 15739-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
Full ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Central Eye Bank of Iran and the ethics committee of the Ophthalmic Research Center (IR.SBMU.ORC.REC.1398.012), Research Institute for Ophthalmology and Vision Science, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishan, M.A., Balagholi, S., Chamani, T. et al. Potential of a novel scaffold composed of human platelet lysate and fibrin for human corneal endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Bank 23, 171–183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-021-09931-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-021-09931-x